In this topic, you study Sodium Vapour Lamp – Working Principle, Construction & Circuit Diagram.
Construction of Sodium Vapour Lamp
Fig. 1 illustrates one form of the modern low-pressure sodium vapour lamp. The sodium vapour lamp is similar in construction to the mercury vapour lamp. The two electrodes (E1, and E2) are mounted in a glass tube or bulb (G1) containing sodium along with a small quantity of neon or argon. Sodium vapour being chemically very active, the glass of the tube is of special composition in order to resist the action of hot sodium vapour. As already mentioned previously, to obtain best operating conditions and efficiency, it is essential to maintain the correct temperature in the discharge tube (about 300°C) and to reduce loss of heat from it.
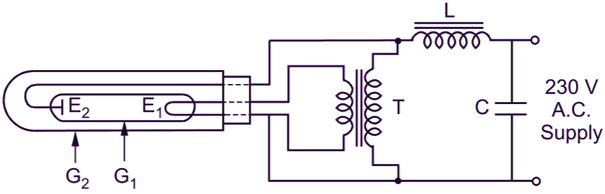
Fig. 1: Sodium vapour lamp
Therefore, the discharge tube itself is placed in an evacuated outer tube (G2). In addition to the stabilizing choke (L) and the capacitor (C), a small step-down transformer (T) is also included in the circuit for heating the cathode (E1).
Operation of Sodium Vapour Lamp
Similar to mercury vapour lamp, an initial discharge on switching on takes place in the neon (or argon) gas and the heat generated during the next few minutes is then sufficient to vaporize the sodium. This enables the main discharge to take place through the sodium vapour. Thus, the lamp starts emitting its characteristic bright yellow light. The choke stabilizes the discharge and the capacitor improves the power factor.
Applications of Sodium Vapour Lamp
These lamps are extensively used for the illumination of roads, goods yards, air-ports, etc. They are also sometimes used for advertisement purposes. The lamps with 250 watts and upward ratings are more commonly employed.
Advantages of Sodium Vapour Lamp
- Highest efficiency, about 3 to 4 times that of the filament lamps.
- Longer life.
Disadvantages of Sodium Vapour Lamp
- Bright yellow colour is not suitable for indoor lighting.
- Long tubes ale required for sufficient light output.
- Requires 5 to 10 minutes for giving full output. This factor is however of little importance in its practical use.
- Since the sodium solidifies when the tube cools, it is necessary to ensure that the sodium is deposited reåLsonably uniformly along the whole length of the tube and not concentrated at one end. Consequently, the lamp is to be used preferably in a horizontal