A gear tooth vernier caliper is a precision instrument used to measure the dimensions of gear teeth, such as the chordal thickness and depth of a gear tooth.
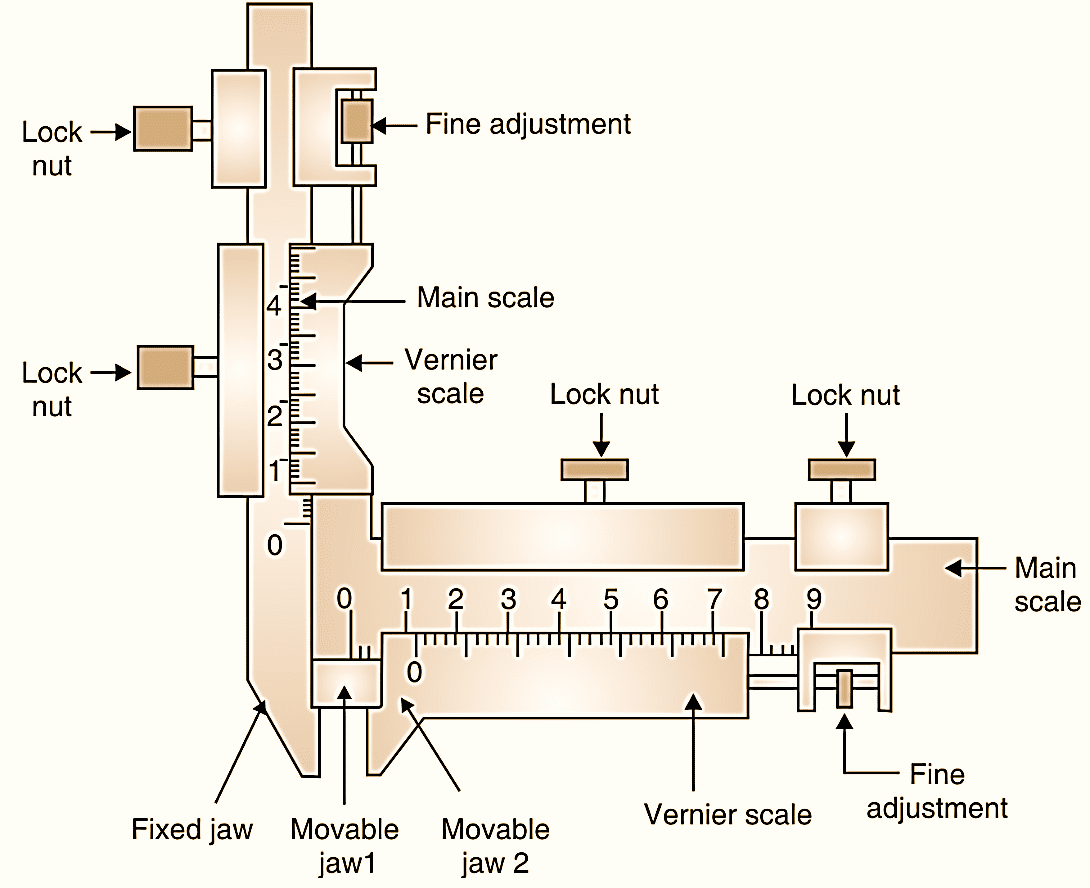
Figure 1: Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper.
The gear tooth thickness measuring vernier is as shown in Fig. 1. It measures the thickness of the tooth on pitch circle i.e. chordal thickness.
Construction of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
- Main Scale: A fixed linear scale used to measure lengths and provide a reference for the vernier scale.
- Vernier Scale: A secondary scale that provides precise measurements by dividing the main scale’s least division into smaller increments.
- Fixed Jaw: A stationary jaw used as a reference point during measurements.
- Movable Jaws:
- Movable Jaw 1: Measures the chordal thickness of the gear tooth.
- Movable Jaw 2: Measures the depth of the gear tooth.
- Lock Nuts: Used to fix the movable parts of the caliper in position during measurement to avoid errors.
- Fine Adjustment Screw: Enables precise movement of the movable jaws for accurate measurements.
- Bevel Edge: The edges of the jaws are beveled to fit the contours of gear teeth.
Working of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper consists of two beams which are in square with each other. There are two sliding vernier scales which moves along the beams of main scale. The tooth thickness on the pitch circle is measured as the distance between a fixed jaw and a movable jaw by fixed adjustable jaw of vertical vernier beam. In other words it is a combination of two vernier with a common jaw.
Working Principle of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
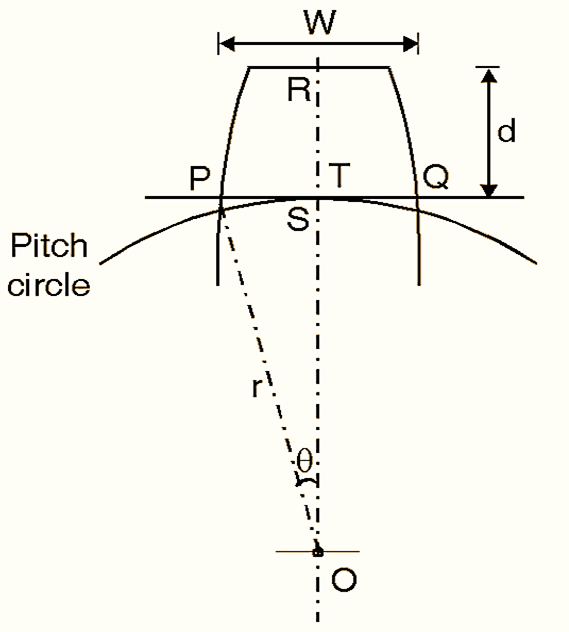
Figure 2: Working Principle of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
Gear tooth thickness is measured at pitch circle, and it is also called as pitch line thickness (See Figure 2). In the above sketch ‘d’ is chordal addendum, which can be calculated as,
\[\text{d = }\frac{\text{Nm}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{1 + }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{N}}-\text{cos}\left( \frac{\text{90}}{\text{N}} \right) \right]\]
Where,
N – Number of teeth
m – Module
Tooth thickness can be calculated using gear tooth vernier. By setting ‘d’ in vertical vernier, horizontal vernier gives ‘W. ‘W’ can be verified by,
\[\text{W = N}\text{.m sin}\left( \frac{\text{90}}{\text{N}} \right)\]
Procedure for Measurement using Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
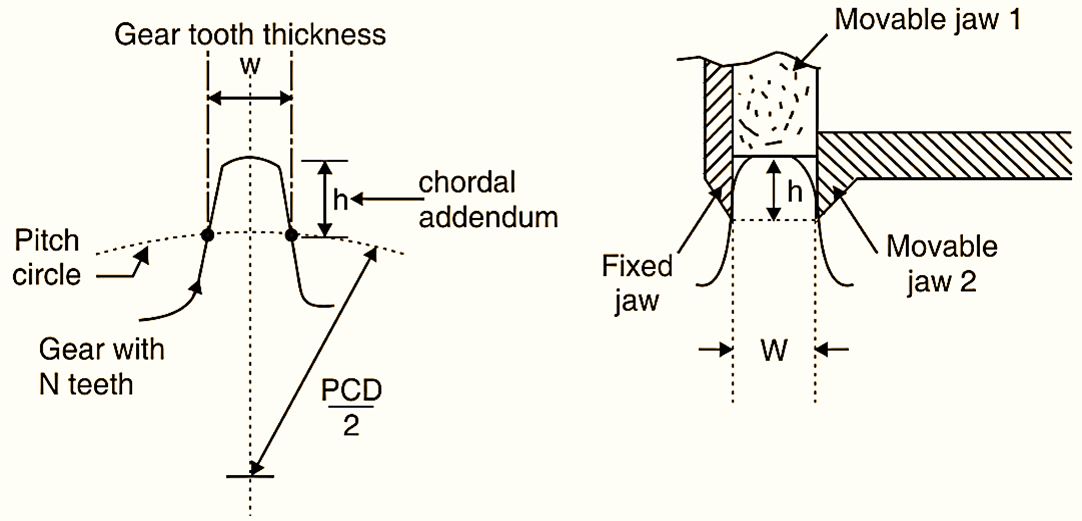
- Find chordal addendum by using by using Equation (Fig. 3).
\[\text{h = }\left( \frac{\text{mN}}{\text{2}} \right)\left[ \frac{\text{2}}{\text{N}}+1-\text{cos}\frac{\text{90}}{\text{N}} \right]\]
- Set height ‘h’ on vertical vernier by using fine adjustment screw.
- Apply vernier to gear tooth as shown in Fig. 3, so that the fix jaw can touch the flank of tooth.
- Push movable jaw of horizontal vernier and lock it.
- This gives the gear tooth thickness ‘W’.
Applications of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper
- Gear Manufacturing: To inspect the accuracy of gear dimensions during production.
- Maintenance: To measure wear and tear on gear teeth and determine if replacements are needed.
- Quality Control: Used in industries to ensure gears meet design specifications.