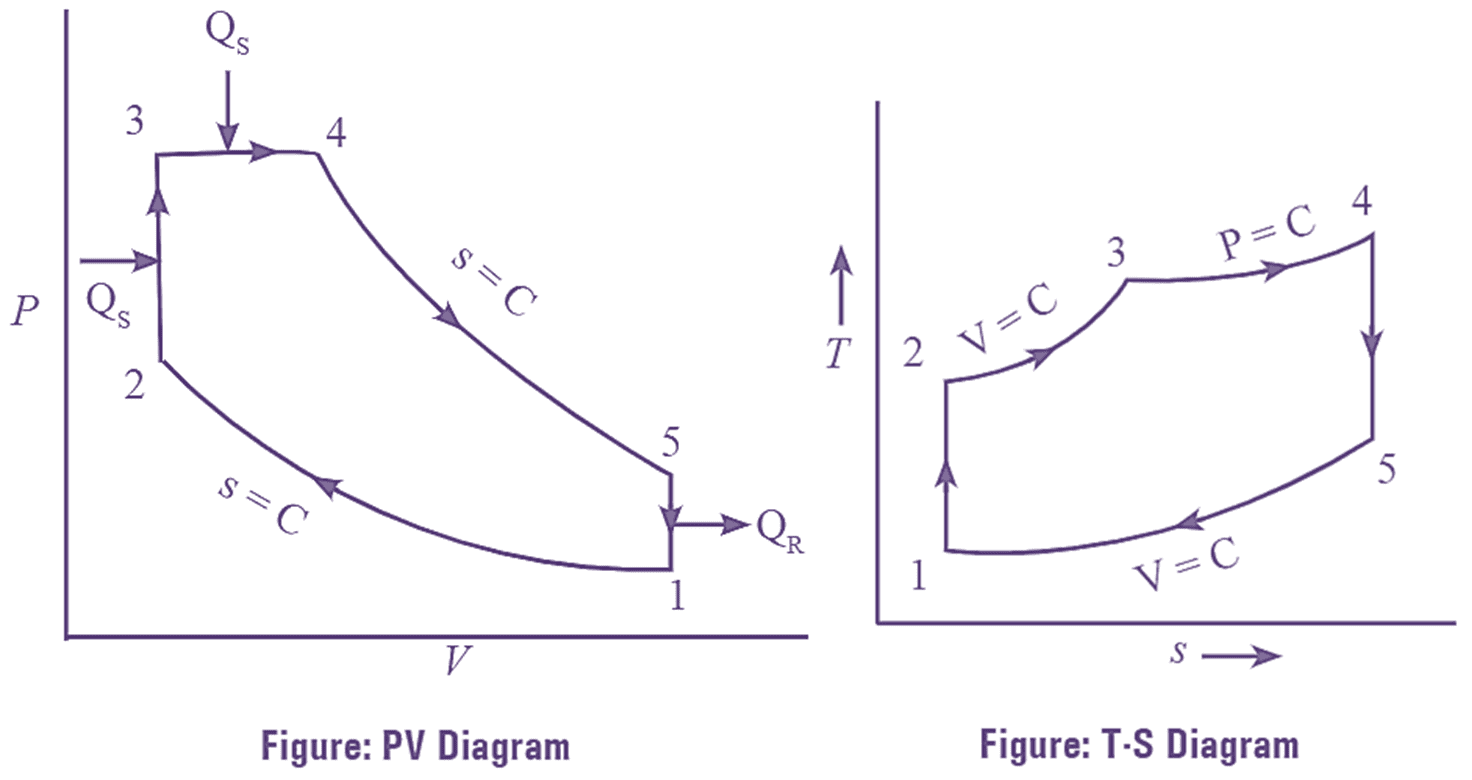
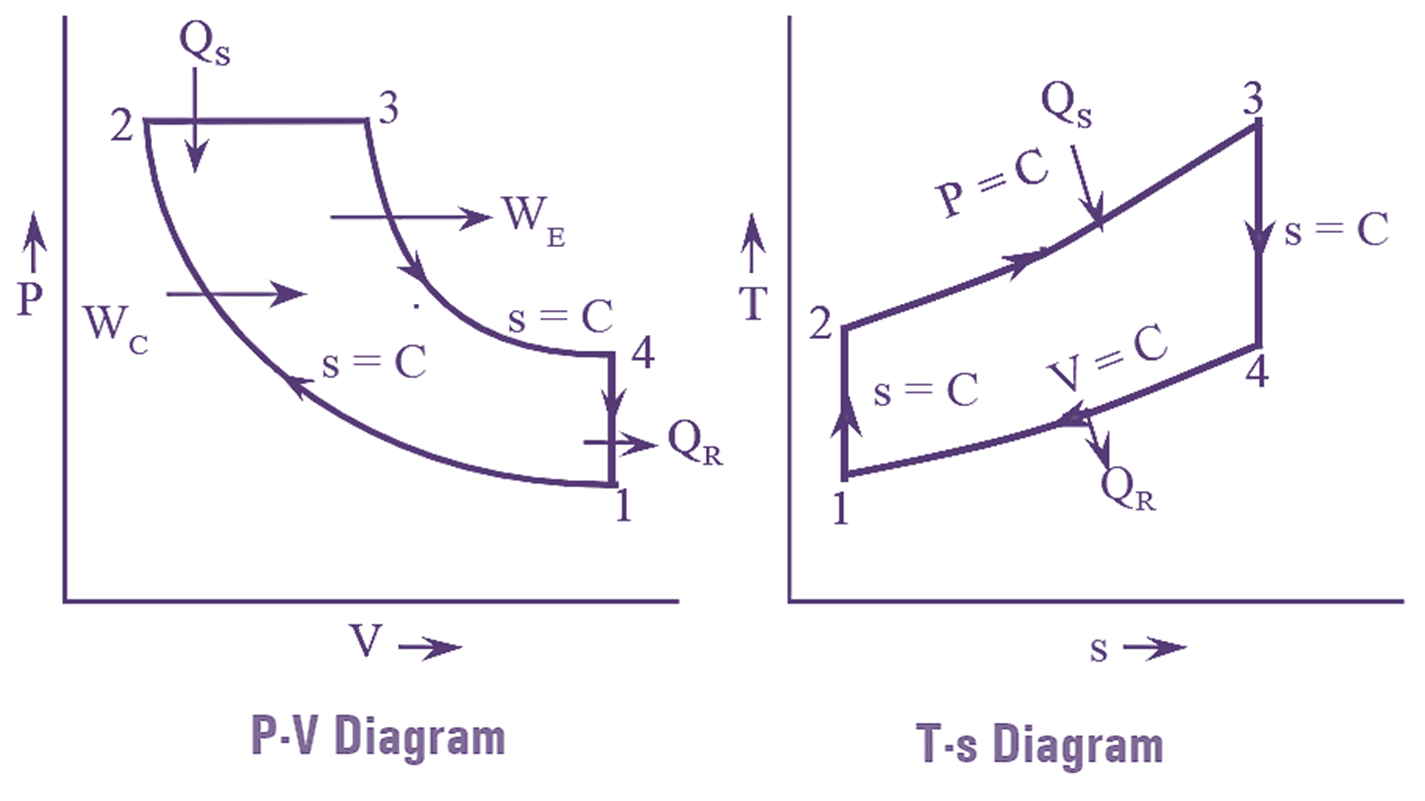
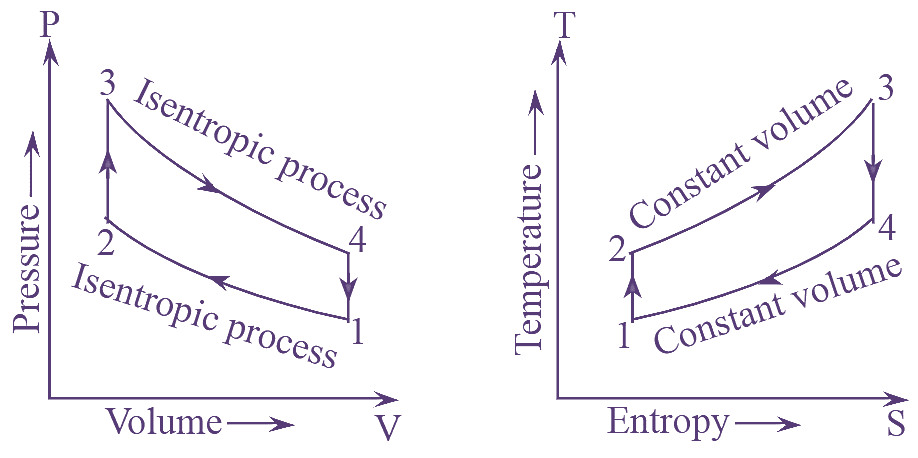
The efficiency of Rankine cycle can also be increased by reheating the steam. In reheat cycle, the steam in the turbine is expanded in number of stages. After partial expansion of steam in high pressure turbine, it is reheated to the initial temperature at constant pressure in reheated. This reheated steam is further expanded in low pressure turbines. The process of reheating is shown in figure (1).
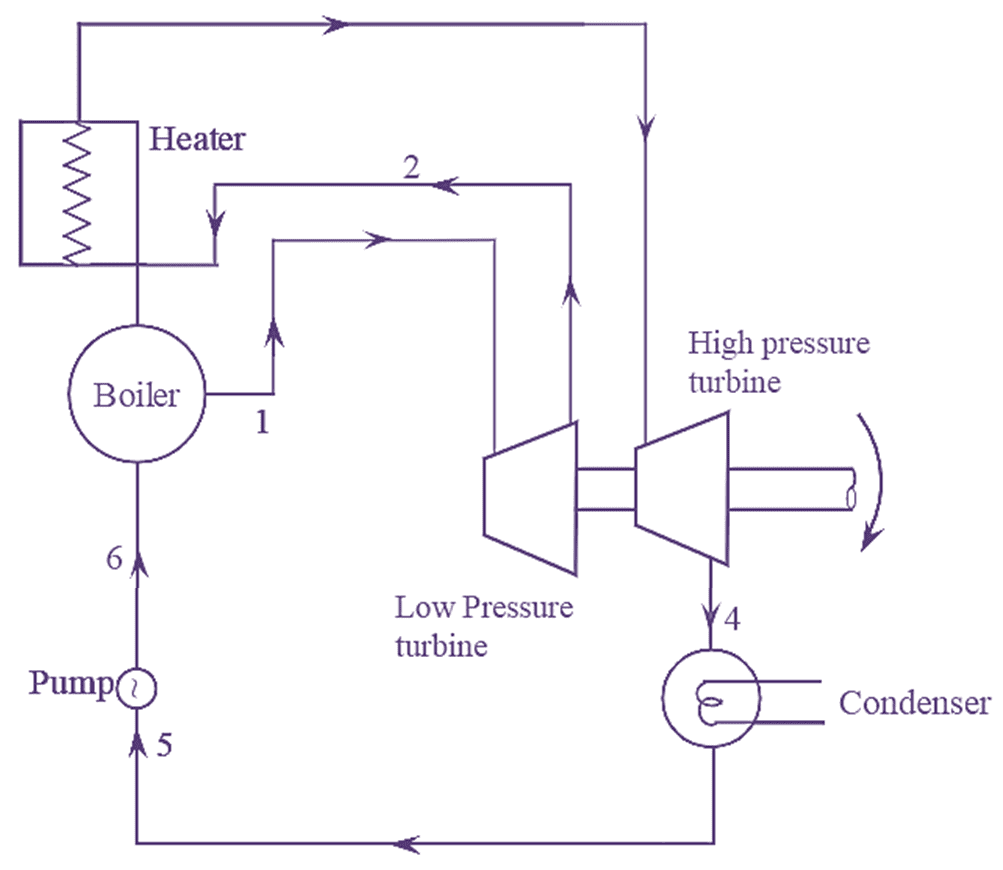
Figure 1: Reheat Cycle. Continue reading What is Reheat Cycle? Process, Derivation, Diagram & Efficiency