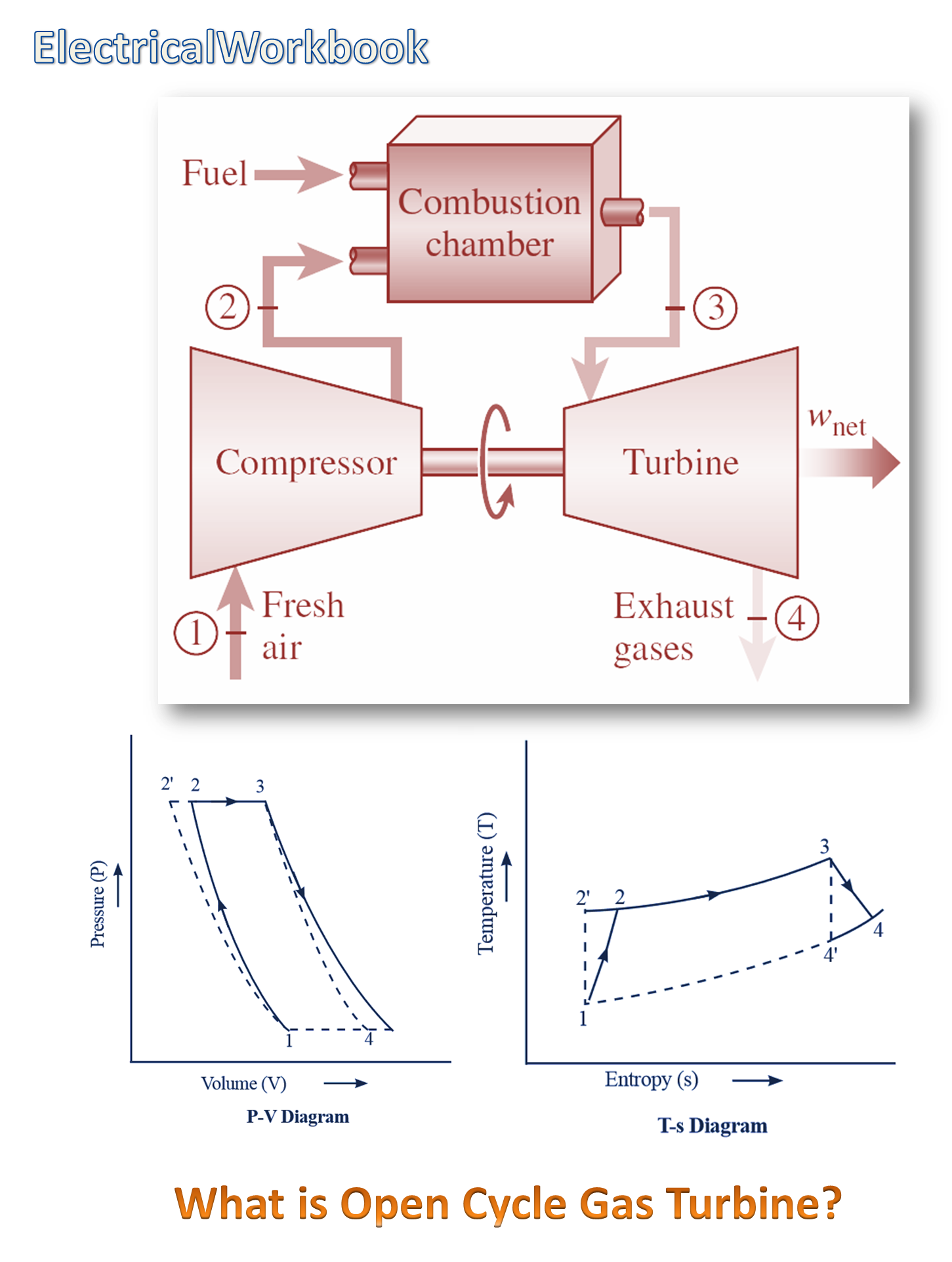
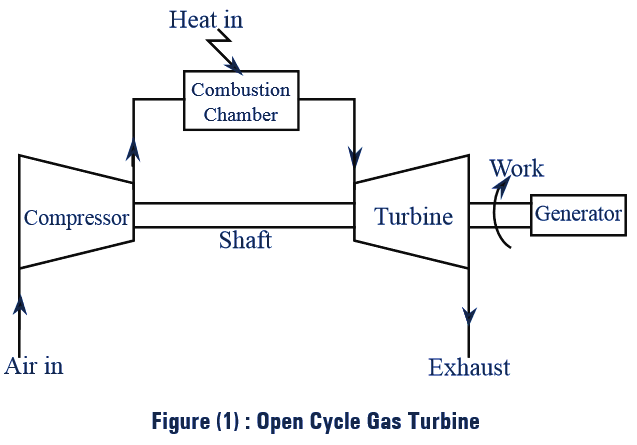
In an open cycle gas turbine, the compressor and the turbine are mounted on a common shaft. Atmospheric air from the surroundings is drawn into the rotary compressor, where the air is compressed isentropically.
Then, this air is passed into the combustion chamber, where the combustion of fuel takes place at constant pressure. Thus, the compressed air is heated and gets mixed with combustion products. As a result, mass of the compressed air increases, and is made to flow over the turbine blades, thereby producing mechanical work at the loss of pressure and temperature. After expansion, the air is exhausted the atmosphere and fresh air is sucked into the system continuously.
As the compressor is directly coupled to the turbine, a part power developed by the turbine is utilised for driving the compressor and the remaining is used for electricity generation or for other propelling applications. The thermal efficiency of an open cycle gas turbine depends on inlet temperatures and efficiencies of compressor and turbine.
Advantages of Open Cycle Gas Turbine
- It occupies less floor space.
- Maintenance cost is low.
- Low capital cost.
- Less weight and smaller size.
- It requires no cooling water.
- Warm up time is considerably less.
Disadvantages of Open Cycle Gas Turbine
- Part load efficiency is low.
- Only air is used as working medium.
- The system is sensitive to component efficiency and
- The efficiency depends on ambient conditions (pressure and temperature).