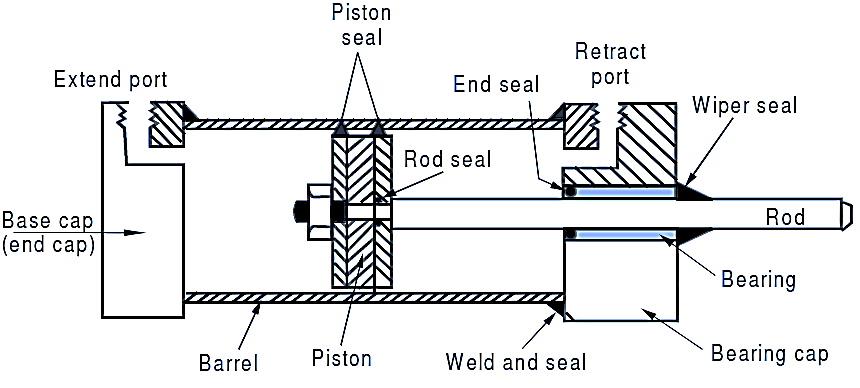
Figure 1: Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder.
In double acting Hydraulic cylinder, the pressurized liquid is admitted on both sides of the piston alternately. Work is performed during forward motion as well as backward motion of the piston (see Fig. 1). Double acting Hydraulic cylinders are most commonly used hydraulic cylinders in industrial applications. In these cylinders, the pressure is applied on both end ports to obtain power in both directions. They are also termed differential cylinders, as they have different extension and retraction areas.
Construction of Double acting Hydraulic Cylinder
- The main parts of double acting cylinder are,
Two end cover plates (or) Two end caps with port connections
- Base Cap
- Bearing cap
- Cylinder barrel
- Piston
- Piston rod
The end caps are welded to barrel (or) joined by the tie rods (or) by fasteners. The end caps are fixed to the barrel by means of tie rods or thread sections by weld joint. For any lengths of cylinder barrel, the size of end caps and piston remains same. The barrel should be wear resistant and leak proof. It is made of seamless drawn steel tube, which is precisely finished. Piston is made of cast iron, transmits force to the rod. It acts as sliding bearing in the cylinder barrel and also, as seal, in order to reduce the leakages and thus, avoids the use of piston seals. A bronze bearing surface is deposited on piston surface, which is accurately finished.
Working of Double acting Hydraulic Cylinder
During retraction process, the reduction in piston area, due to the cross-sectional area of rod inside piston, causes the effective area difference. But the extension process takes place slowly as the fluid has to be filled in more area compared to retraction process. As pressure is given by the force per unit area, it implies that more effective area results in the greater force in extension process. Also, less force acts during retraction process, due to reduced fluid volume displaced by the rod inside the piston.
During the extraction operation, the cylinder rod comes in contact with the atmosphere and thus, undergoes corrosion because of dust and impurities in the air. These impurities enter the barrel during retraction and damage the cylinder. Hence, heat-treated chromium alloy steel is added to prevent corrosion. While the dusty particles can be eliminated by fixing the wipers or scraper seal fixed to the end caps.