Single plate clutch is the most commonly used type of clutch in automobiles. It provides quicker disengagement.
Construction of Single Plate Clutch
Single plate clutch consists of clutch disc, pressure plate, and a cover assembly, which are bolted to the engine flywheel (Fig. 1).
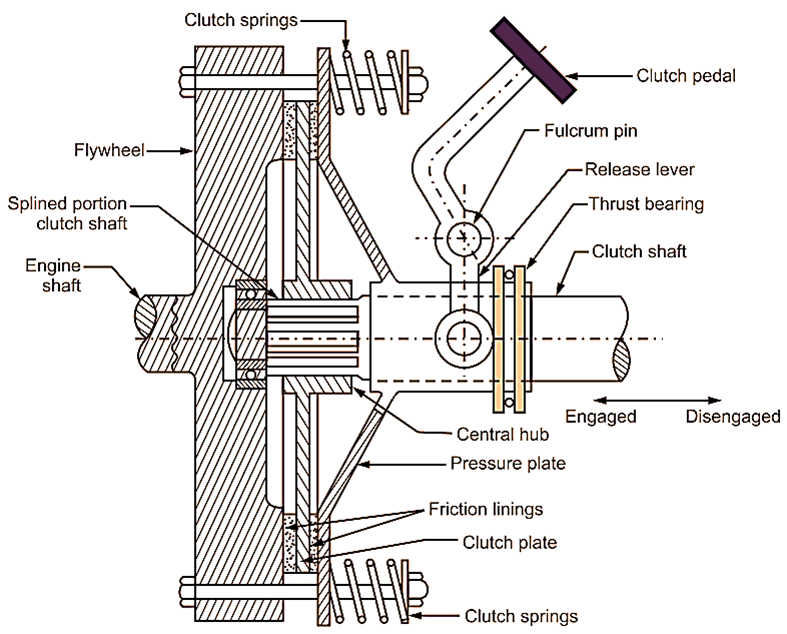
Fig. 1: Single Plate Clutch
Flywheel
Flywheel is a circular disc of heavy mass, which is bolted to engine crankshaft. Flywheel has a flat surface, which engages with the clutch plate.
Clutch Plate with Friction Linings
Clutch plate is a metal disc. Friction surfaces (i.e. linings) are provided on both sides of clutch plate. Clutch plate has a central hub machined internally, due to which, it can slide on a splined shaft.
Pressure Plate
Pressure plate is a heavy mass plate. One side of pressure plate has flat surface, which engages with the clutch plate.
Clutch Springs
In case of single plate clutch, six to eight clutch springs are radially mounted in between one clutch plate and pressure plate. Clutch springs are used to keep the clutch in engaged position, when pedal position is up.
Release Lever
Release lever is pivoted at fulcrum pin. Release lever is used to transmit the motion of clutch pedal to pressure plate, when clutch pedal is pressed by driver to disengage the clutch.
Clutch Shaft
Clutch shaft is connected to input shaft of gearbox. Clutch shaft is splined near the central hub, where the clutch plate can slide.
Thrust Bearing
Thrust bearing takes care of the axial load, which comes during sudden release of clutch springs, when they are compressed in axial length due to axial force applied by release lever at the time of disengagement of clutch.
Working of Single Plate Clutch
To understand the working of single plate clutch, let us consider following two cases:
When the clutch is in engaged position
Fig. 1 shows single plate clutch assembly in engaged position. It means that, clutch pedal is not pressed by the driver. This condition is referred as Clutch Pedal Position-Up. When the pedal position is up, the axial force offered by clutch springs is pressed against the flywheel (i.e. towards flywheel) with clutch plate being sandwiched between pressure plate and flywheel. Therefore, drive is engaged and power is transmitted from the flywheel to the clutch plate due to friction existing between their contacting surfaces. Further, the power is transmitted from clutch plate to clutch shaft through mechanical splines.
When clutch needs to be disengaged:
For disengaging the clutch, the clutch pedal is pressed by the driver. This condition is referred as Clutch Pedal Position – Pressed – Down. When the clutch pedal is pressed down, release lever pulls the pressure plate away from clutch plate against the axial force offered by clutch springs and thereby, compressing clutch springs. This loosens the contact between clutch plate and flywheel. Therefore, drive gets disengaged and power is not transmitted to clutch plate and hence, clutch shaft
Advantages of Single Plate Clutch
- Simplicity in design.
- Easy to construct.
- Better heat dissipation (heat is generated due to friction between contacting surfaces).
- Shifting of gear is easy, if single plate clutch is used.
- Better availability to damp out torsional vibrations.
Disadvantages of Single Plate Clutch
- Use of single plate clutch is not preferred, if large magnitude of power is to be transmitted, because surface area of clutch plate has to be increased considerably for high power transmission. Due to this, overall size of single plate clutch gets increased. Therefore, single plate clutch cannot be used in the applications, where space availability is a problem.
- Large effort (or force) is required to be applied on clutch plate as compared to multi-plate clutch.
Applications of Single Plate Clutch
- Trucks, Buses, etc., where space availability is not a problem.
- Medium duty vehicles, such as Jeeps, Cars etc.