An electronic weighing machine has become very popular instrument for weight measurement in various industrial and commercial applications due to its high accuracy, fast response, stability, ruggedness and ease of operation.
Block Diagram & Working of Electronic Weighing Machine
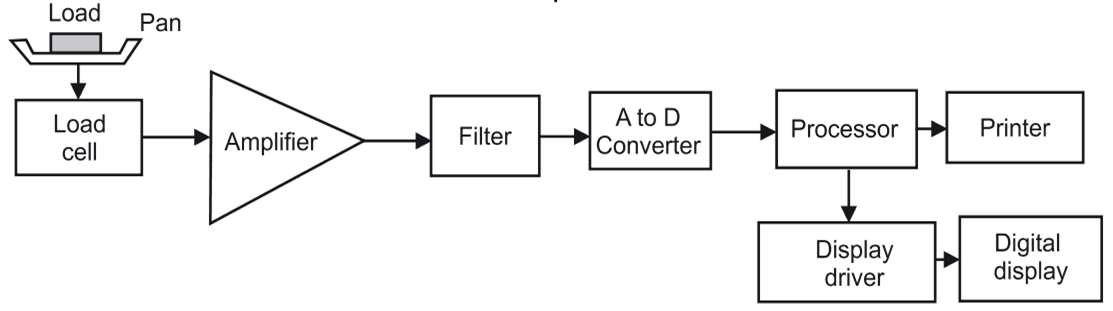
Fig. 1: Block Diagram of Electronic Weighing Machine.
Fig. 1 shows the block diagram of an electronic weighing machine which mainly consists of load cell, amplifier, filter, analog to digital converter, processor and the display unit. The load is placed on the load cell pan. The load cell contains bounded strain gauge transducers which convert the applied weight into equivalent electrical output using Wheatstone bridge. Zero setting arrangement is provided for the load cell. The output voltage from the Wheatstone bridge is then amplified by the amplifier and further filtered to remove the unwanted noise. This amplified and filtered analog signal is then fed to the Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) to convert it into equivalent digital form. The processor processes this input data stores it in the memory and calculates the cost of the item. The display driver generates the control signals for the printer and displays the data on the digital display unit. The processor also supports various functions. This type of weighing machine is used in super markets.
Advantages of Electronic Weighing Machine
- High accuracy.
- Fast response.
- Small in size.
- High resolution.
Applications of Electronic Weighing Machine
These machines are utilized in almost all industries and commercial applications.
- In grocery shops and super markets, for precision weight measurements like weighing gold, silver, diamond and other precious stones.
- In platform weighers, animal and human weighing, truck weighing, crane weighing and textile industries, etc.