In this topc, you study Moving Iron (MI) Instrument or Permanent magnet Moving Iron (PMMI) Instrument Theory, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Diagram.
Most common form of ammeters or voltmeters for use in laboratory etc. are moving iron type. They can be manufactured at cheaper cost and the required accuracy can be obtained. There are two types of moving iron instruments.
(a) Attraction type
(b) Repulsion type
Attraction Type
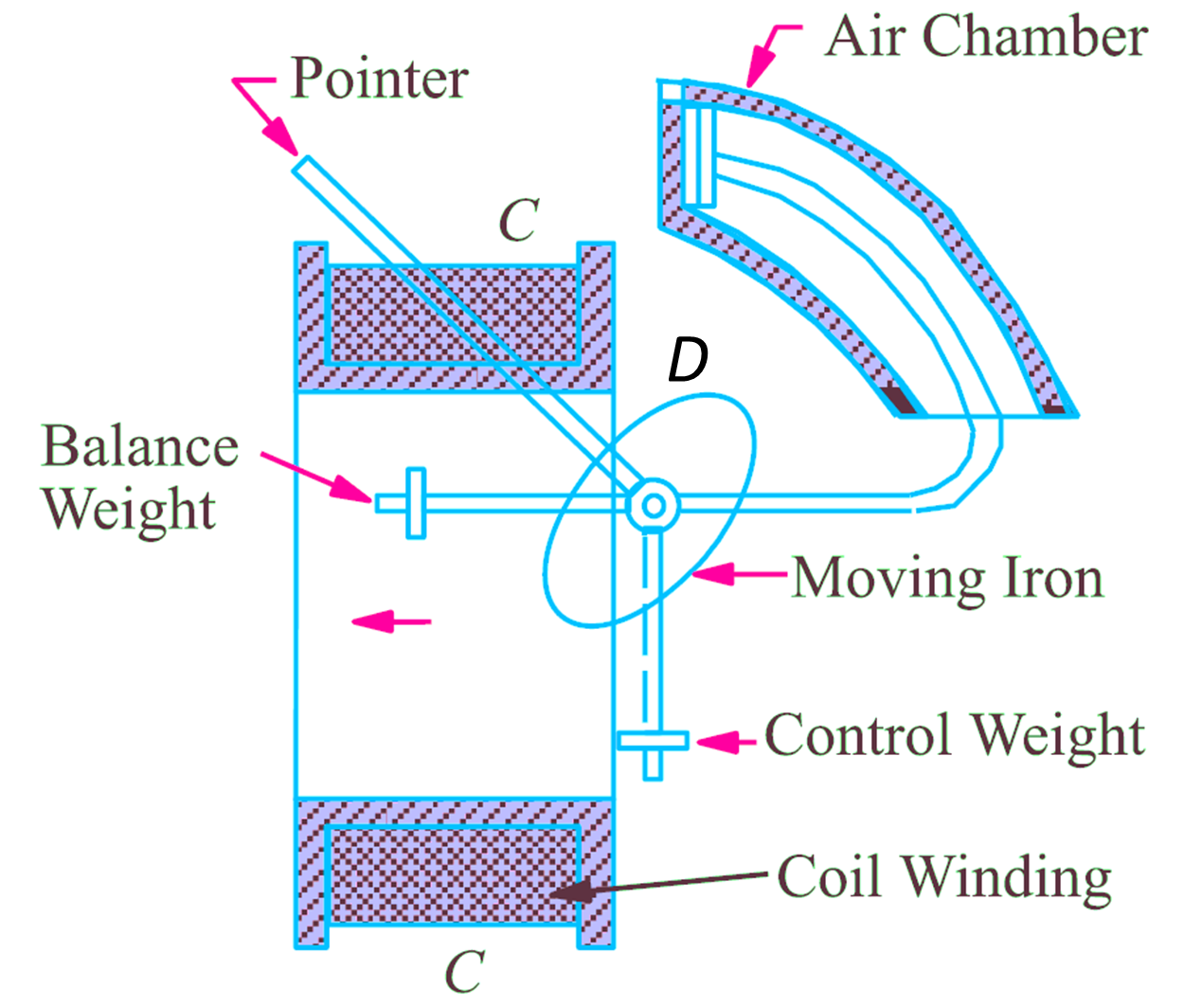
It consists of a fixed coil C of insulated copper wound on the bobbin and an iron disc D. The current to be measured (or a current proportional to the voltage to be measured) is passed through a coil of wire, the number of turns of which depends upon the current passing through it. A certain number of ampere turns are required for the operation of the instrument and this number can be made up by having few turns and large current or vice versa depending upon whether it is a ammeter or voltmeter. In this form of instrument, a small piece of iron is drawn into the core of the coil when the current flows.
Fig. 1: Moving Iron Attraction type
- Whatever be the direction of current in the coil, the magnetisation of the moving iron is always such that it will get attracted. Thus the instruments are unpolarized instruments i.e. they are independent of the direction in which the current passes, hence it can be used on AC or DC. The principle of moving iron attraction type instruments is represented in Fig. 1.
In the instrument shown, the gravity control is used which was previously used, but now-a-days spring control is used. The damping method used is air friction damping. In this type, the moving iron, which is made of high permeability steel is essentially pivoted and consists of thin disc. The shape of the disc is such that a suitably divided scale is obtained. The stray field (field due to neighbouring currents) usually influence the readings, hence magnetic shielding is required.
Repulsion Type
The essential parts of a moving iron, repulsion type instrument are shown in Fig. 2. Insulated copper wire is wound around a bobbin in the form of a coil. The size of wire and number of turns depends upon the ampere turns required and the magnitude of current to be measured. Inside the space of bobbin (coil), two pieces of soft iron are placed face to face. One piece is fixed on the wall of bobbin which is called as fixed iron and the other is fixed to the spindle which is free to move and called as moving iron. When a current is passed through the coil, a magnetic field is produced within the hollow space. The two iron pieces are within the field. They are magnetised in the same direction of polarity, irrespective of direction of current in the coil. Hence, the two iron pieces will repel each other. Hence, a deflecting torque is produced and moving iron is deflected. The deflection ¡s indicated by the pointer attached to the spindle. Generally, a spring is used to produce controlling torque. Air friction damping is adopted to produce damping torque in such type of instruments.
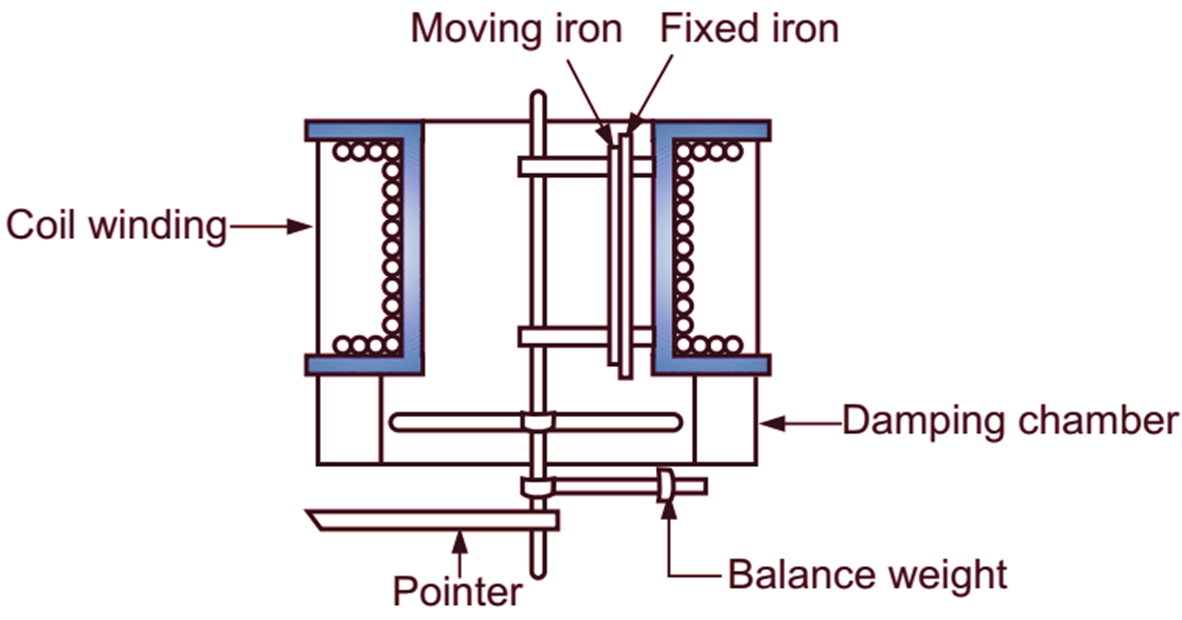
(a) Front view
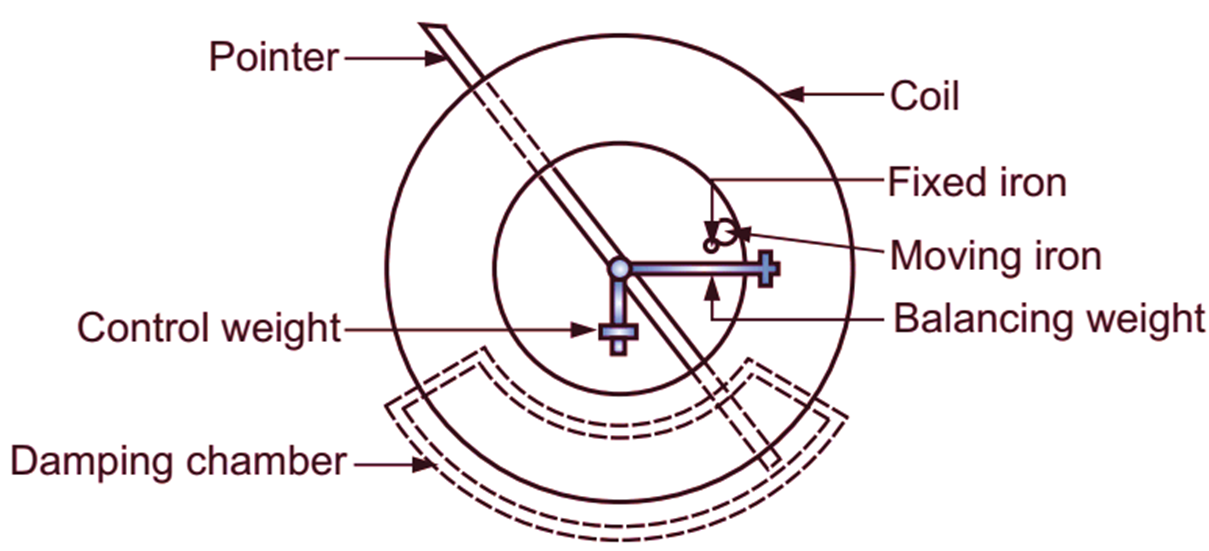
(b) Top view
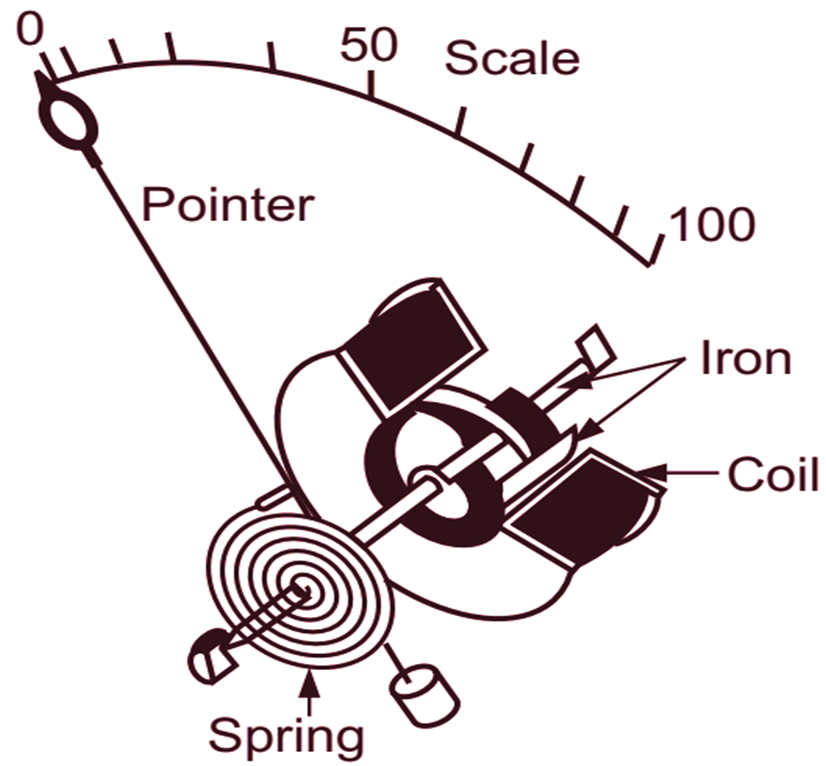
(c) Assembly
Fig. 2: Moving Iron Repulsion type
Advantages of Moving Iron Instrument
1. Since there is no current lead to the moving part of the instrument, it is quite rhobust and can be operated in vertical/horizontal position.
2. The instrument can be used on both a.c. as well as d.c. system. Give reliable service and are capable of giving an accuracy within the limits of both precision and industrial grades.
3. Have high operating torque.
4. Suitable for low frequency and high power circuits.
5. As stationary parts and moving parts are simple. their cost is the cheapest.
Disadvantages of Moving Iron Instrument
1. The readings shown by the meter get affected due to:
(i) Increase in resistance of coil.
(ii) Decrease in permeability and
(iii) Decrease in stiffness of spring, which are the effects due to increase in temperature.
2. Error is caused due to hysteresis in the iron.
3. The readings are affected due to stray fields.
4. The scale is not uniform because the deflection θ ∝ I2 (crowded at the beginning).
5. The instrument readings are true for only one frequency for which it has been designed.
Comparison of Attraction and Repulsion Type PMMI Instrument
An attraction-type instrument will have generally lower inductance than the corresponding repulsion-type instrument, hence the voltmeters will therefore be accurate over a wide range of frequency and there is a greater possibility of using shunts and ammeters.
Repulsion-type instruments are however more reliable for economical production in manufacture and a nearly uniform scale is more easily obtained. These instruments are much more common than attraction type.