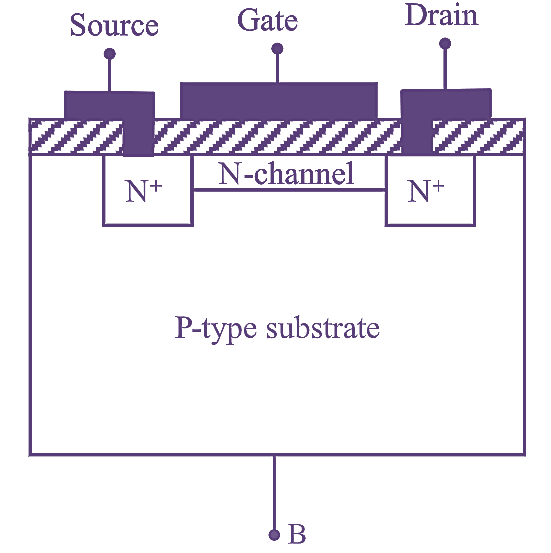
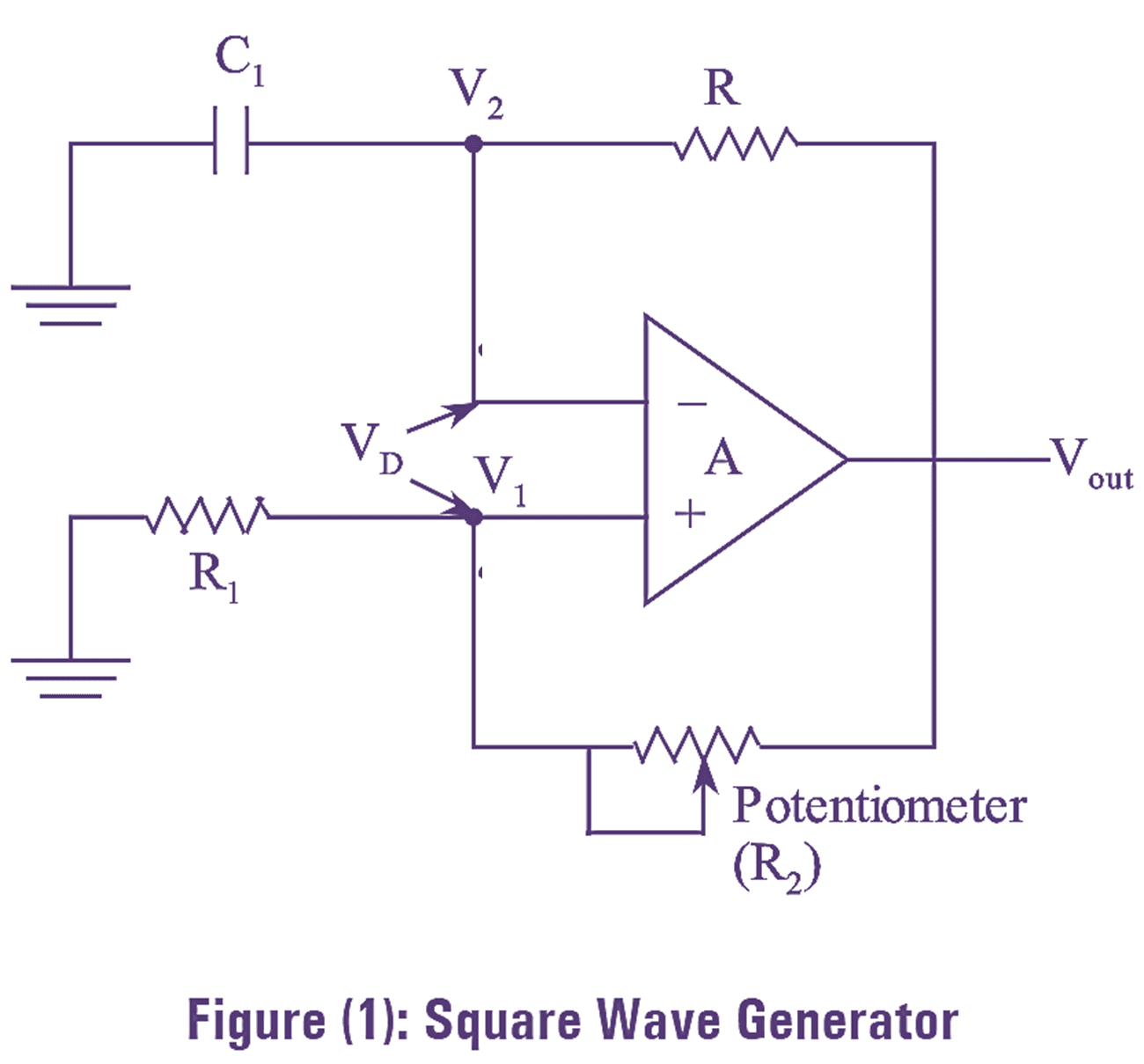
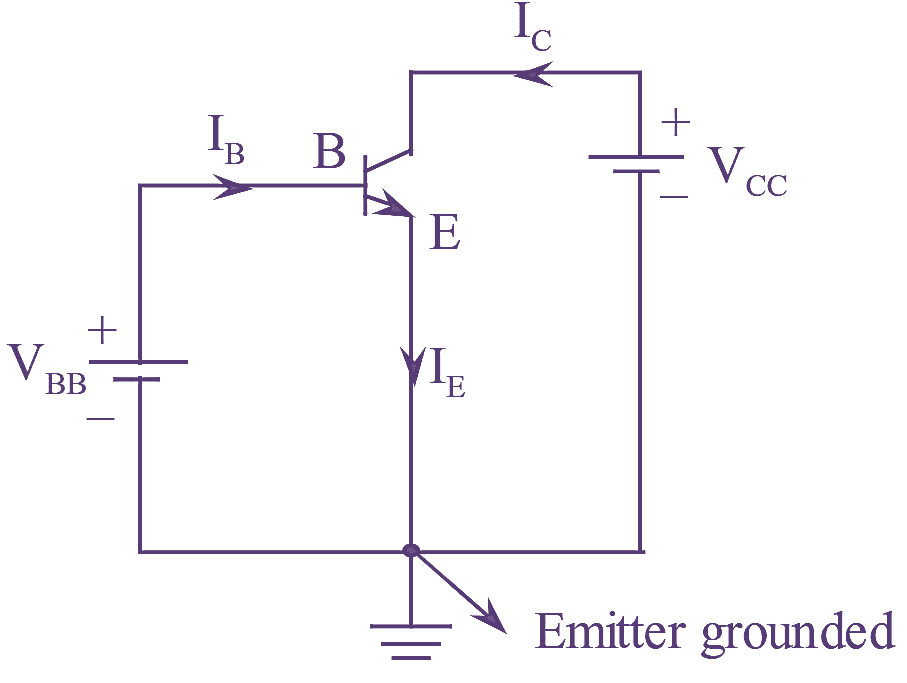
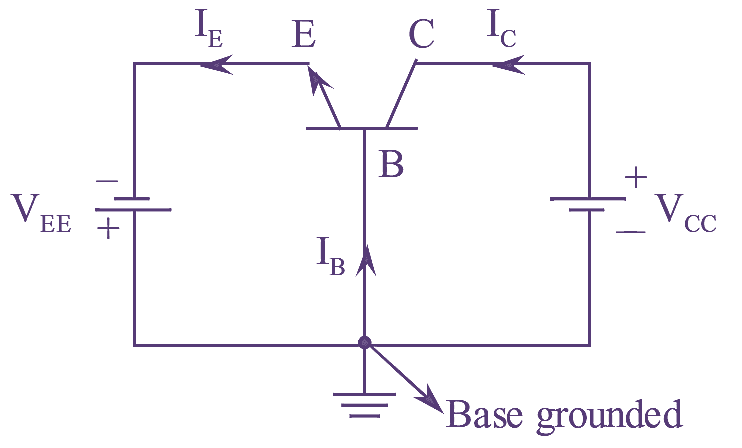
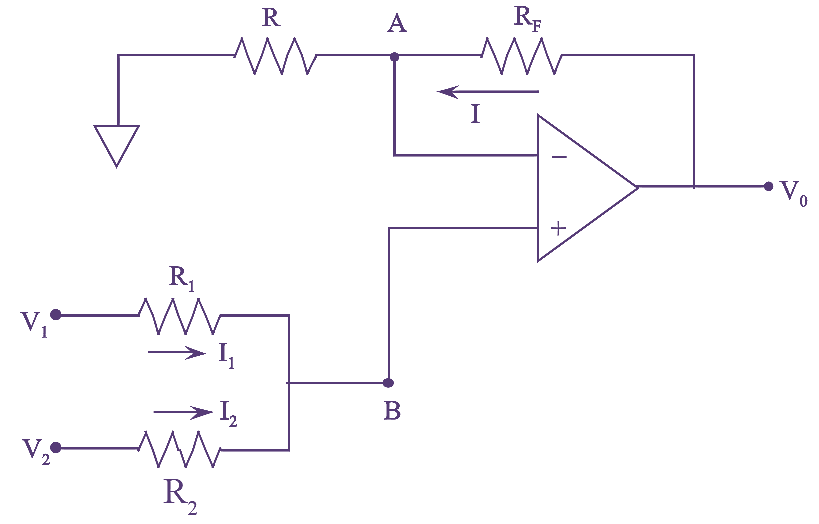
Diode is the most fundamental two terminal non-linear circuit element. The relationship between the current flowing through the diode and the voltage appearing across it is nonlinear. In other words, the diode has non-linear V-I characteristics.
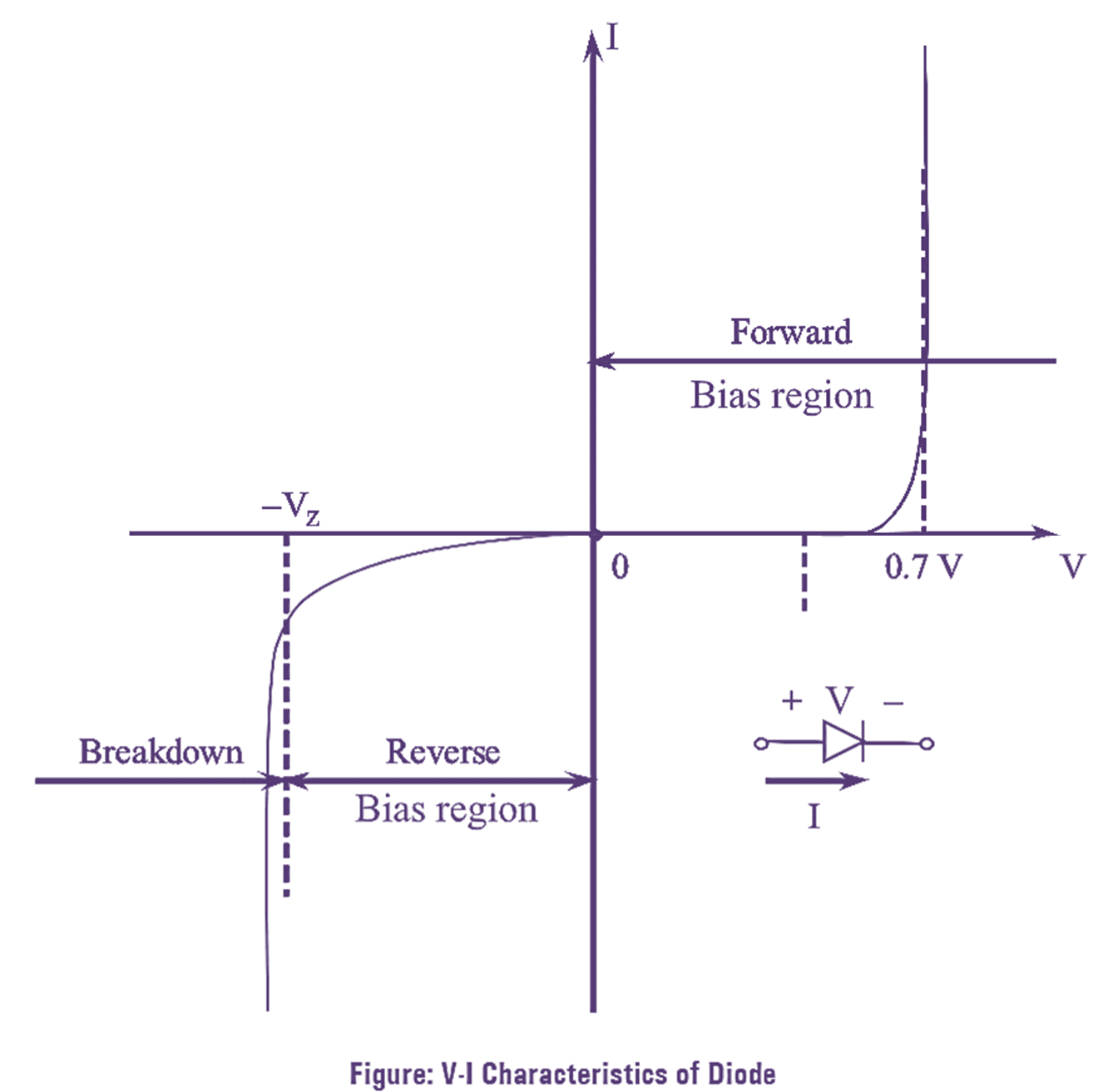
Continue reading VI Characteristics of PN Junction Diode – Explanation & Diagram