In this topic, you study Lenz’s Law.
This fundamental rule based upon electrical principles is enunciated by a German physicist, Heinrich Lenz. It can be expressed as follows:
The direction of an induced e.m.f. produced during the process of electromagnetic induction is always such that it tends to set up a current opposing the basic cause responsible for inducing that e.m.f.
Consider a coil (C) connected to a galvanometer (G) as shown in Fig. 1. Assume that the magnet is being withdrawn from the col. The induced current in this condition will flow in such a direction that the end of the col facing the magnet will be South pole. Thus, the force of attraction exerted by the South pole of the coil working as an electromagnet on the North pole of the magnet will oppose the withdrawal of the magnet from the coil. The direction of current in this condition will be, therefore, as indicated in the above figure. Opposite will be the case when the magnet is moved towards the coil. Thus, the motion of the magnet in either direction which is responsible for inducing the e.m.f. in the coil will be opposed by the current set up by that e.m.f.
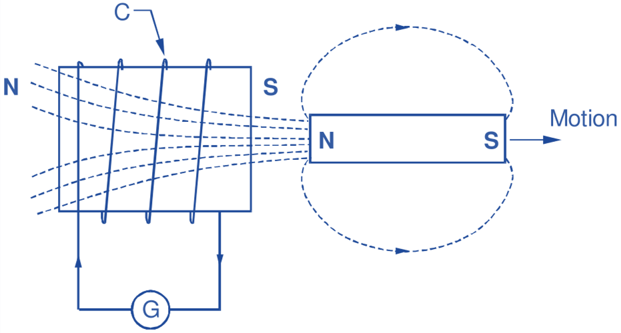
Fig. 1: Lenz’s Law
Owing to the fact that the induced e.m.f. circulates a current tending to oppose the alteration of flux linking with the circuit, its direction is regarded as negative. Hence, the Equation 1 which gives the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. is as follows:
\[\text{e}=-\text{N}\frac{\text{d}\phi }{\text{dt}}….(1)\]