In this topic, you study Power Electronics – Definition & Applications.
Power electronics is the branch of electrical engineering which deals with the study of various high-power switching semiconductor power electronic devices i.e. thyristor family devices. The study of power electronics has assumed great importance in the recent electrical engineering and plays a vital role in the field of electrical engineering.
With the advent of power semiconductor devices like thyristor, TRIACS, power MOSFET and power transistors, power electronics have become very important in the control of large power.
Classification of Power Electronic Circuits
The power electronic circuits can be classified into six types as shown in Fig. 1.
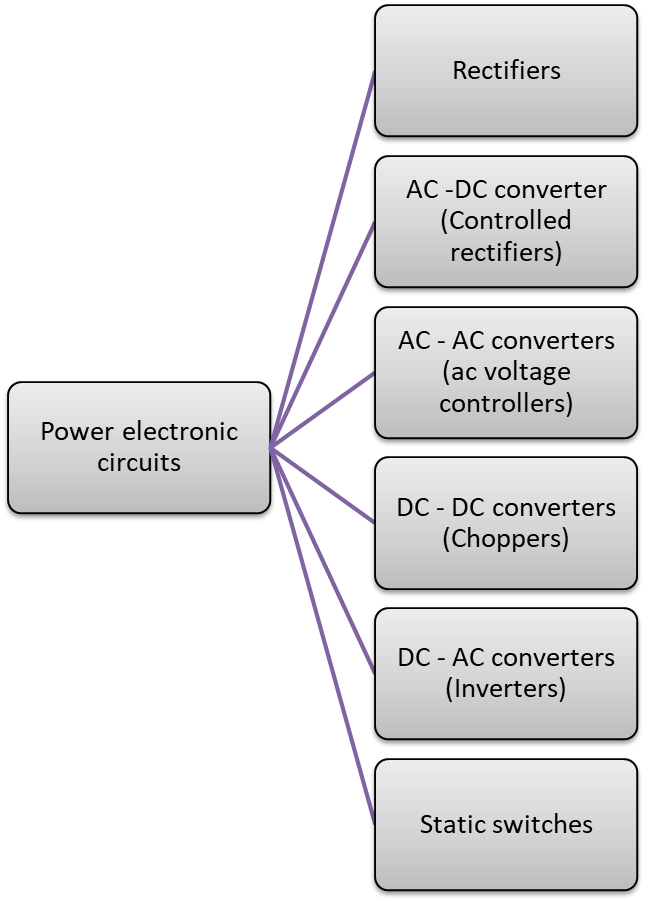
Fig. 2: Classification of power electronic circuits
Types of Power Electronic Circuits
For various applications, the electrical energy should be converted from fixed voltage, fixed frequency ac form into some other form as per requirement. Fig. 2 shows the basic power electronic system. At the input of this system, we have a constant voltage, constant frequency ac voltage and the power converter and controller block converts it into a suitable form of electrical energy. The function of the controller is to control the amount of electric energy to be delivered to the load.
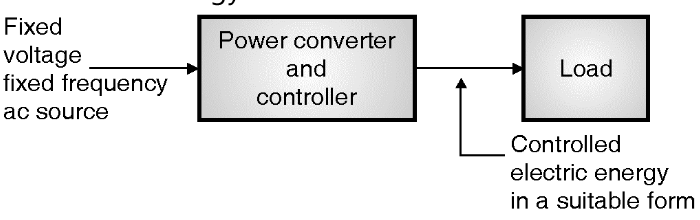
Fig. 2: Basic power electronic system
APPLICATIONS OF POWER ELECTRONICS
Power electronics have already found an important role in modern technology. Examples of successful applications are as follows:
- Speed controllers for AC and DC motors.
- Temperature and illumination controllers.
- AC and DC circuit breakers.
- HVDC transmission lines.
- Heat control (Induction heating).
- Power supplies for aircrafts.
- Vehicle propulsion systems.
- Conveyors, cranes and hoist control.
- Electric vehicles and locomotives.
- Air conditioning, refrigerators.
- Machine tools.
- Servo systems.
- Light dimmers and flashers.
- Washing machines, dryers and blowers.
- Furnaces and grinders.
- VAR compensation.
- VLF transmitters.
- Pump and compressor control.
- Variable frequency DC to AC inverters.
- Variable voltage DC to DC converters.
- Variable frequency AC to AC converters.
- Variable voltage AC to DC rectifiers.