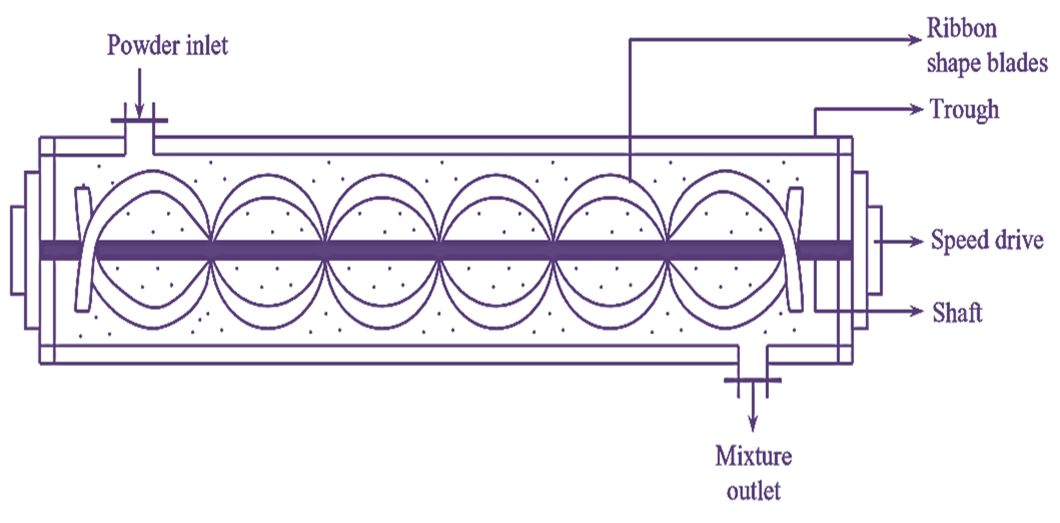
Figure 1: Ribbon Blender.
Working Principle of Ribbon Blender
The principle involved in ribbon blender is shear, which is supplied to the material (powder bed) by the rotating blades. Along with shear, convective mixing also occurs. High shear forces are developed which break the lumps and aggregates.
Construction of Ribbon Blender
Ribbon blender is a static mixer which consists of a pair of ribbon-shaped blades fitted onto a shaft in opposite directions i.e., one left-handed (anti-clockwise) and another right-handed (clockwise) (see Figure 1). These blades are made tip of stainless steel and the shaft holding the blades is fixed horizontally in the centre such that the blades do not touch the inner surface of the metal trough. The shaft is rigid while the blades are connected to a fixed-speed drive. The trough is provided with an inlet at the top and an outlet at the bottom.
Working of Ribbon Blender
Powders are introduced into the trough through the inlet and blades (ribbons) are allowed to rotate with the help of a fixed speed drive. Ribbons move the powder in two directions i.e., initially powder moves slowly towards right and then suddenly towards left. The entire equipment is a closed system which prevents the loss of dust during dry mixing and solvent evaporation during wet mixing. The curved ribbons facilitate the lip and down movement of the powders. High shearing forces get developed which break the lumps and aggregates. Finally the mixture is collected from the bottom outlet.
Advantages of Ribbon Blender
- Apart from solid-solid, it can also be used for liquid-solid mixing.
- The rate of shear can be increased with the help of perforated blades.
- Requires less space.
Disadvantages of Ribbon Blender
- Formation of dead spots (unmixed areas) may occur.
- The ribbon speed cannot be altered because of fixed speed drive.
- Produces less shearing force compared to planetary mixer.
- Since the particles move in two directions, the mixing is inefficient.
Applications of Ribbon Blender
- Ribbon blender is used for mixing solids containing fine particles, wet masses, plastic solids, fibrous and sticky materials.
- It is also used for mixing solids having uniform density and particle size.