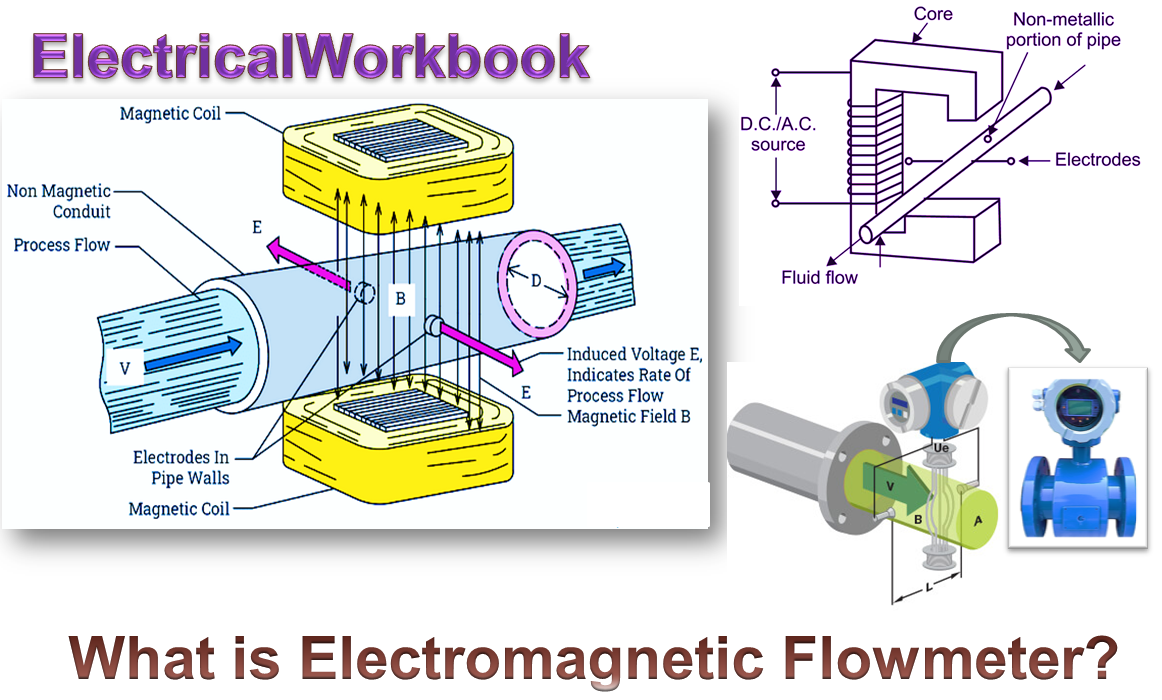
Working Principle of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Electromagnetic flowmeter works on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction for flow measurement, according to which, ‘Whenever conductor moves through magnetic field of given field strength, a voltage (e.m.f.) is induced in the conductor, which is proportional to relative velocity between the conductor and magnetic field.” OR
“Whenever a conductor cuts magnetic flux lines (magnetic field), an emf is induced in the conductor, which is directly proportional to rate of change of magnetic flux”.
In case of electromagnetic flow meter, fluid flow acts as a conductor.
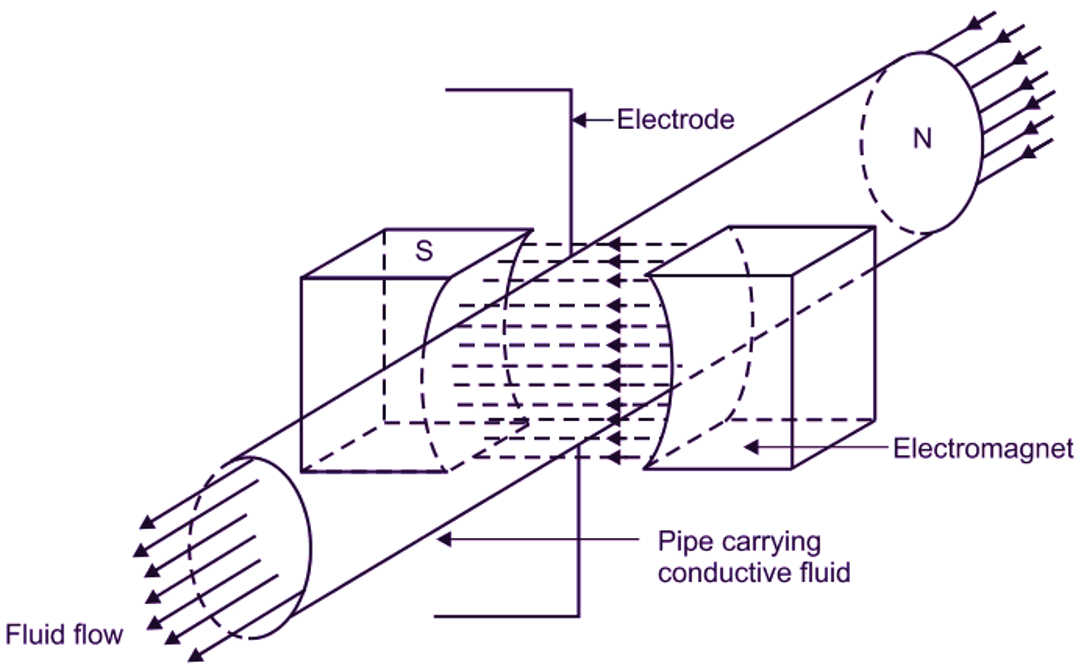
Fig. 1: Working principle of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Construction of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Electromagnetic flow meter consists of electrically insulated or non-conducting pipe such as fiber glass. A pair of electrodes is mounted opposite to each other and flushes with the inside wall of pipe carrying the fluid, whose flow is to be measured. In the figure, it can be observed that, two electrodes are placed at right angles to the plane of magnetic field, i.e. magnetic flux lines. The pipe is surrounded by an electromagnet, which produces magnetic field. This magnetic field is generated by the current flowing through the coil wounded on the electromagnet. The coil is powered by a steady D.C. supply.
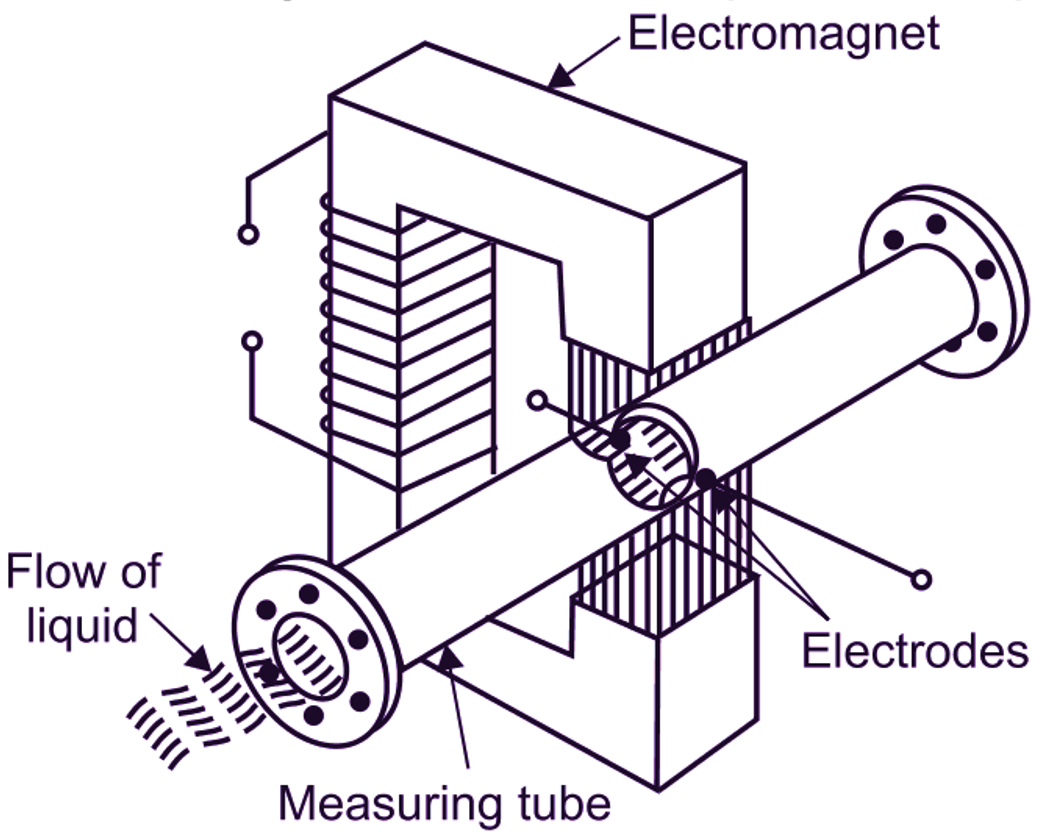
(a)
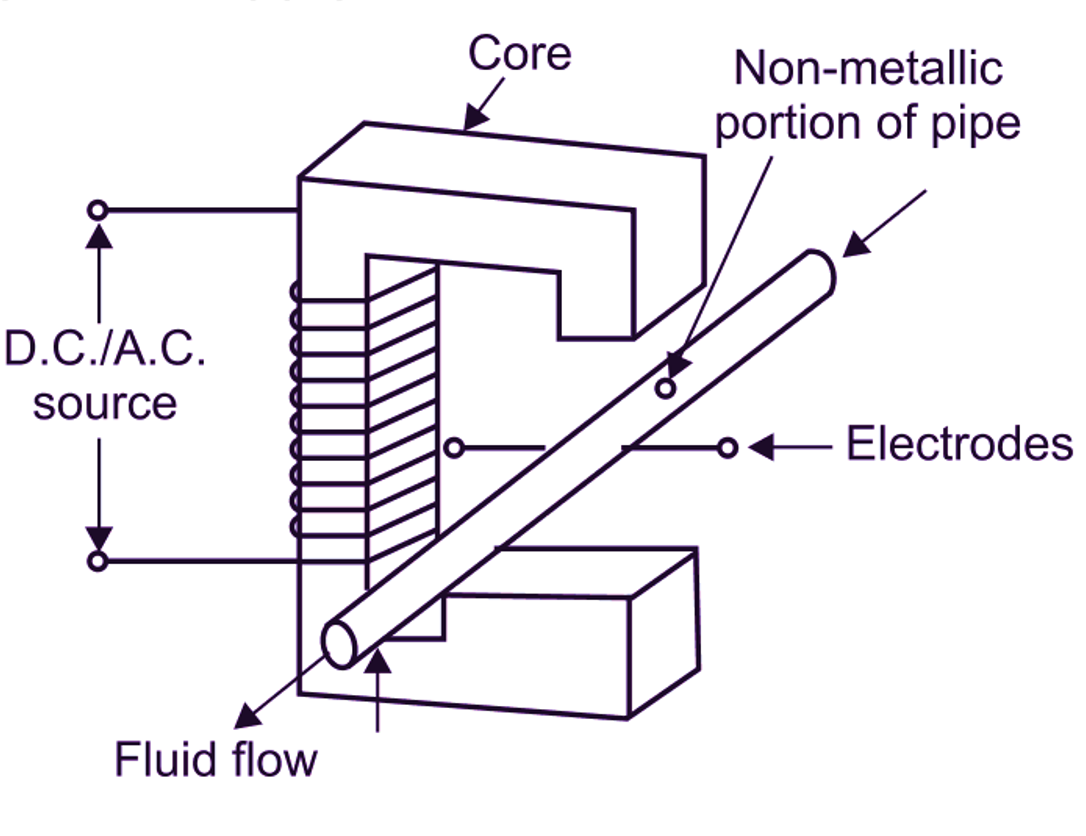
(b)
Fig. 2: Schematic Arrangement of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Working of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
A conductive fluid is passed through the pipe. As the fluid passes, its motion relative to magnetic feld produces an e.m.f proportional to velocity of fluid. It is given by Faraday’s law as,
E = B. L. V in Volts
where,
B = Magnetic flux density in Weber / m2
L = Length of conductor (fluid)
= diameter of pipe in m
V = Velocity of conductor (fluid) in m/sec.
This induced emf E is collected by the electrode and it is given to the external circuit. Since, this induced emf E is assumed to be directly proportional to velocity of flowing fluid, therefore, the emf so induced or produced becomes a measure of flow.
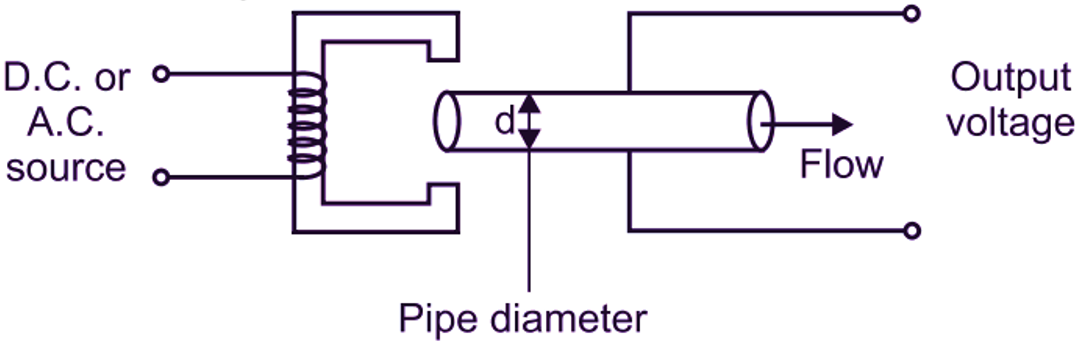
Fig. 1: Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Advantages of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
- Existing pipes can be converted into flow meters by adding a pair of electrodes externally and introducing a magnetic field.
- No obstruction to flow.
- High accuracy and better reliability.
- Linearity over wide range of flow measurements.
- Fast or rapid response to change in flow.
- No need of any obstruction in fluid flow, hence, no problem of error arising due to pressure drop.
- It is suitable for laminar as well as turbulent flow.
- Preferred in flow measurement of slurries, corrosive and greasy liquids, and liquids containing suspended particles or impurities.
- Bidirectional flow measurement is possible with this meter.
- Measurement is independent of viscosity, density, pressure and temperature.
Disadvantages of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
- If the flow rate to be measured is ow, then the emf or voltage produced is very small. Therefore, amplfers are to be used for conversion of induced voltages into usable form.
- It works only for those fluids, Which are electrical conductors.
- Highly expensive.
- Trapped gas bubbles cause errors.
- Some portion of liquids flowing through pipe may be deposited In the form of coating on inner surface of pipe. It will lead to fouling of electrodes, due to which, output signal obtained will be less as compared to actual value. If fouling is considerably more, then there are more chances of errors in measured value of flow.
Applications of Electromagnetic Flow Meter
- Used for measuring flow of fluid like corrosive acid.
- Widely used for flow measurement of cement slurries, sewage, paper pulp, detergents, greases and sticky fluids.
- Useful for any electrically conducting fluid.
- It is known as “No obstruction to Flow” meter, hence suitable for highly accurate and reliable measurement of flow of slurries, greasy materials and liqu’d containing suspended matter.