In this topic, you study 2 Point Starter (Two Point Starter) – Working, Diagram & Construction.
Manually operated face-plate type starters used for starting dc series motors are commonly known as two-point starters as they have only two terminals for their insertion in the motor circuit.
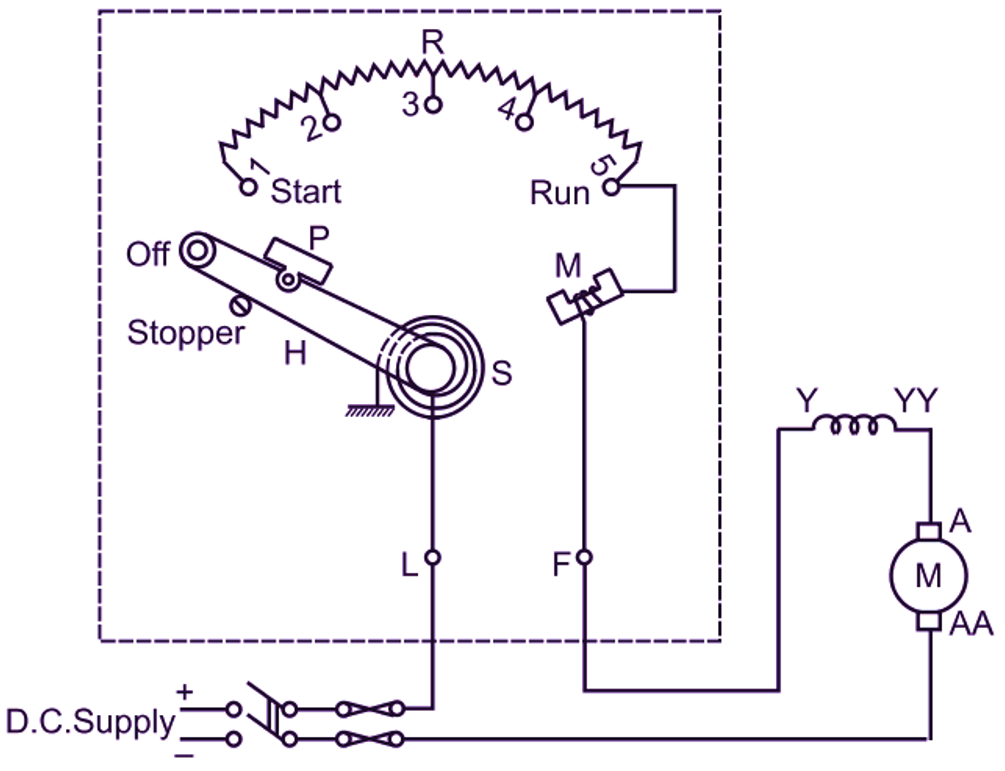
Fig. 1: Two-point starter for a dc series motor
Construction of Two-point starter
Similar to three-point and four-point starters, it consists of a starting resistance R subdivided between number of contact studs (1 to 5). The starting handle (H) is pivoted on one side and its other side is free to move against a strong spring S and make contact with each stud during the starting operation. The starter is provided with a protective device called no-load release. This no-load release consists of an electromagnet M and a hinged soft iron piece P carried by the starting handle. The coil of this electromagnet has a few turns wound on a U-shaped iron core and it is connected in series with the motor as shown in Fig. 1.
Operation of Two-point starter
For starting the motor, the dc supply is first switched on. The starting handle is then slowly moved in the clockwise direction from its OFF position against the spring tension. When the handle makes contact with the first stud, the motor gets connected across the line through the entire starting resistor and the coil of no-load release. As the handle is moved further, the starting resistor is gradually cut off from the motor circuit. Finally, in the running position (i.e. at final stud), the starting resistor is completely cut off and the motor achieves its full speed. Handle is held in this position against the spring tension by the electromagnet M of the no-load release.
Functions of No-load Release
Various functions carried out by no-load release are listed below :
- The starting handle is held in ON position against the spring tension by the electromagnet M of no-load release by attracting the soft iron piece P carried by the handle. This electromagnet is energized by the motor current passing through its coil.
- On no-load or on light load, the electromagnet of no-load release becomes weak due to low motor current. Hence the handle returns to OFF position due to spring tension, thus preventing the motor from overspeeding. This is the most essential protection required by a series motor.
- The handle is also returned to OFF position when the supply fails, or is switched off or when the supply voltage decreases appreciably. This prevents the starting of the motor without any starting resistance when the supply is again restored.