Air Conditioning system can be defined as, “an assembly of different parts of the system to produce a specified condition of air within a specified enclosed space “. The basic components of air conditioning systems are:
Fans: For moving and circulating air.
Filters: For cleaning air, either fresh or re-circulated or both.
Refrigerating plant: Connected to heat exchange surface, such as finned coils or chilled water sprays.
Means for warming: Such as hot water or steam heated coils or electrically heated coils or elements.
Humidifiers and dehumidifiers.
Control system: To regulate (control) the amount of cooling or warming automatically.
Classification of Air Conditioning System
The air conditioning systems may be broadly classified as follows:
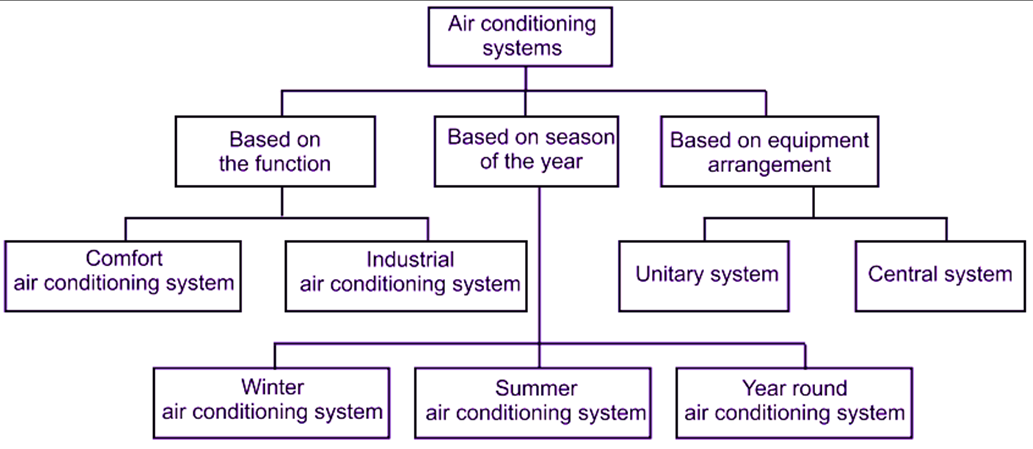
- According to Purpose/ Measure Function
Comfort air conditioning system
Purpose of this air conditioning system is to create atmospheric conditions conducive (desired) to human health, comfort and efficiency. This system is used for home, office, shop, restaurant, hospital, school etc.
Industrial air conditioning system
Purpose of this air conditioning system is to control internal atmospheric conditions primarily essential for proper research and manufacturing processes. This type of air conditioning is used in textile mills, paper mills, machine parts manufacturing industry, tool rooms, printing, photo processing plant etc.
- According to Season of the Year
Winter air conditioning system
It maintains indoor atmospheric conditions for human comfort during winter season (Cold weather). It involves functions such as “to heat the air” and “to bring moisture content up to an acceptable level”.
Summer air conditioning system
It maintains indoor atmospheric conditions for human comfort during summer season (Hot weather). It involves functions such as “to cool the air” and “remove excess moisture from air”. Here, cooling is done by mechanical refrigeration.
Year round air conditioning system (All Weather Air conditioning)
This system is composed of heating and cooling equipments with automatic controls to be operated according to the season requirement. This system must be capable of maintaining a specified temperature and humidity within the conditioned space regardless of outside conditions. It involves functions such as “heating with humidification in winter” and “cooling with dehumidification in summer”
- According to Arrangement of Equipments
Central air conditioning
This system is used, when the desired indoor conditions like temperature and relative humidity are approximately same for numbers of rooms in the same building. Central system is suitable for large spaces, such as cinema theatres, exhibition halls, restaurants etc. The compressor, condenser, dampers, heating and cooling arrangements, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, fan etc. are located and assembled at one place (basement).
Unitary air conditioning
Unitary air conditioning system has all the equipments and controls for fulfilling the requirements of air conditioning assembled in a single casing. Its all components are factory assembled, tested and balanced. The system is ‘installed in or near the vicinity to be air conditioned. This system has the advantage of more flexibility of operation and low initial cost.
Types of unitary air conditioning
- Window air conditioning
- Split air conditioning
- package air conditioning
- According to Working Substance Used in the System
- All air system,
- Chilled water system, and
- Air water system.
- According to Volume of Air Handled by the System
- Constant volume system,
- Variable air volume system (VAV)
Function of Air Conditioning System
Basics of Air Conditioning
- Primary function of an air conditioning system
“To provide human comfort by maintaining an artificial and comfortable environment for the occupants within a building or an enclosed premise”. The comfort parameters are generally temperature, humidity, purity and air motion.
- Secondary functions of an air conditioning system
Good quality products: For better efficiency and effectiveness of a manufacturing process, or to maintain the quality and life of a stored product.
Control of energy and moisture: Since the space to be air conditioned is continuously subjected to gain or loss of heat and moisture, therefore energy and moisture must be transferred ‘to’ or ‘from’ the space to compensate for the same.
Air purity: An air conditioning system provides filtered outdoor (ventilation) air to maintain acceptable indoor air quality.
Control of essential parameters: Air conditioning systems are designed to provide sufficient ventilation, cooling/heating and humidifying/dehumidifying capacity.
Better combination of relative humidity and temperature: In the majority of applications, the cooling of a space to a specified temperature is desired, with relative humidity of 70 to 75%. For example: offices, stores, classrooms etc.
In some critical applications, precise control of both temperature and relative humidity is required. For example: Hospitals, Computer Rooms, Laboratories etc.