When a single block brake is applied to a rotating drum for braking action, an additional load is produced on shaft bearings due to normal reaction (RN). This leads to unbalanced situation. In such cases, this unbalanced load acting on the shaft may lead to bending of shaft. Hence, to overcome this drawback of single block brake, double block (shoe brake) is used. Refer Fig. 1.
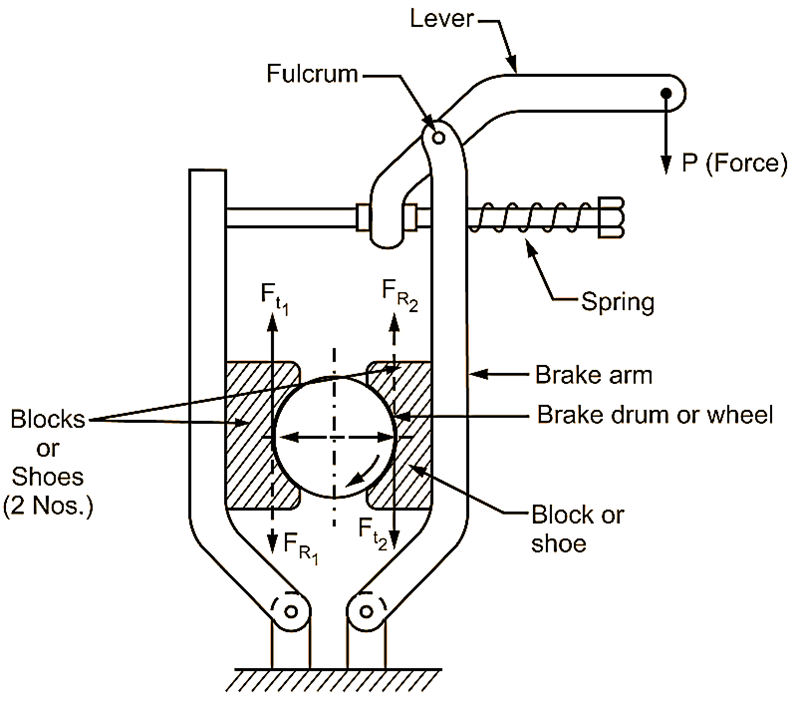
Fig. 1: Double Block (Shoe) Brake.
Construction of Double Block (Shoe) Brake
Double block or shoe brake consists of two blocks or shoes situated at opposite ends of circumference of brake drum (wheel). This arrangement reduces the unbalanced force acting on the shaft, when brake is applied. The upper ends of brake arms are set together by using a spring.
Working of Double Block (Shoe) Brake
When brake is in released position (i.e. brake is disengaged)
Using an electromagnet or solenoid, electric current is supplied to apply an actuating force ‘P’ to the lever. Due to this actuating force ‘P’ applied to the lever, the spring gets compressed and brake gets released. At this condition, brake drum (wheel) will rotate continuously, since brake is disengaged due to current being supplied.
When brake is to be applied (i.e. brake is to be engaged)
For braking action, current supply is stopped. Due to this, actuating force ‘P’ acting on the lever suddenly vanishes and becomes zero. This makes the spring to elongate freely. Therefore, brake gets automatically engaged causing both blocks or shoes to move inward, i.e. towards the brake drum. Contacting or frictional surfaces of blocks start retarding the motion of brake drum and finally, it is stopped. Unless and until, supply of electric current is not restarted, brake will not be released or disengaged.
Application of Double Block (Shoe) Brake
Electric cranes.
In these brakes, the braking torque is given by,
TB = (Ft1 + Ft2) × r = μ (RN1 + RN2) × r
where, Ft1 and Ft2 = Braking forces on the two blocks in ‘N’, and
RN1 and RN2 = Normal reactions on the two blocks in ‘N’.
Limitations of Double Block (Shoe) Brake
- As brake drum assembly is enclosed, it does not allow the cooling air to enter the assembly. Due to this, heat generated during action of braking is not dissipated to atmosphere with enough rate of heat transfer required. This heat generated remains inside the brake assembly for longer period. This causes the radius of the drum to increase more than radius of brake shoe. This reduces braking ability of a vehicle by 15 – 20% due to change in pressure distribution between the brake linings and drum.
- Enclosed assembly of brake drum does not allow to use water as cooling medium, because water carrying the heat generated in drum assembly finds difficulty in expelling out rapidly. Also, water use makes the brake cavity wet, which reduces frictional properties of brake system and hence, braking ability of vehicle.
- Use of many clips and springs make the overhauling or maintenance activity much time consuming in addition to fatigue.
- Dust of asbestos gets collected in the brake cavity due to enclosed assembly