Single phasing means, one of the three phases is disconnected from the 3-phase supply so that the motor’s two phases are only remaining electrically connected. This happens due to the burning out of one fuse out of three fuses. Generally, this happens in the operation of star-delta starter or Auto-transformer starter used to start the motor due to defective contact in ‘run’ side of starter. When single phasing occurs, and the motor is running on load, the speed of the motor suddenly decreases and motor tries to stop or run-slow (stalling).
If in such case the motor does not stall and if it is carrying more than half the full load, both stator and rotor will be seriously over heated. Because the load is shared by two phases of winding, instead of three phases and stator and rotor current increases increasing temperature. The temperature rise in the stator will be most marked in two phases if it is star connected and in one phase if stator is delta connected. The protections used for single phasing fault are:
- Thermal overload relays
- Single-phase preventer
Thermal Overload Relays
Thermal over load relays operate due to increase in current of two phases due to single phasing. These relays can operate trip circuit and disconnect the motor from supply.
Single Phasing Preventer
Main parts of the circuit.:
- Control coil,
- Negative sequence filter,
- Contactors,
- Normally closed NC contact,
- Normally open NO contact,
- C.T.S.,
- Thermal relay.
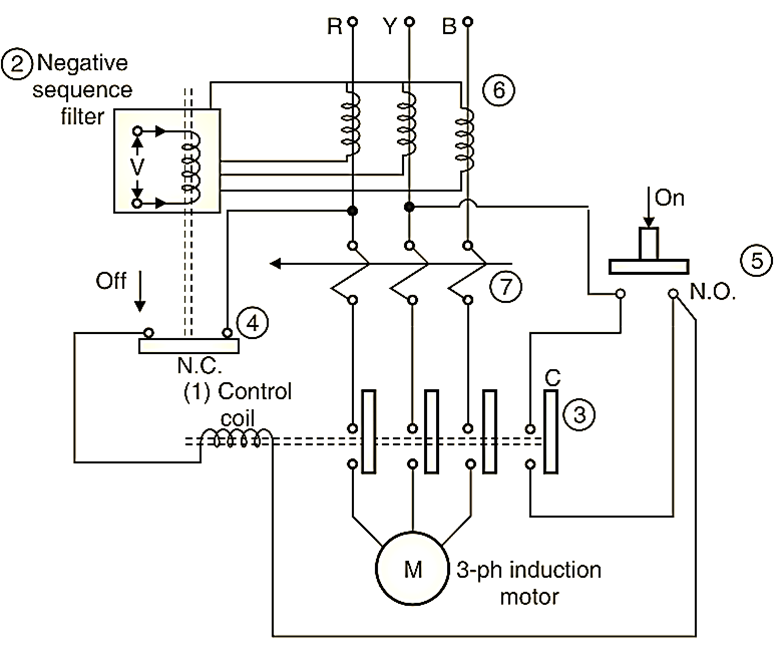
Fig.1: Single Phasing Preventer.
In Fig. 1 the parts are shown connected to the protective circuits and motor. The preventive circuit is connected in secondary of C.T. and R.Y.B. lines act as primaries of the CT. The negative sequence filter is shown connected. The output of this lifter is fed to a level detector. This sends the tripping command to the starter and NC contact gets opened and contactors get opened, stopping the motor as it is disconnected from the supply R.Y.B. This type of preventer is generally used for small/medium capacity motors.