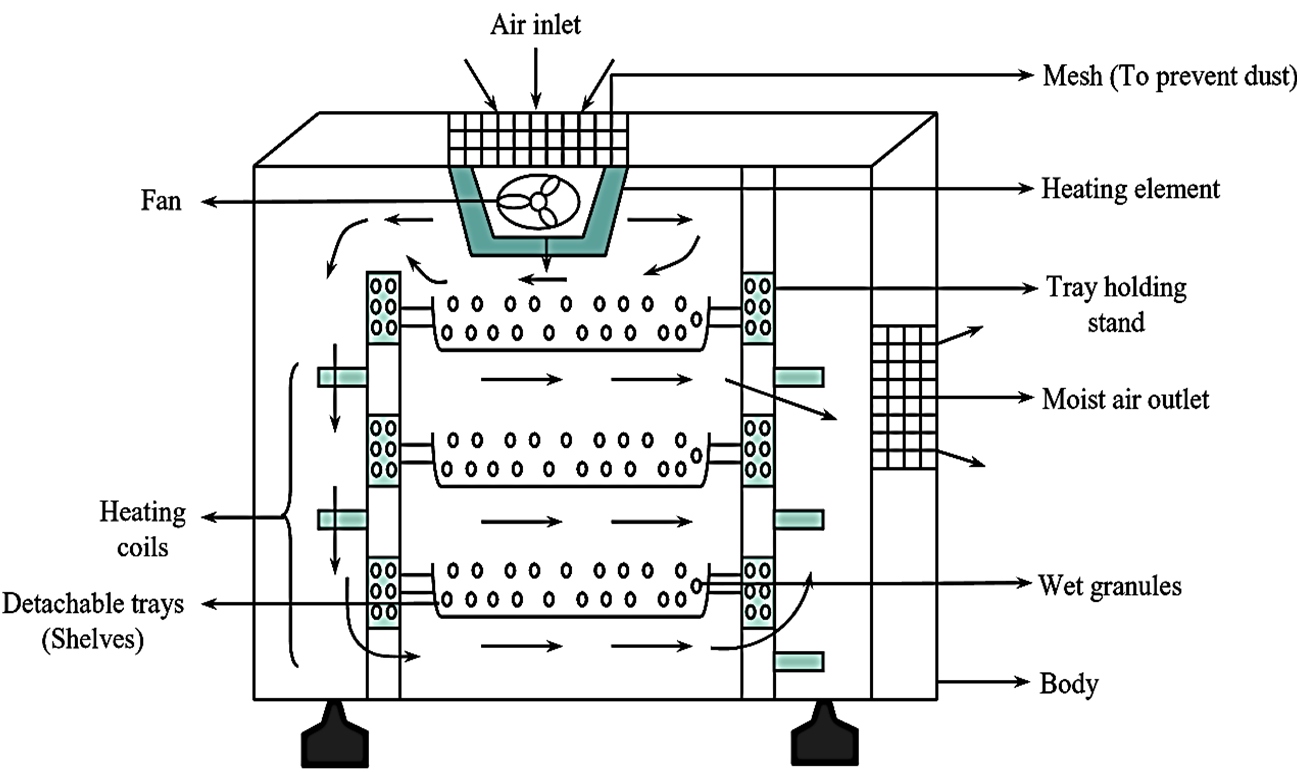
Figure 1: Tray Dryer.
Working Principle of Tray Dryer
The principle involved in tray dryer is forced convection where hot air is circulated continuously over the wet material. Water vapours formed, mix with the circulating air and are eliminated through the outlet provided. The supply of (fresh) hot air and the removal of moist air must be parallel to each other and in continuous motion.
Construction of Tray Dryer
The figure 1 represents a simple Tray dryer. It consists of a set of trays that are arranged in a horizontal manner and held in position with the help of a stand. The trays are detachable i.e., they can be easily removed and replaced in their respective positions. The number of trays vary depending upon the need (i.e., 3-4 trays for laboratory purpose while 15-20 trays for industrial need). The size usually ranges from 120 to 240 square cm. A gap of 40 mm is maintained between the bottom of upper tray and the surface of the load present in the subsequent tray.
The tray holding stand has a number of perforations in order to facilitate efficient circulation of air. A fan is fitted at the topmost position of the dryer which is surrounded by heating elements. This fan drags air from the environment which is then heated by the heating element. Additional heaters are fitted on either side of tray holding stand to achieve approximate heating of air. An outlet is present at the right side of the dryer. The entire equipment is enclosed in an insulated body provided with a door in the front.
Working of Tray Dryer
The trays are loaded with material (i.e., wet solid). Care must be taken not to overload the trays due to which non-uniform drying may occur. The fan and the heating element are switched on. Air enters through the mesh provided above the fan and subsequently gets heated up (due to heating element). The hot air is continuously circulated above the trays, due to which the water present in the wet solid gets evaporated. Hot air passes above the wet solid with a high velocity, due to which only small amount of moisture is held (by air) during its first pass, and hence such air will be useful for recirculation. Thus, vapours are removed along with the exhaust air through the outlet provided. The dryer is allowed to cool for some time after which the dried material is obtained.
Advantages of Tray Dryer
- It avoids the loss of material during loading and unloading.
- Handling of material is easy.
- Can be used for batch-wise operation.
- Does not require skilled labour.
- More efficient for valuable materials.
- Simple in construction.
Disadvantages of Tray Dryer
- Labour cost is high.
- It is a time consuming process.
- Not suitable for thermolabile and oxidizable products.
Applications of Tray Dryer
- Tray dryer can be used for drying sticky substances, pastes and granules, crystalline materials, precipitates etc.
- It is also used for drying crude drugs, chemicals powders and tablet granules including parts of equipment.
- Modified tray dryers such as vacuum tray dryer is used for drying vitamins and other heat sensitive products.