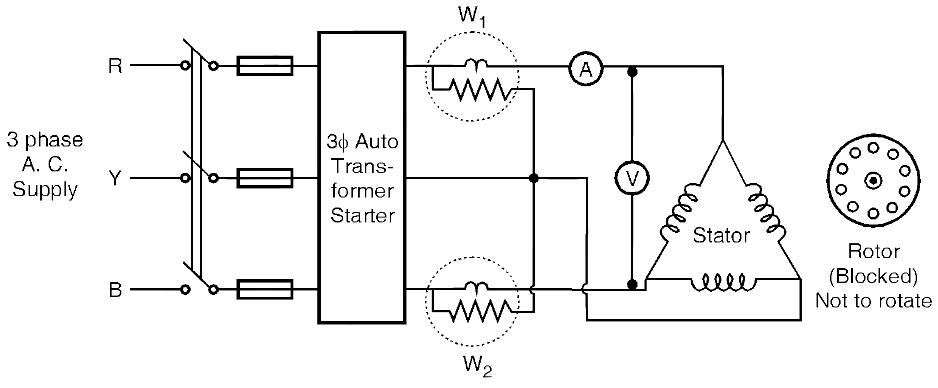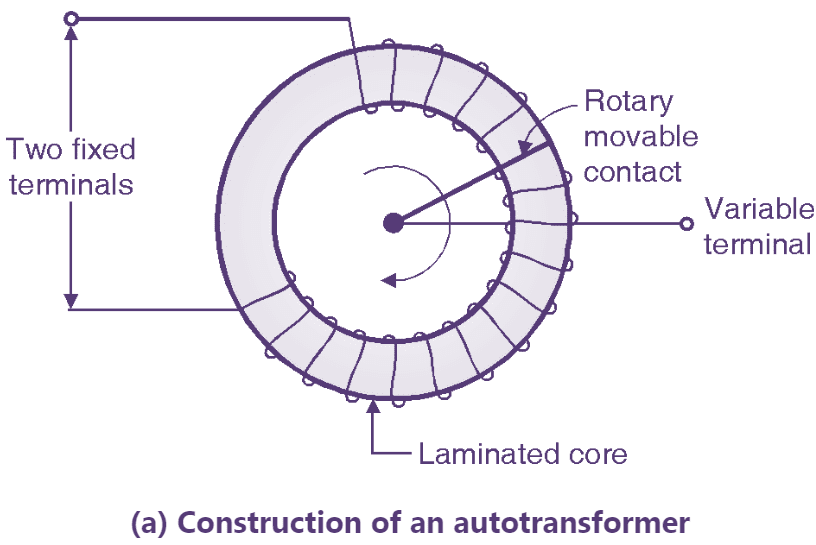
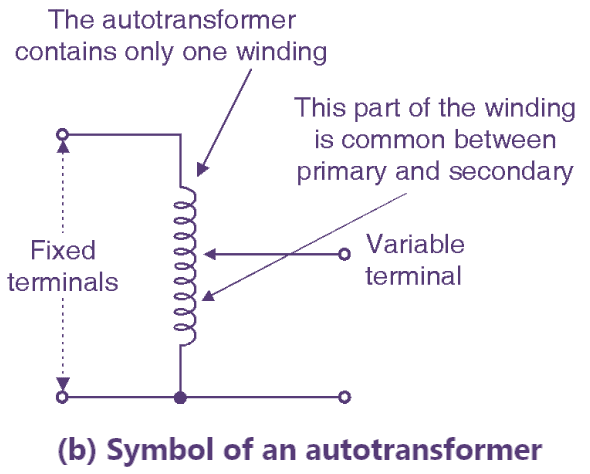
Fig. 1: Autotransformer (Construction & Symbol).
The normal transformer has separate primary and secondary windings. But the autotransformer is a special transformer in which a part of winding is common for the primary and secondary windings. The construction of an autotransformer is as shown in Fig. 1. It consists of only one winding wound on a laminated magnetic core, with a rotary movable contact. Thus from the autotransformer three terminals are brought out for connection. The autotransformer can operate as a step down or a step up transformer. Continue reading What is an Autotransformer? Connection Diagram, Symbol, Construction, Working Principle & Applications