Evaporator can be defined as, “a heat transfer surface, in which, a volatile liquid refrigerant is vapourized by removing heat from the refrigerated space or product”. The evaporator is also known as cooler or freezer or chiller. It is connected in the low pressure side of the refrigeration system. It is installed in-between expansion device and compressor.
Function of evaporator: ‘To absorb the heat from the substance or space, which is to be cooled, by means of refrigerant’.
The liquid refregerant from the expansion valve enters the evaporator, where it “boils off” by absorbing the latent heat from the space or material being cooled. Keeping of low pressure is necessary in evaporator to evaporate the refrigerant at lower temperature than the temperature required to be maintained in the refrigerated space. When the liquid refrigerant boils and changes to a vapour state in the evaporator due to low pressure, it absorbs large quantities of heat from itself and cools down. The cold refrigerant cools the evaporator coil surface, which further cools whatsoever comes in contact with it.
Evaporators Types
Evaporators are classified as,
According to the type of construction
- Bare tube coil evaporator,
- Plate evaporator,
- Shell and coil evaporator, and
- Finned tube evaporator,
- Shell and tube evaporator,
- Tube in tube evaporator.
According to the method of refrigerant feed/operating conditions
- Dry expansion evaporators,
- Flooded evaporators.
According to mode of heat transfer
- Natural convection,
- Forced convection.
According to ‘Frost’
Frosting evaporators: This type of evaporator always operates at temperatures below 0°C. The cooling coil frosts continuously, when in use.
Non-frosting evaporators: This type of evaporator operates nearly at temperatures above the freezing point of ice. Since this type of evaporator does not draw moisture rapidly, so it is used for the preservation of vegetables, fruits and other perishable stuffs.
Defrosting evaporators: Here, frost gets accumulated, when compressor and hence, the refrigeration system is running. And, the frost melts, when compressor and hence, the refrigeration system is stopped.
Ideal Conditions for an Evaporator
- The largest possible surface area, which may be kept fully refrigerated.
- Rapid air circulation around clean and frost free evaporation unit surfaces.
- A low temperature difference of 8°C to 10°C between the refrigerant and air.
- A high suction pressure resulting in high capacity and efficiency of the condensing unit.
- A low quantity of water vapour removal leaving a high humidity to preserve food appearance, moisture content and weight.
Capacity of Evaporator
The evaporator is the component in the refrigeration system, across which, the heat transfer takes place from the materia /space to be cooled to the liquid refrigerant flowing through the evaporator. Therefore, the evaporator should have the capacity to absorb the heat to keep the substance or space at the desired temperature. Capacity of evaporator is defined as, “the rate, at which, the heat will pass through the evaporator walls from the refrigerated space or substance to the vapourizing liquid refrigerant flowing through evaporator coil”. It is expressed in tonnes of refrigeration (TOR). Heat absorption or heat transfer capacity of an evaporator is given by:
\[\text{Q = U }\times \text{ A}\times \text{ LMTD}\]
Where,
Q = Quantity of heat transferred in kW
A = Outside surface area of the evaporator in m2
U = Overall heat transfer coefficient in kW /m2.°C
LMTD = Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference between the temperature outside the evaporator and the temperature of refrigerant inside the evaporator in °C
Bare Tube Evaporator
Bare tube evaporators are usually constructed either of steel pipe or copper tubing pipes. Bare tube evaporators are available in number of sizes, shapes and designs. Because of its simple construction, the bare tube or coil is easy to clean and defrost. Effective length and diameter of the tube are governed by the capacity of expansion valve.
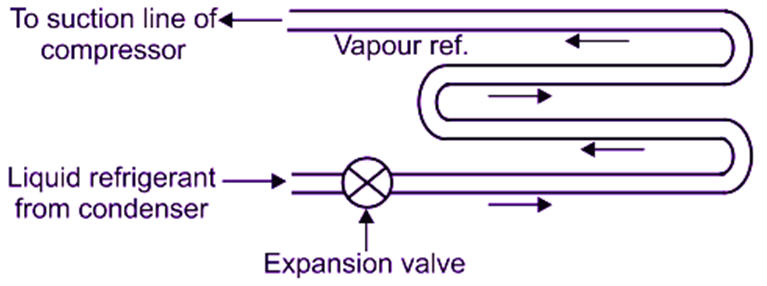
Fig. 1: Bare tube coil evaporator
Applications of Bare Tube Evaporator
- Bare tube evaporators are most frequently used for cooling applications, where the space temperature is maintained below OCC.
- They are widely used in domestic refrigerators, because they are easier to clean.
Plate Surface Type Evaporator
A common type of plate surface type evaporator is shown in Fig. 2. In this type of evaporator, the coils are either welded on one side of a plate or between the two plates, which are welded together at the edges.
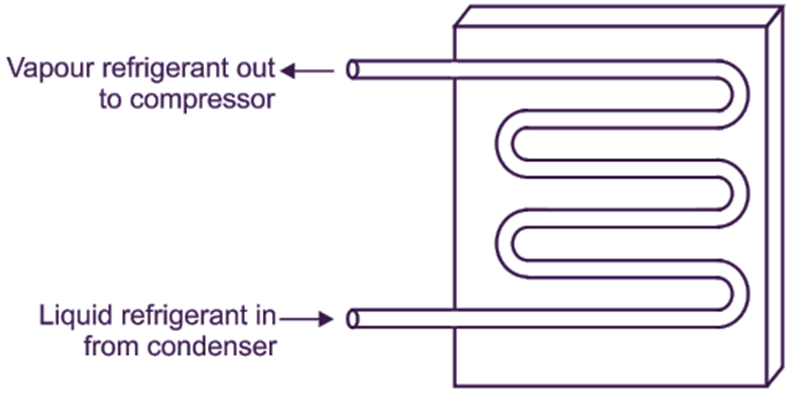
Fig. 2: Plate surface type evaporators
Applications of Plate Surface Type Evaporator
The plate surface type evaporators are general y used in,
- Household Refrigerators,
- Beverage Coolers,
- Home Freezers,
- Ice Cream Cabinets etc.
Finned Evaporator
Finned evaporator consists of bare tubes or coils, over which, the metal plates or fins are fastened. The metal fins are made up of thin sheets of metal having good thermal conductivity. The shape, size and spacing of the fins can be adopted to provide best rate of heat transfer for a given application. Since the fins greatly increase the contact area of heat transfer surface, finned evaporators are also called as extended surface evaporators. They are generally used for applications, where the refrigeration temperature is above 0C. Because of the rapid heat transfer ability of the finned evaporator, it will defrost itself during the “OFF” cycle, when the temperature of the coil is near 0C. A finned coil should never be allowed to frost, because the accumulation of frost between the fins reduces the heat transfer capacity. The air conditioning coils operating at high suction temperature have fin spacing as small as 3 mm to avoid frosting. Some finned coils have wider spacing between the fins. These finned coils frost on the “ON” cycle and defrost on the “OFF” cycle.
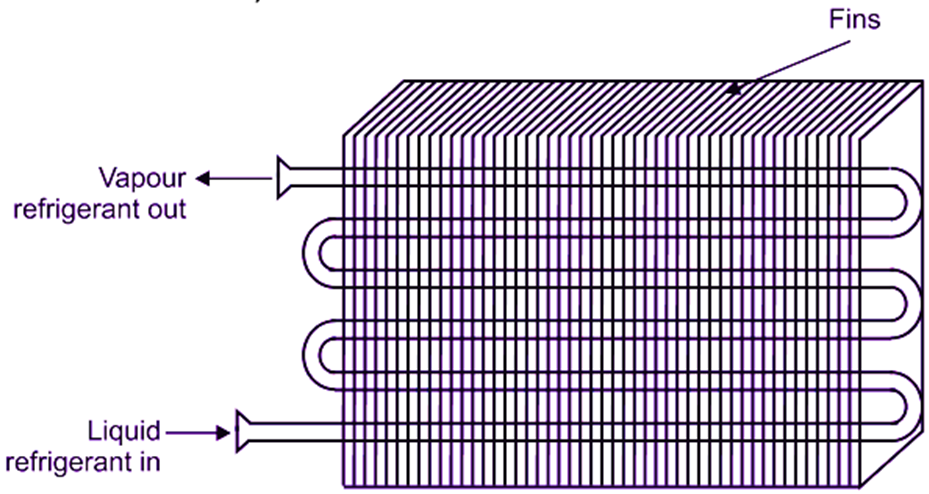
(a)
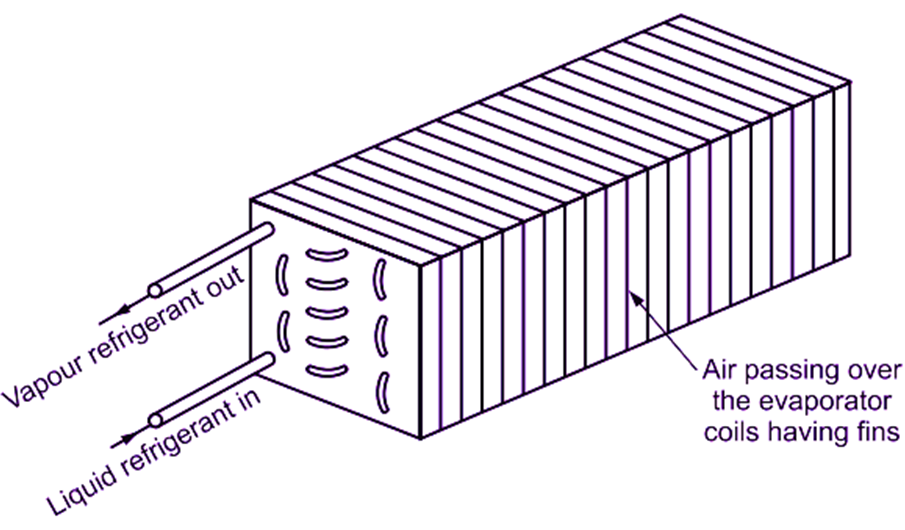
(b)
Fig 3: Finned evaporators
Applications of Finned Evaporator
- Air conditioning systems.
- Deep freezers.