In RC Phase Shift Oscillator, the oscillations are developed due to the resistor and capacitor, which determines the frequency of oscillations.
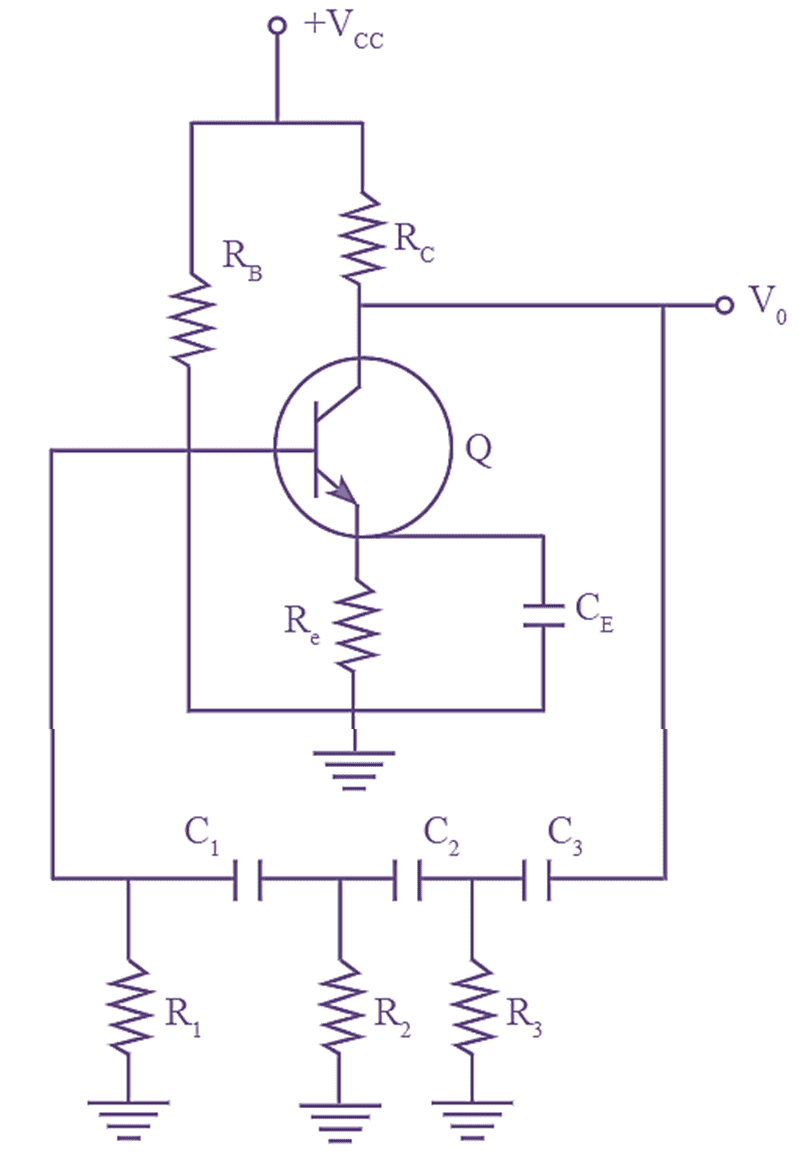
Figure 1: RC Phase Shift Oscillator.
Circuit Diagram of RC Phase Shift Oscillator
The circuit diagram of RC Phase Shift Oscillator is as shown in figure 1. It can be observed from figure 1 that the RC phase shift oscillator employs an n-p-n transistor (Q) in CE configuration. It also consists of a feedback or phase shift network containing three identical RC sections. At a particular frequency, each RC section of the feedback network produces a phase shift of 60º. Thus, the total phase shift produced by the RC network is 3 x 60º= 180º. Moreover, the transistor (or CE amplifier) also provides a phase shift of 180º to the applied input. Thus the total shift in the circuit becomes 360º or 0º.
Working of RC Phase Shift Oscillator
The supply voltage (Vcc) produces variations in the base of the transistor. These variations get amplified at the collector output and applied to the RC feedback network. The feedback network produces a phase shift of 180º and outputs a voltage Ei to the transistor amplifier. The CE transistor amplifier produces a phase shift of 180º. Hence, the total phase shift becomes 360º, which is the essential condition for sustained oscillations. The expression for frequency of oscillations of RC phase shift oscillator is given by,
\[f=\frac{1}{2\pi RC\sqrt{6}}=\frac{0.065}{RC}\]
Advantages of RC Phase Shift Oscillator
- As RC oscillator contains lumped elements, it is less expensive and the circuit is simple.
- It is used as a audio signal generator.
- It has high frequency stability
- It can be operated over a frequency range of several kHz.
- The output of RC oscillator is mostly distortion free.
- It does not require any feedback for stabilization.
Disadvantages of RC Phase Shift Oscillator
- The frequency stability of RC oscillator is less than that of Wien bridge oscillator.
- Due to smaller feedback it provides small output.
- In RC oscillator, there is a difficulty in generating oscillations due to small feedback signal
- It requires high voltage batteries.