Colloid mills can be sterilized and therefore can be used for size-reduction of sterile products.
Working Principle of Colloid Mill
Colloid mill works on the principle of high-velocity fluid shear due to the suspended particles or liquid droplets are milled, to form a uniform and stable suspension or emulsion respectively.
Construction of Colloid Mill
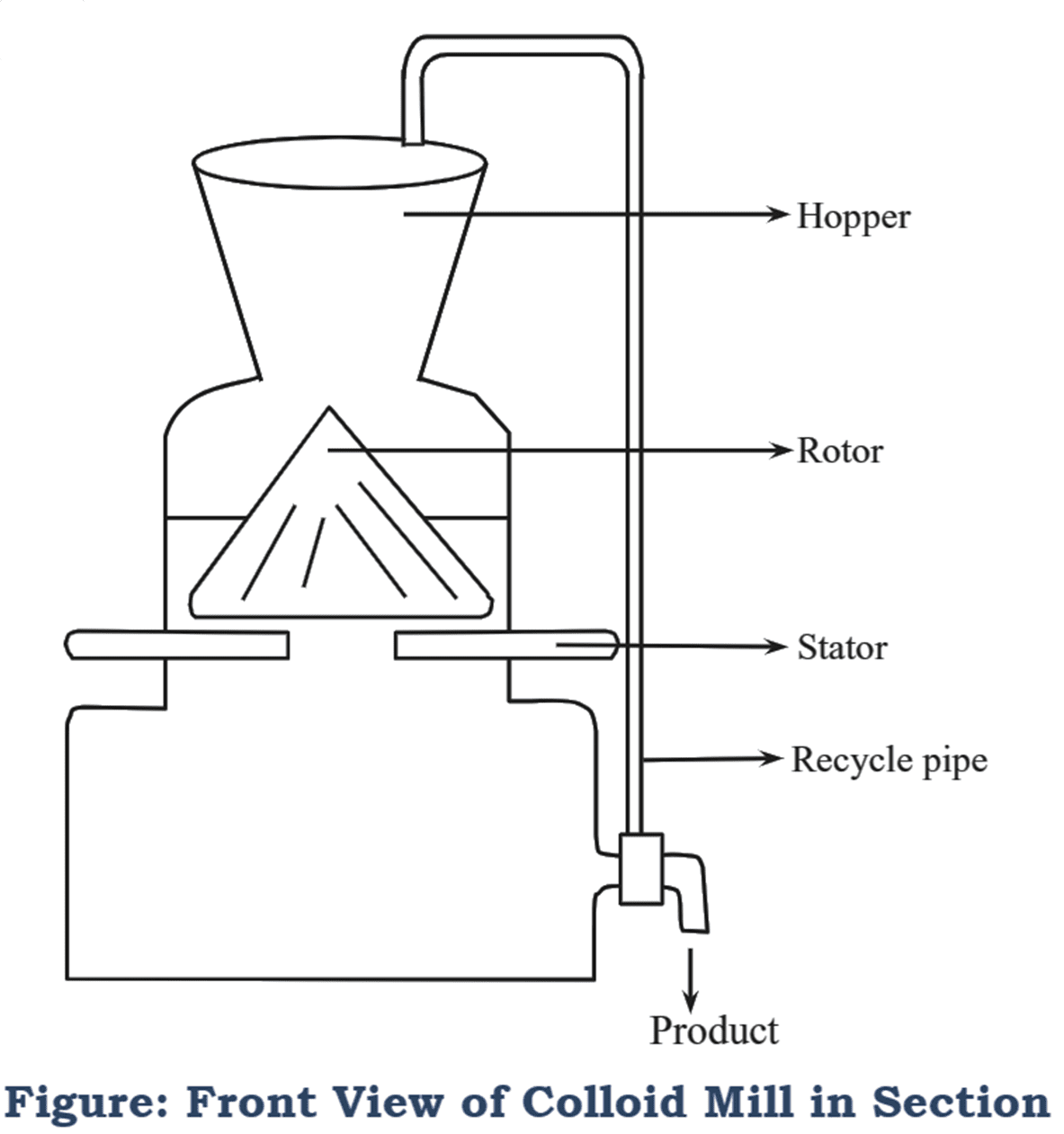
It consists of a cone-shaped rotor and a stator enclosed in a vessel (See Figure 1). Space between the rotor and stator can be adjusted up to 25 μ depending upon the particle size required. The rotor is rotated while the stator is kept stationary. Diameter of the rotor ranges from 6-15 inches. Small mills have low capacity i.e., about 30 to 50 gal/hr of the feed can be processed, while in large mills 7000 gal/hr of feed is processed. The rotor and stator are made up of invar alloy. This material expands to a very- less extent such that the grinding capacity of the mill is not changed due to the heat generated. The rotor is made wear resistant by lining it with silicon carbide. In most of cases, cooling water jacket is installed for reducing the heat generated during the process, “While in others a heating jacket is installed in case of formulation of an emulsion. At the top, a feed inlet is present. The outlet present at the bottom of one side of the vessel is connected to a hopper to recycle the discharge. The dispersion colloid mills are of 4 types; orifice device, hammer mill, smooth surface disk and rough surface disk.
Working of Colloid Mill
Pre-milled feed is added to the mill via the hopper and the motor is switched on. If the capacity of the mill is up to 1500 gal/hr, rotor is operated at 3600 rpm. This allows the feed to enter the clearance between the rotor and stator. Due to this, high velocity fluid shear is generated, which helps in size reduction. Clusters or liquid droplets are disrupted and the particles are dispersed uniformly. The product is received from the discharge which is 1 m or less in size. The heat generated during the process (40ºC) is reduced by circulating cold water in the jacket, which brings down the temperature to 20ºC. The discharge is recycled until the desired particle size is obtained.
Advantages of Colloid Mill
- Ultrafine grinding upto the size of 1 μ or less is achieved.
- Mill can be sterilized and hence sterile milling is achieved.
Disadvantages of Colloid Mill
- During milling, air gets trapped in the product. This is removed by keeping the product aside to facilitate de-aeration.
- Heat up to 40ºC is generated during the process, which has to be reduced by cooling water jacket.
- Not suitable for dry milling.
Applications of Colloid Mill
- Syrups and paints are processed.
- Milk and purees are processed.
- Ointments, suspensions, emulsions and colloidal dispersions are processed
- Fibrous materials can also be processed by using rough surfaced rotor and stator.