Climbing Film Evaporator is a type of long tube evaporator, in which high-velocity feed enters the tubes from the bottom, hence the apparatus is named as climbing or rising film evaporator.
Working Principle of Climbing Film Evaporator
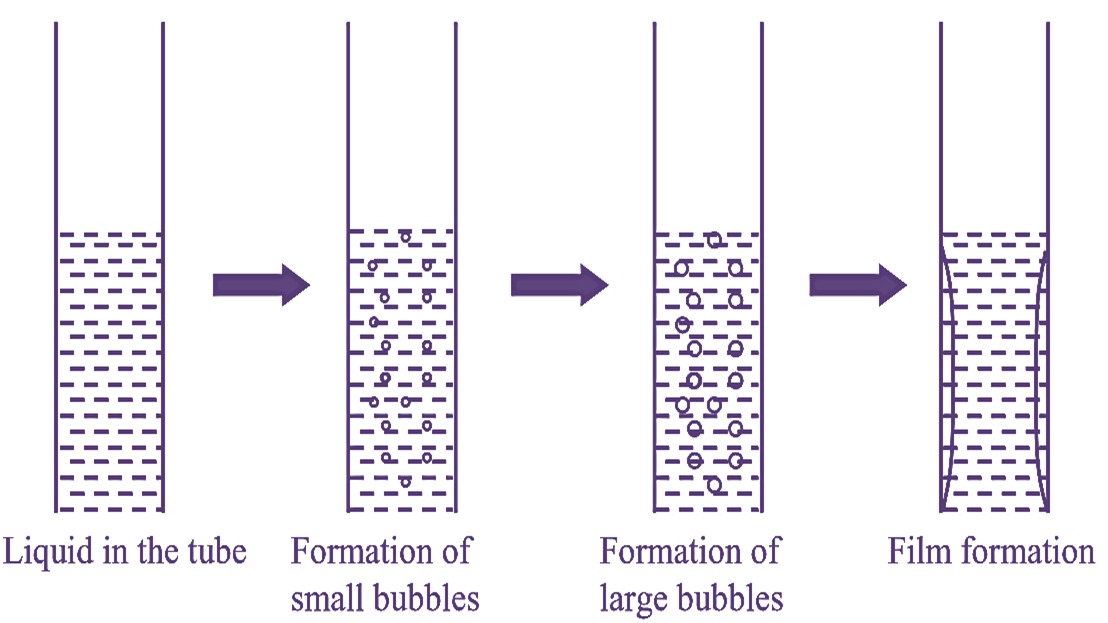
Figure 1: Principle Involved in Climbing Film Evaporator.
As the temperature is uneven within the tubes (due to steam), the feed begins to boil when it has travelled half way in the tubes. As the feed moves further upwards, its temperature decreases due to evaporation resulting in the formation of vapours. These vapours form small bubbles which aggregate to form large bubbles and travel upwards. This mixture of liquid and vapour cornes out from the tubes (i.e., from above) and strike the deflector, which separates the liquid and vapour. Vapours are removed from the vapour outlet while the liquid is sent into the recirculation pipe.
Construction of Climbing Film Evaporator
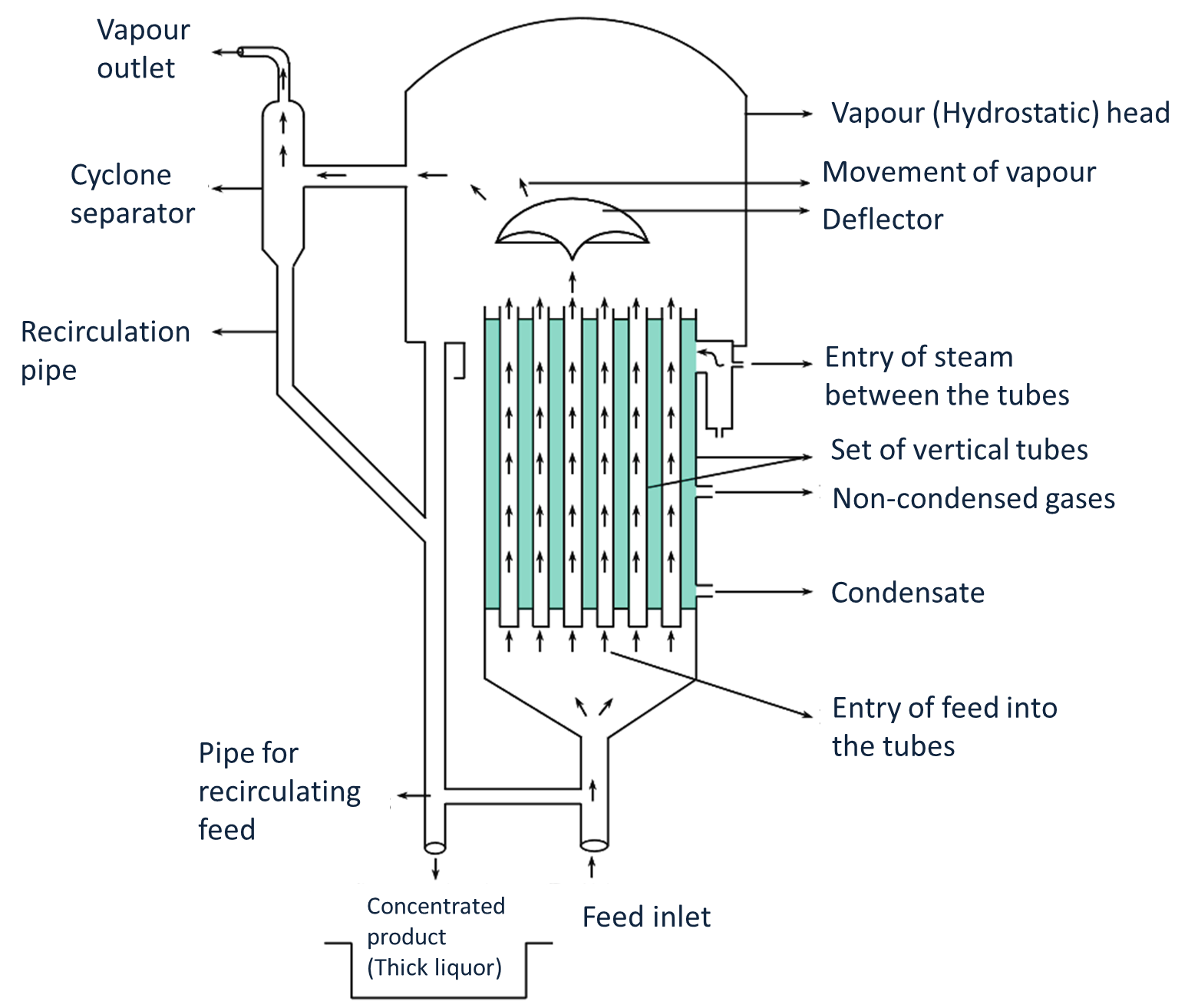
Figure 2: Climbing (Rising) Film Evaporator.
In the climbing (rising) film evaporator tubes of diameter 2.5-5 cm and length of 20-30 ft are held by tube sheets both at the top and bottom. Feed and steam inlets along with two outlets for condensed and non-condensed gases are present. A curved deflector is present in the vapour head of the evaporator. A cyclone separator is also attached to the vapour head of the evaporator.
Working of Climbing Film Evaporator
Feed is made to enter from the bottom of the tubes and its level is maintained only 2-3 feet above the bottom tube sheet. Steam is made to enter the evaporator through the steam inlet and circulates in between the tubes. Initially, the feed within the tubes does not boil. When it travels a little distance upwards, it acquires enough heat and starts to boil, thereby forming small bubbles. These bubbles fuse to form large bubbles. As large bubbles move up the evaporator, they carry a part of the liquid (slug) along with them. The large bubbles grow and form films which spread over the walls of the evaporator.
This phenomenon occurs at the top part of the tube sheet. The mixture of liquid and vapour strikes the deflector present in the vapour head and the vapours get separated from the liquid. These vapours are removed from the vapour outlet present in the cyclone separator. Thus, the curved deflector prevents entrainment as well as helps in breaking the foam. Liquid concentrate is withdrawn from the bottom part of the evaporator and is obtained as a thick liquor.
Advantages of Climbing Film Evaporator
- Liquid feed gets distributed within the tubes evenly as it enters from the bottom.
- Boiling point of the feed does not get elevated due to the presence of vapour head, as the tubes are not submerged.
- Due to high velocity of the feed, the heat transfer coefficient (HTC) is also high.
- It is suitable for foam forming or frothing liquids as it contains a deflector.
- Slug deposits can be removed by increasing the feed rate or decreasing the steam rate.
- Occupies less floor space.
Disadvantages of Climbing Film Evaporator
- Cleaning and maintenance is difficult.
- Requires large head space.
- Associated with high pressure drop when compared to falling film evaporator.
- Scaling of liquid occurs.
- Varying the rate of entry of feed affects the evaporator. High feed rate prevents sufficient concentration of the product, whereas low feed rate prevents the formation of film and leads to dry patches onto the walls of the tube.
- Not suitable for viscous and salting liquids.
Applications of Climbing Film Evaporator
- It is basically used for concentrating thermolabile (heat sensitive) materials like insulin, vitamins, extracts of liver etc., due to its short contact time (around 20 seconds).
- It is mainly used in sugar industry.
- It is used to concentrate black liquor in paper industry.
- It is used for handling corrosive solutions, clear and foaming liquids.
- It is used to concentrate non-salting liquors.