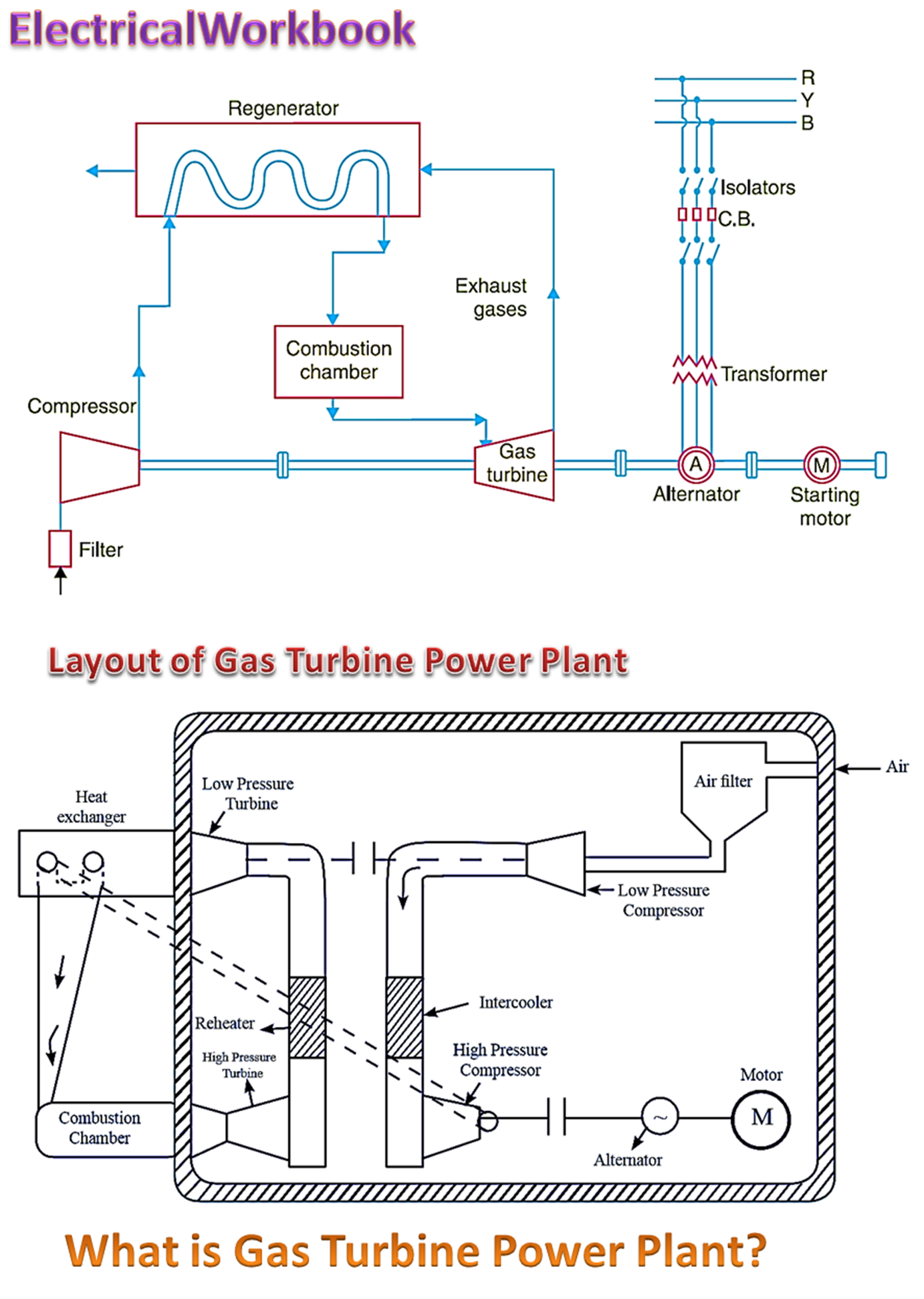
In the gas turbine power plant, electrical energy generation takes place by using gas turbine as the prime mover.
Layout and Working of Gas Turbine Power Plant
The layout of gas turbine influences the performance of the plant. The sharp bends in the pipelines may cause reduction in the power developed. Thus, the gas turbine plant must be designed carefully as per the standards. The air from atmosphere enters into low pressure compressor through air filters and then high pressure compressor through intercooler. This pressurised air is sent to heat exchanger, where it gets heated. Further, it is passed into combustion chamber and undergoes combustion process. The products of combustion enter high pressure turbine where they get expanded and then passes into the low pressure turbine. for further expansion. Therefore, the turbine power (rotation) is converted into electrical energy by means of a generator. Layout of a typical gas power plant is shown in below figure 1.
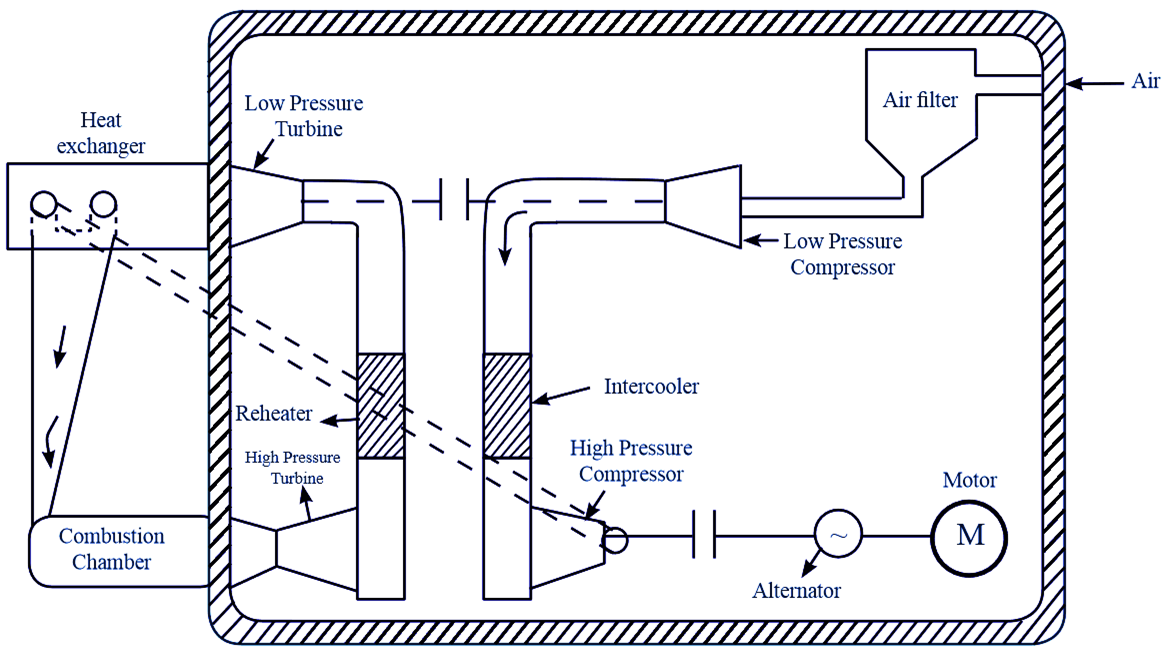
Figure 1: Layout of Gas Turbine Power Plant
Components of Gas Turbine Power Plant
Compressor
The function of compressor is to compress the atmospheric air to high pressure. The compressor used for gas turbine plant is of axial type. It produces high pressures upto 15 bars. It is run by coupling it with the shaft of turbine.
Following two types of compressors are used in gas turbines.
Centrifugal Compressor: In this compressor, air flow is in radial direction. The pressure ratio per stage is 4-5. The efficiency of the compressor is about 80% – 82% and delivery pressure is upto 400 bar. This type of compressors are simple in construction and available at low cost.
Axial Flow Compressor: In this type. air flow is parallel to axis of compressor. The pressure ratio is about 1 – 2. The efficiency of the compressor is 86% – 88% and delivery pressure is about 20 bar. The cost of compressor is relatively high.
Combustion Chamber
The high pressure air coming out of the compressor enters into the combution chamber. The fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, where the combustion of air-fuel mixture takes place. It is located between the compressor and the turbine, The fuels used for combustion are coal gas, producer gas, oil petrol, etc.
Turbine
It is an essential component of the open cycle gas turbine plant. High temperature and high pressure gases are expanded in it. A jet of hot gases and air mixture is made to flow over rings of moving blades of the turbine wheel. The velocity of the jet decreases as its kinetic energy is absorbed by the rings of blades, imparting rotary motion to the shaft of the turbine. The mechanical power obtained from the turbine is then converted into electrical power by coupling a generator to the turbine shaft.
Regenerator
The temperature of the gases leaving the turbine is considerably higher than that of air delivered from the compressor. The heat of exhaust gases can be used to preheat the air delivered from the compressor, thus reducing the mass of fuel supplied in the combustion chamber. A counter flow heat exchanger, which traufers heat from hot gases to air is known as regenerator.
Intercooler
In gas turbine power plants, inter-cooler is used only when the pressure ratios are very large and the compression is accomplished. Cold water is used for cooling the compressed air. The purpose of intercooler is to reduce the temperature of working fluid between the stages, approximately to initial temperature. Cross-flow type of intercooler is mostly used for obtaining higher efficiency.
Advantages of Gas Turbine Power Plant
- The capital cost required to generate the power is less.
- Gas turbine power plant has high reliability
- Gas turbines are more flexible during the operation.
- These type of power plants can be started quickly by using various types of ihels.
- The overall efficiency of gas turbine and conventional system power plant is same and is about 35%.
Applications of Gas Turbine Power Plants
The various applications of gas turbines are as follows,
- Power Generation: Gas turbines are extensively employed for generation of electricity. Depending upon the utilization of power, the gas turbines are classified into three types,
Small Sized Gas Turbine: It generates power less than 2 MW. The turbine contains centrifùgal compressor. which is driven by radial inward flow turbine.
Medium Sized Gas Turbine: This turbine gen rates power in the range of 5 MW to 50 MW. It consists of axial-flow compressors and axial flow turbines.
Large Sized Gas Turbine: These turbines generates power more than 50 MW. They are operated at a pressure ratio of 35:1 and a very high temperature of about 13-15°C.
- Aviation: The gas turbines are widely employed in the aircraft field to drive air compressors in turbo-jets and turbo-propeller engines. These engines are operated at a temperature range of about 800°C- 1000°C.
- Supercharger: The gas turbines can also be used in superchargers to produce the compressed air. These superchargers are fitted in the aviation gasoline engines and also heavy duty diesel engines.
- Marine Engines: The gas turbines can also be used in marine engines, since these turbines does not require water storage tanks or distillation plants.
- Railway Engines: The main purpose of gas turbine is to drive the air compressor in the railway engines.
Other applications of gas turbines are to run turbo pumps, rotary compressors and can also be used in high speed racing cars and hovercrafts.