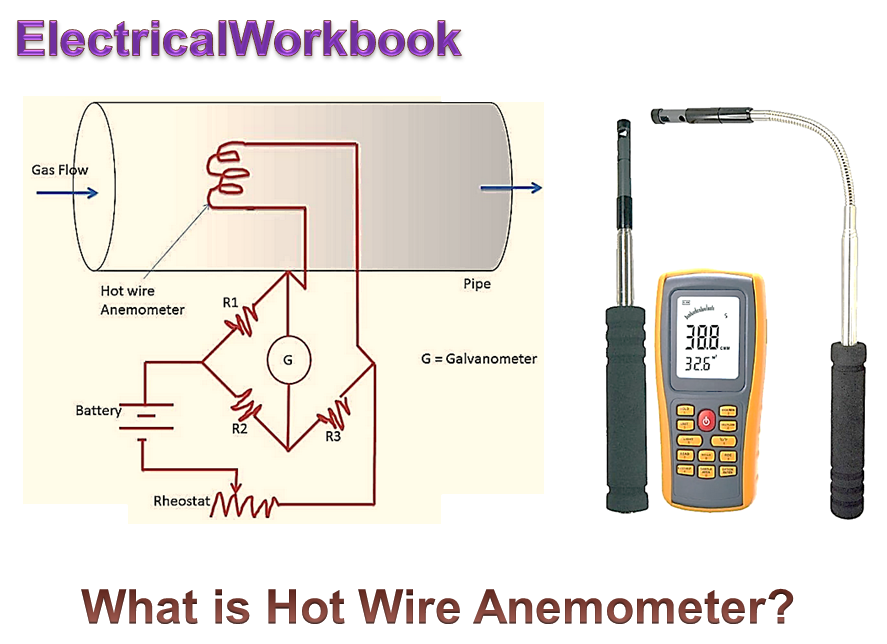
Hot wire anemometer is a type of variable velocity meter and uses thermal method for flow measurement. It uses the property that, resistance of wire is directly proportional to its temperature.
Working Principle of Hot Wire Anemometer
“When fluid flows over a heated surface, the surface temperature reduces due to transfer of heat from the heated surface to the fluid. This rate of reduction in temperature is a measure of flow rate (Fig. 1).”
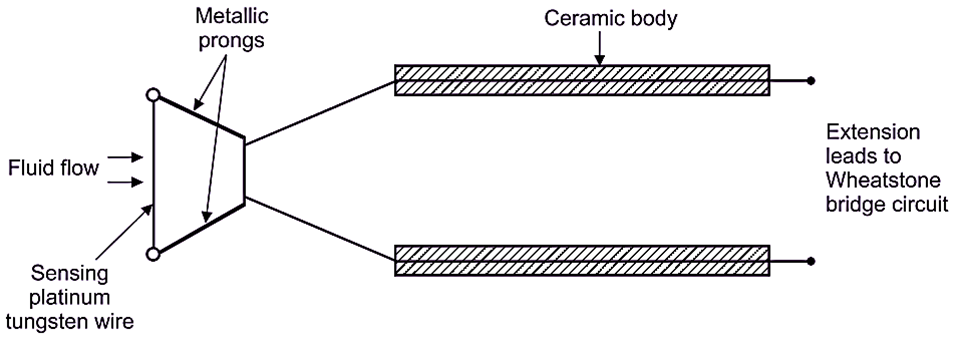
Fig. 1: Working principle of Hot Wire Anemometer
Construction of Hot Wire Anemometer
Hot wire anemometer consists of a platinum-tungsten wire (with diameter 5 pm) of short length and stretched between two supports. This wire acts as a sensor. The stream of air or gas is kept perpendicular to wire. This wire of platinum-tungsten (sensor) is welded between the two prongs of probe. The wire (sensor) is heated electrically and forms one arm of the Wheatstone’s bridge. The Wheatstone’s bridge has a balance detecting galvanometer.
Working of Hot Wire Anemometer
Here, the wire is heated electrically. The temperature of wire is determined by measuring its resistance with Wheatstone’s bridge (Fig. 2). When the wire along with the probe is introduced in the flowing fluid, it gets cooled due to velocity of fluid and resistance of wire decreases. Rate of cooling of wire (sensor) depends upon following properties:
- Dimensions and physica properties of wire.
- Temperature difference between the wire and the fluid.
- Thermodynamic properties of fluid (i.e. P, V and T).
- Stream velocity of fluid flow under measurement (i.e. Velocity of fluid flow).
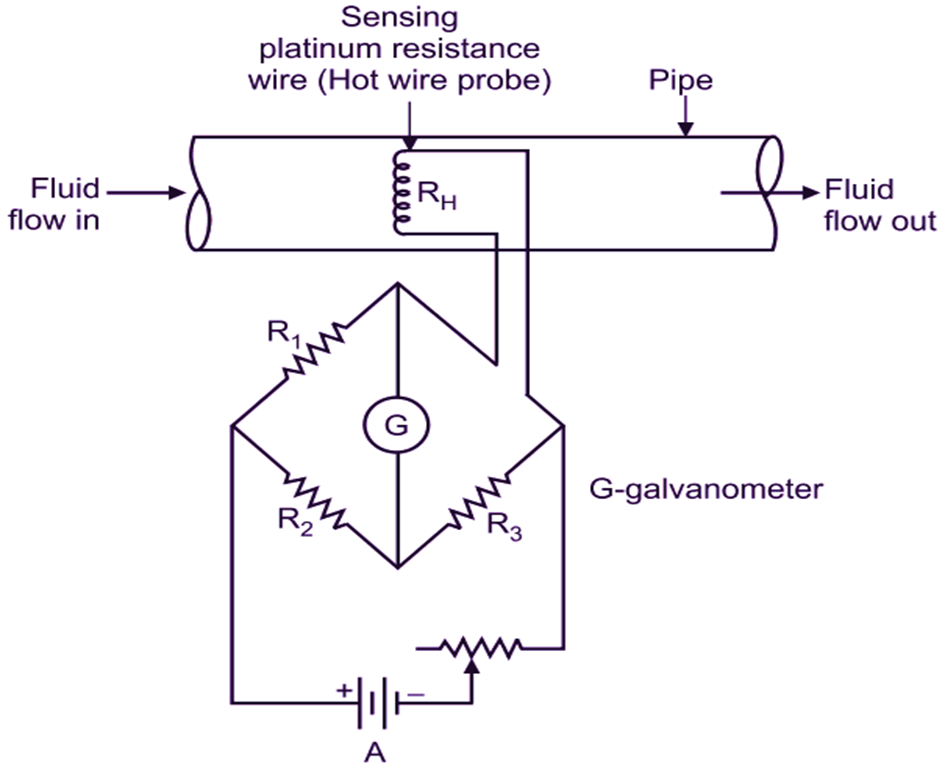
Fig. 2: Wheatstone’s Bridge Circuit Arrangement for Flow Measurement of Fluid
Amongst all the above properties, fluid velocity is the variable and rest of the properties almost remain constant. Therefore, Stream velocity is the measure of instrument response or we can say that, the instrument response is direct measure of flow velocity.
Methods of Measurement
There are two methods of measuring fluid flow:
- Constant current mode
- Constant temperature mode
Constant current mode
Here, voltage across the bridge is kept constant i.e. heating current is maintained constant (Fig. 3). Initially, the circuit is so adjusted that, when the heated wire lies in stationary air, the galvanometer reads zero. When the air flows, the hot wire (sensor) gets cooled and resistance of wire decreases causing the galvanometer to deflect. The galvanometer deflection is amplified, measured and correlated with the air velocity using a suitable calibration method.
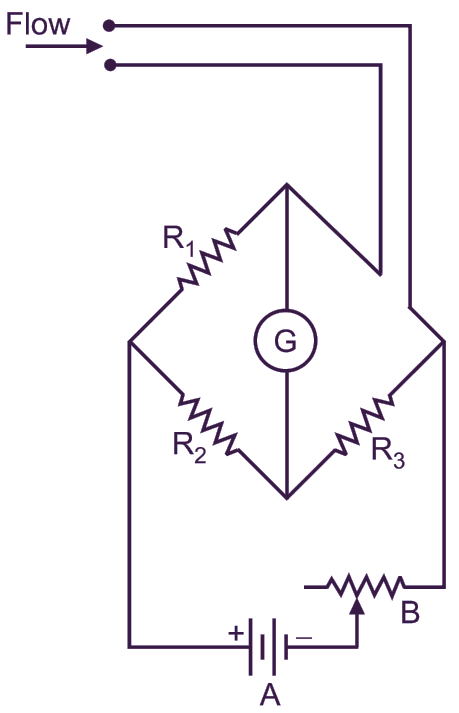
Fig. 3: Constant current mode.
Constant temperature mode
Here, the operating resistance of wire and hence, the temperature is maintained constant (Fig. 4). When the air flows, the hot ware gets cooled due to the flowing fluid. To keep the operating resistance of wire and its temperature constant, external bridge voltage is applied to the wire. This external bridge voltage is varied and adjusted to bring the galvanometer pointer to zero position. The external bridge voltage supplied can be measured by voltmeter. Now, the reading of voltmeter is recorded and then correlated With air velocity using a suitable calibration method.
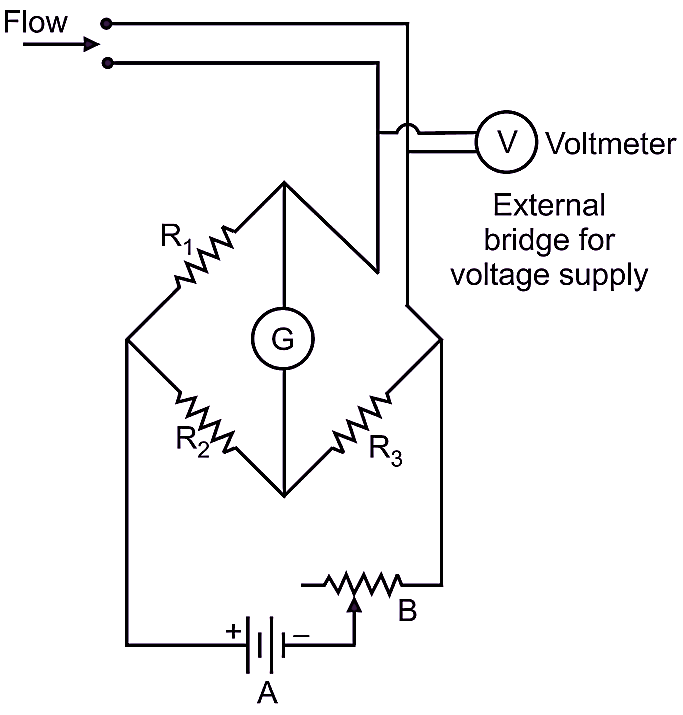
Fig. 4: Constant temperature mode.
Advantages of Hot Wire Anemometer
- Simple construction.
- Direct relation of flow rate with current and temperature, which makes easier to calibrate instrument.
- High mechanical strength.
- It can be preferably used for flow measurement of fluctuating flow.
- Output is electrical; therefore, the readout can be analog or digital.
- Excellent accuracy up to ± 0.1 %.
- Suitable for both, liquid and gas measurements.
- Measurement in any direction is possible.
Disadvantages of Hot Wire Anemometer
- It requires external power.
- It can be used for clean fluid only.
- Accumulation of dust particles on the Wire leads to serious heat transfer error.
- In constant current method, current has to be kept large with sudden drop in fluid velocity. Otherwise, there may be chance of lead getting burn out.
- Fine wire (small/minute diameter) has limited physical strength.
Applications of Hot Wire Anemometer
- It is widely used in measurement of air velocity, which is fluctuating in nature.
- It is used in measurement of wind velocity.
- In research applications to study varying flow conditions.
- Used for flow measurements of liquid as well as gas.