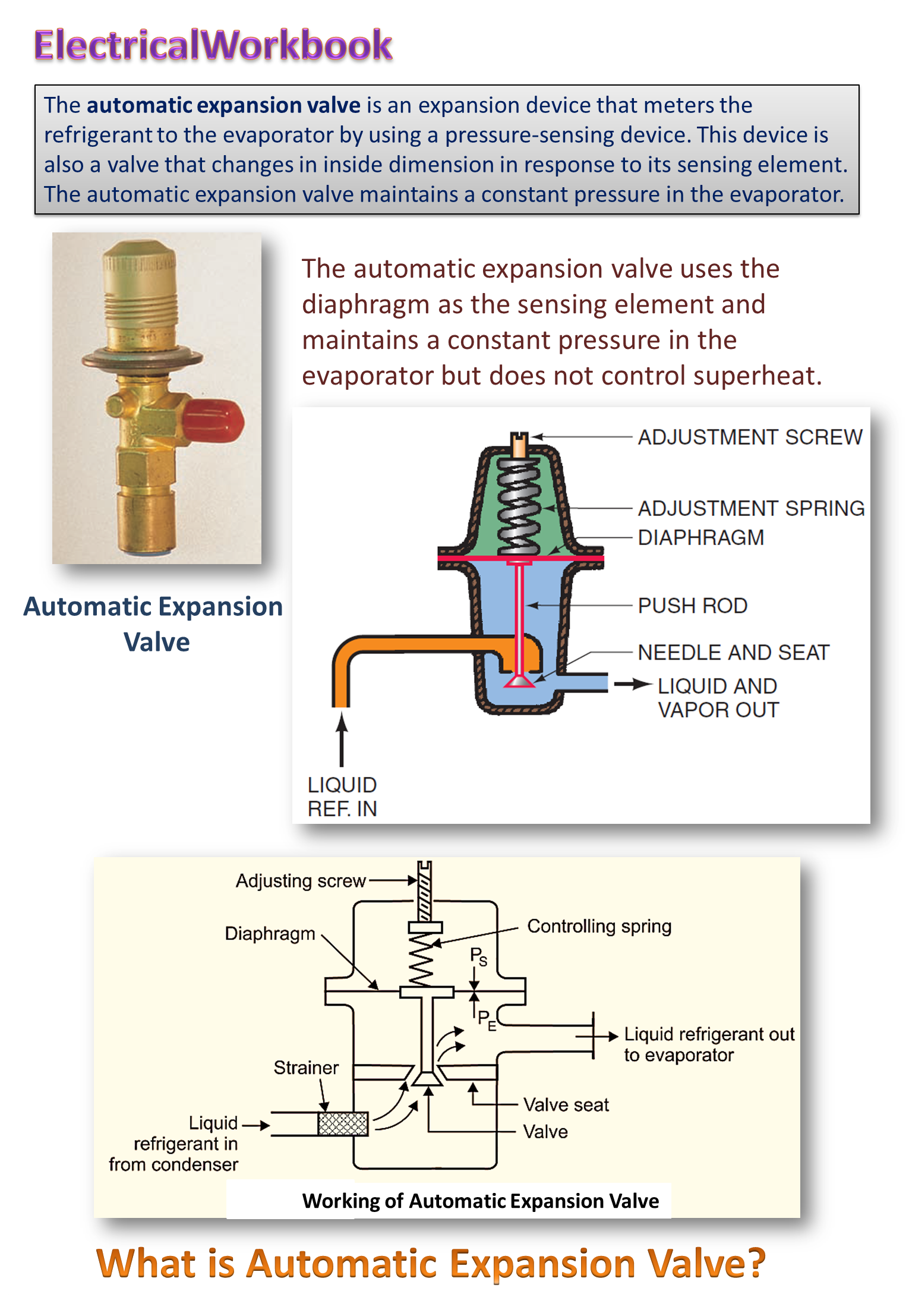
Automatic expansion valve works in response to the pressure changes in the evaporator due to increase in refrigeration load (pressure increases) or due to decrease in refrigeration load (pressure decreases). This valve maintains constant pressure throughout the range of varying load conditions on the evaporator by controlling the quantity of refrigerant flowing into the evaporator. Therefore, this valve is also known as constant pressure expansion valve. It is used with dry expansion evaporators, where the load is relatively constant.
Construction of Automatic Expansion Valve
The automatic expansion valve consists of a needle valve and a seat (which forms an orifice), a metallic diaphragm or bellows, spring and an adjusting screw. Refer Fig. 1.
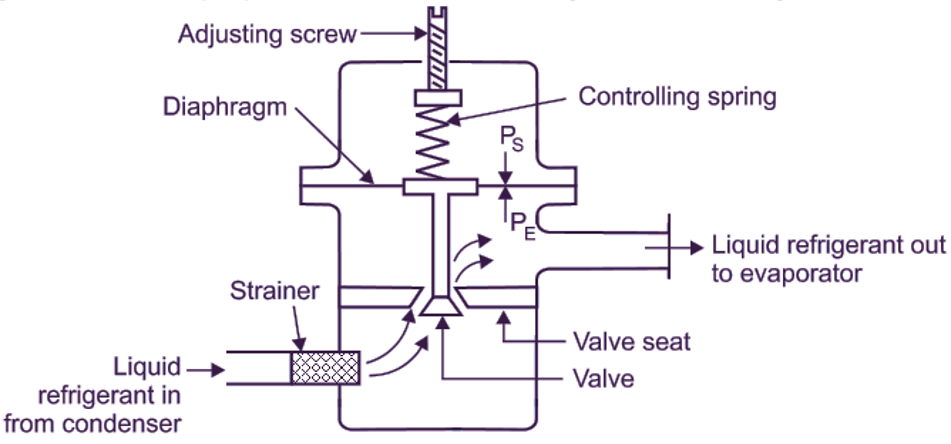
Fig. 1: Automatic expansion valve.
The opening and closing of the valve with respect to the seat depends upon the following two opposing forces acting on the diaphragm:
- A force exerted by the spring pressure (PS), Which acts on the top of diaphragm in vertically downward direction causing the valve to open.
- A force exerted by the evaporator pressure (PE), which acts beneath (under) the diaphragm in vertically upward direction causing the valve to get closed.
When the compressor is running, the valve maintains an evaporator pressure in equilibrium with the spring pressure and the atmospheric pressure. The spring pressure can be varied by adjusting the tension of the spring with the help of adjusting screw. Once the spring is adjusted for a desired evaporator pressure, then the valve operates automatically to maintain constant evaporator pressure by control ing the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator.
Working of Automatic Expansion Valve
When refrigeration load decreases, thereby reducing the evaporator pressure
Due to decrease in evaporator pæssure, PE will be less than PS. Therefore, diaphragm will move downwards, causing the valve to open. This allows more liquid refrigerant to enter into the evaporator and thus increasing the evaporator pressure, till the desired evaporator pressure is reached.
When refrigeration load increases, thereby increasing the evaporator pressure
Due to increase in evaporator pressure, PE will be more than PS. Therefore, diaphragm will move upwards, causing the opening of the valve to reduce. Since, opening of is less, the flow of liquid refrigerant to the evaporator Will reduce, which in turn, lowers the evaporator pressure, till the desired evaporator pressure is reached. When the compressor stops, the liquid refrigerant continues to flow into the evaporator and increases the pressure in the evaporator. This increase in evaporator pressure causes the diaphragm to move upwards and the valve is closed. It remains closed until the compressor starts again and reduces the pressure in the evaporator.
Important: Automatic expansion valve keeps the pressure constant in the evaporator. Therefore, it is also known as Constant pressure Expansion Valve.
Advantages of Automatic Expansion Valve
- AEV is inexpensive.
- It does not require maintenance, due to absence of moving parts.
Limitations of Automatic Expansion Valve
Automatic expansion valve is not used in actual practice or engineering applications due to following two major limitations.
- When the refrigeration load decreases, the evaporator pressure will decrease. This makes the valve to open fully, attempting to bring the evaporator pressure up to the pressure setting of the valve. This results in the liquid refrigerant flooding back to the compressor and causing serious damage to the compressor.
- When refrigeration load increases, the evaporator pressure will increase above the pressure setting of the valve. This makes the valve to close, until the evaporator pressure is reduced up to the pressure setting of the valve ‘starving’ the evaporator.
Applications of Automatic Expansion Valve
- Domestic refrigerators.
- Ice cream storage cabinets.
- Water coolers.
- Low capacity freezers.
- Milk chilling units.
- Package type air conditioners.