Stroboscope is a simple, portable, manually operated device used for measurement of periodic or rotary motion.
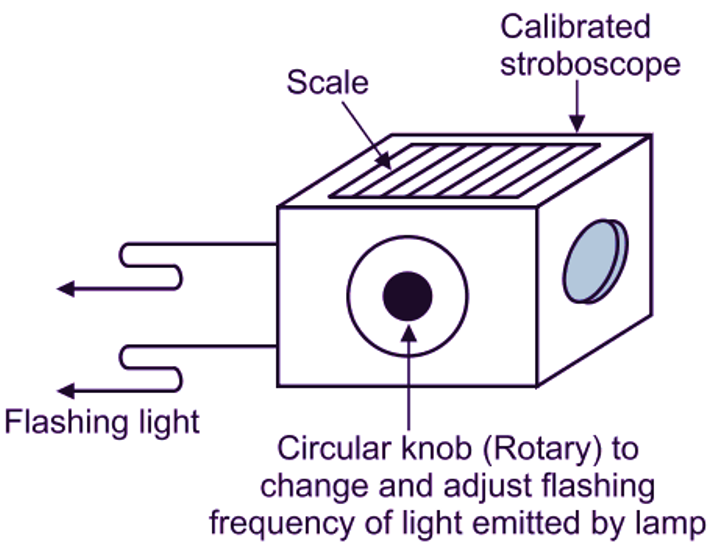
Fig. 1: Stroboscope
Stroboscope Principle of Working
If a strong light is caused to flash on the moving object, the object will appear stationary, if the flashing frequency is equal to speed of moving object. In other words, working principle of stroboscope is “To synchronize a flashing light with rotation of shaft, making it appear as standstill (stationary).”
Condition of Stroboscope
Frequency of flashing light should be equal to angular speed of shaft. Therefore, we need a source of light, having provision of changing flashing frequency of light emitted. Stroboscope or light source emits light radiations on the circular disc.
Construction of Stroboscope
Basically, stroboscope is a source of variable frequency flashing brilliant light (see Figure 1). The flashing frequency can be set manually by the operator. Thus, in short, stroboscope consists of a source of flashing light, whose frequency can be varied or controlled. This source is called as Strobotron. A distinct or reference mark is made (put) on the shaft (rotating body), whose speed is to be measured.
Working of Stroboscope
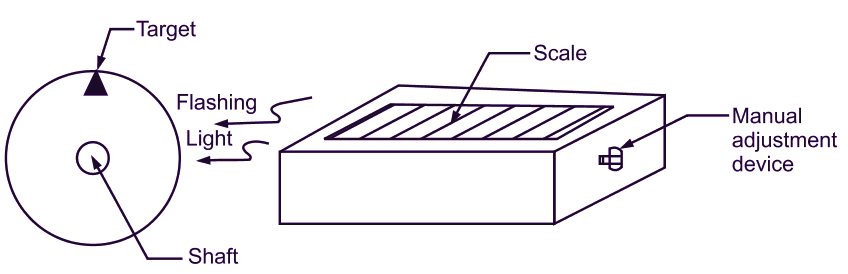
Fig. 2: Measurement of speed using Stroboscope.
The stroboscope is made to strike light on the mark. Refer Fig. 2. Circular (Rotary) knob is rotated manually and flashing frequency of light is adjusted, until mark appears stationary. When this condition is achieved, it means that, flashing frequency of light is equal to angular speed of shaft. Rotation of circular knob can be read from the scale of stroboscope, which is directly calibrated to give angular speed of shaft in r.p.m.
Advantages of Stroboscope
- It requires no special attachment With the shaft.
- This method imposes no load on shaft.
- Contactless operation.
Disadvantages of Stroboscope
- Variable frequency of oscillator cannot be stabilized to give fixed frequency.
- This method is less accurate. Therefore, it requires the use of digital meters.
- It cannot be used, where ambient lighten-ng is above a certain value. If it has to be used, then surrounding light must be dim to get effectiveness.
Applications of Stroboscope
- It is a portable and manual y operated deuce used to measure periodic or rotary motions.
- It is used to measure speed.
- It is very convenient to use a stroboscope for spot check on machinery speeds and for laboratory work.