In this topic, you study Mercury Vapour Lamp – Working Principle, Construction & Circuit Diagram.
Mercury vapour lamps are available in various forms. Fig. 1 shows one form of this lamp.
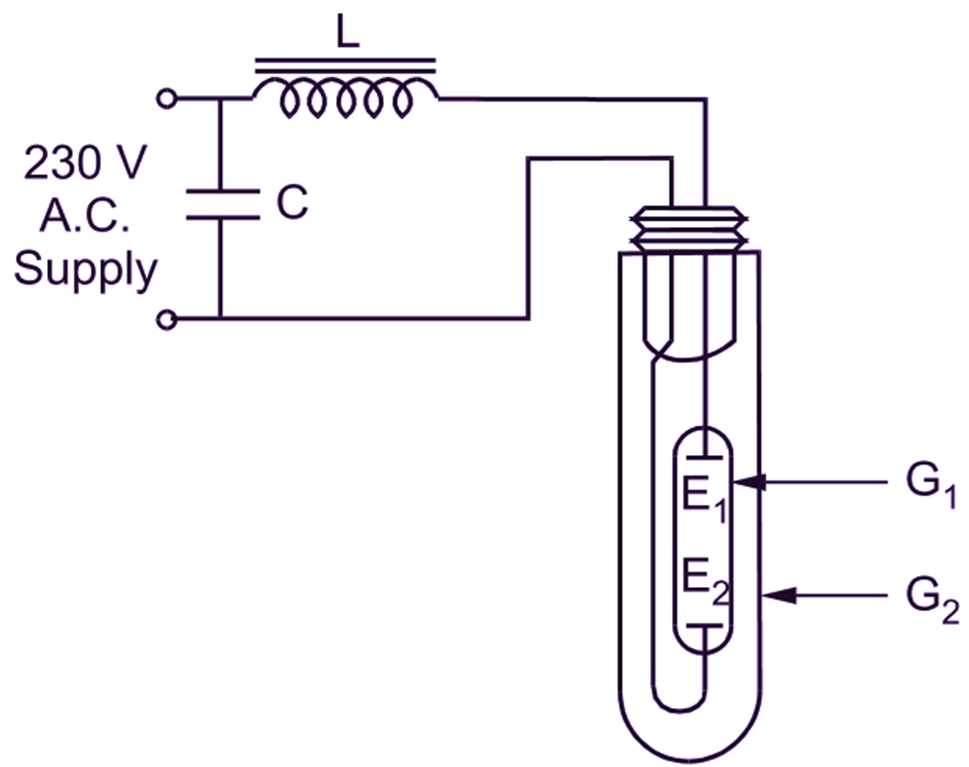
Fig. 1: Mercury vapour lamp
Construction of Mercury vapour lamp
It consists of the discharge tube (G1) enclosed within an evacuated outer glass tube (G2) as shown in Fig. 1. This arrangement reduces heat loss thereby improving the operating efficiency of the lamp. The inner tube contains a small quantity of mercury and argon (or neon). The two cathodes made from electron emitting material and held in tungsten wire helices form the main electrodes (E1 and E1). The pressure inside the discharge tube is of the order of 1 to 2 atmospheres. The control circuit of the lamp consists of a stabilizing choke (L) and a capacitor (C).
Operation of Mercury vapour lamp
When the lamp is switched on, the initial discharge takes place through neon or argon gas. The heat produced during the next few minutes due to the discharge through this gas vaporises the mercury. The lamp then commences normal operation and emits its characteristic light with a bluish tinge. During normal operation, the cathode is maintained incandescent (at very high temperature) by the ionic bombardment and therefore no heating of the cathode is necessary. The choke stabilizes the discharge i.e. limits the current to a safe value as already explained in the case of a fluorescent lamp. The power factor lowered by the presence of the choke is improved with the help of a capacitor connected across the supply.
Applications of Mercury vapour lamp
These lamps are widely used for out-door yard lighting and street lighting where a high level of illumination is essential and the colour of the light is not important. Such lamps are made in sizes of 125, 250 W and upwards.
Advantages of Mercury vapour lamp
- Efficiency well in excess of that of filament lamps (nearly 3 times). Therefore, gives more light output for a given wattage.
- Longer life (about 3000 working hours).
Disadvantages of Mercury vapour lamp
- Requires warming up time of about 3 to 5 minutes.
- If the lamp goes out while in service, for its restarting, cooling is necessary. Cooling reduces the vapour pressure to sufficiently low value, which then allows restriking of the discharge in the neon or argon to take place.