A system in which input has a command over the output or a system in which input has a control over the output is called a control system. A water tap can be taken as simple and best example of a control system. Here the flow of water (i.e., the output) is mechanically controlled by the movement of valve (i.e., input). The diagrammatic representation of simple control system is shown below Continue reading What is Control System? Theory, Diagram, Elements & Examples
Category: Control System
Block Diagram in Control System – Reduction Rules, Procedure & Properties
Block diagram is a pictorial representation of a control sytem. Each element is represented by a separate block and each block is characterised by transfer function of the element. Let us consider element of a control system having transfer function G(s). If the input and output of element are X(s) and Y(s) respectively, then this element is represented by a block as shown in Fig. 1. Continue reading Block Diagram in Control System – Reduction Rules, Procedure & Properties
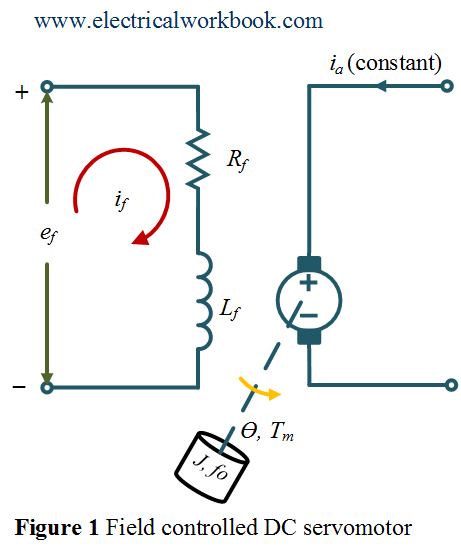
Field controlled DC servomotor
After reading this topic Field controlled DC Servomotor in the control system, you will understand the theory, derivation, expressions, transfer function, and Block diagram.
Let us consider the Field controlled DC servomotor as shown in Figure 1.
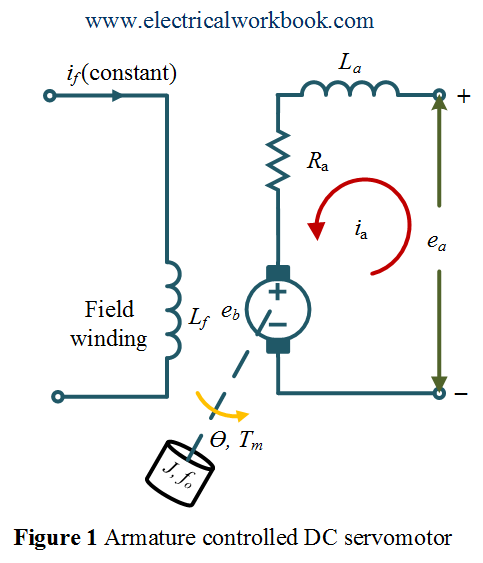
Armature controlled DC servomotor
After reading this topic Armature controlled DC Servomotor in the control system, you will understand the theory, derivation, expressions, transfer function, and Block diagram.
Let us consider the Armature controlled DC servomotor as shown in Figure 1.
Comparison between Open loop and Closed loop control systems
After reading this topic Comparison between Open loop and Closed loop control systems, you will understand the theory and comparison.
Open loop control systems
It is a control system in which the control action independent of the output signal and depends only on its input signal, also the signal flows through the block is unidirectional. It is shown below,
Continue reading Comparison between Open loop and Closed loop control systems
Closed loop or feedback control systems
After reading this topic Closed loop or feedback control system, you will understand the theory, examples, advantages, disadvantages, and comparison.
It is a control system in which the control action dependents on both the output signal and the input signal. It is shown below in Figure 1.
Open loop control systems
After reading this topic Open loop control system, you will understand the theory, examples, advantages, disadvantages, and comparison.
It is a control system in which the control action independent of the output signal and depends only on its input signal, also the signal flows through the block is unidirectional. It is shown below in Figure 1.
Settling time in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system
After reading this topic Settling time $({t_s})$ in Time response of a second-order control system for subjected to a unit step input underdamped case, you will understand the theory, expression, and plot.
A block diagram of the second order closed-loop control system with unity negative feedback is shown below in Figure 1,
Continue reading Settling time in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system
Delay time in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system
After reading this topic Delay time $({t_d})$ in Time response of a second-order control system for subjected to a unit step input underdamped case, you will understand the theory, expression, and plot.
A block diagram of the second order closed-loop control system with unity negative feedback is shown below in Figure 1,
Continue reading Delay time in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system
Peak overshoot in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system
After reading this topic Peak overshoot $({M_p})$ in Time response of a second-order control system for subjected to a unit step input underdamped case, you will understand the theory, expression, plot, and derivation.
A block diagram of the second order closed-loop control system with unity negative feedback is shown below in Figure 1,
Continue reading Peak overshoot in step response (underdamped case) of a second order control system