Digital Voltmeter (DVM) is a voltage measuring device that represents A.C (or) D.C voltage measurement in digital form as discrete numerals.
Working Principle of Digital Voltmeter
The principle on which a DVM operates is analog to digital conversion. DVM converts the analog voltage into a digital display. The input to a DVM is analog voltage and output of a DVM is a digital representation of the input voltage.
Block Diagram of Digital Voltmeter
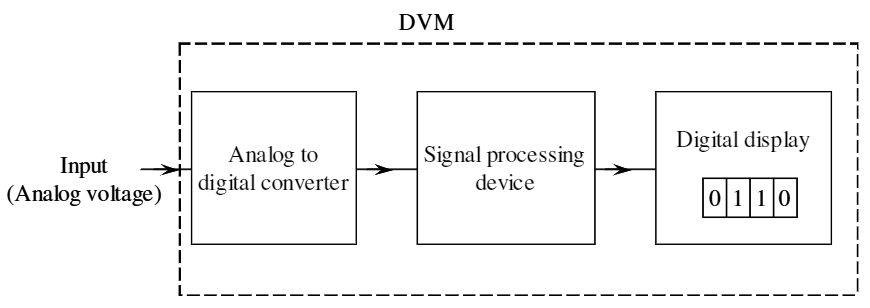
Figure 1: Digital Voltmeter Block Diagram.
A digital voltmeter consists of analog to digital converter, a signal processing and a digital display. The figure 1 shows the block diagram of a DVM.
Working of Digital Voltmeter
The analog input voltage is supplied to the Analog to Digital Converter (ADC). All ADC’s need reference signal which is generated internally. The circuit of the reference generator is based upon the type of ADC used in the digital voltmeter. The output from the ADC is in digital form and is being processed to the signal processing devices. Decoders, amplifiers, filters, rectifiers, modulators, voltage conversion device are used in signal processing device. Desired operations are performed in signal conditioning devices in order to make the signal suitable for display. Data transmission elements are also used for transmitting the data from signal processing device to display. It contains latches, counters, etc., based upon the requirement. A digital readout or the display indicates the readings of the voltage in digital form. A display may be LCD or LED’s.
Advantages of Digital Voltmeter
Digital readout is an important advantage of an digital voltmeter over an analog voltmeter in which a pointer deflects on a continuous scale to indicate the values of unknown voltages. This advantage eliminates the problem of parallax error and approximations by proving accurate digital values. Because of greater developments in the IC technologies. the power requirements, physical size and also cost of these devices are reduced. Therefore, Digital Voltmeters (DVMs) can actively compete with conventional analog instruments both in price and portability.
Specifications of Digital Voltmeter
Some of the general specifications of a digital voltmeter are given in the following table,
| Parameter | Specification |
| Input impedance | 11 MΩ to 1000 MΩ |
| Accuracy | 1% reading or (± 5 digit for A.C. at 40 to 500 kHz) |
| Polarity | AUTO negative polarity |
| Maximum indication | 1999 or – 1999 |
| Over-range indication | Only – 1 or 1 displayed at MSB |
| Display type | 3½ digit, LCD |
| Zero adjustment | Automatic |
| Unit annunciation | Ω, kΩ, MΩ, V, mV, buzzer, etc. |
| Sue | 160 (1) x 80 (b) x 30 (h) |
| Weight | 250 g (without batteries) |
| Power | Two AA-size 1.5 volts batteries. |
| Ranging | Selectable automatic or manual. |
| Sampling rate | 2 samples/s. nominal |
| Functions | Ohms, AC. amps, D.C. amps, A.C. volts, D.C. volts, diode test, continuity test |