In this topic, you study Power Quality – Definition, Importance, Issues & Standards.
The good quality of power at the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of AC electrical power, describes the term electric power quality. There are a number of reasons for the poor quality of the AC supply systems such as lightening, flashover, equipment failure, and faults.
Power quality problems due to the current drawn from the AC mains are poor power factor, reactive power burden, harmonic currents, unbalanced currents, and harmonic currents generated by some nonlinear loads..
Any deviation in the voltage or current from the ideal value is a power quality disturbance. As per The IEEE definition, Power quality is the concept of powering and grounding sensitive equipment in a manner that is suitable to the operation of that equipment.
Power quality has gained its importance in recent years as it plays a vital role in supplying electricity effectively to its end users. Power becomes an important resource at the global level and hence it is important to keep its quality at various level of abstraction. Hence, power quality has increased prominence and has importance in terms of electronic equipments. Both electric utilities and end users of electric power are mounting day by day and are more worried about the worth of electric power.
The term power quality has to turn into one of the most important catchphrases in the power industry since 1980s. The term power quality is rather vague and may be associated with dependability by electric utilities.
Definition of Power Quality
- Power quality is a term that is different to different people.
- Power quality generally refers to quality of voltage supply.
- To a utility, it means supply of adequate and reliable power.
- To a customer, it means adequate, uninterrupted power which does not affect the life of equipments.
- To the manufacturer, it means the quality and tolerance of voltage and current parameters that is within the range of parameters for which he has manufactured and tested the products.
Importance of Power Quality
- Power quality is significant because:
- Customer pays for good quality power, if power quality is poor, it breach of trust.
- Poor quality power damages consumer’s equipments and affects equipments life.
- Increase of system losses.
- Bad power quality causes severe health hazards.
- Poor voltage and high current with harmonics causes heating and high losses.
- The reliability of power supply s affected due to relay operations, frequent faults and equipment failure.
Symptoms of Poor Power Quality
The symptoms of poor power quality are:
- Excessive reactive power.
- Flickering of lights.
- Computers shuuing down.
- Overheating of wires, motors and transformers.
- Process control devices act unpredictably.
- Overloaded generators.
- Supply interruption.
Effects of Poor Power Quality on Economy
- If high harmonics are developed by the load, the rotating machine in generation side and consumer side get overheated.
- Industries like rolling mills, paper mills, textile mills get affected badly as the interruption produced is too high.
- If there is frequent abnormalities, the cost incurred towards the equipment goes high
- Poor quality increases, more losses.
Power Quality Issues
Some power quality issues as follows
Voltage Sag: A momentary voltage decrease in rms voltage for durations of 0.5 cycle to 1 min. The voltage sag waveform is shown in Fig. 1.
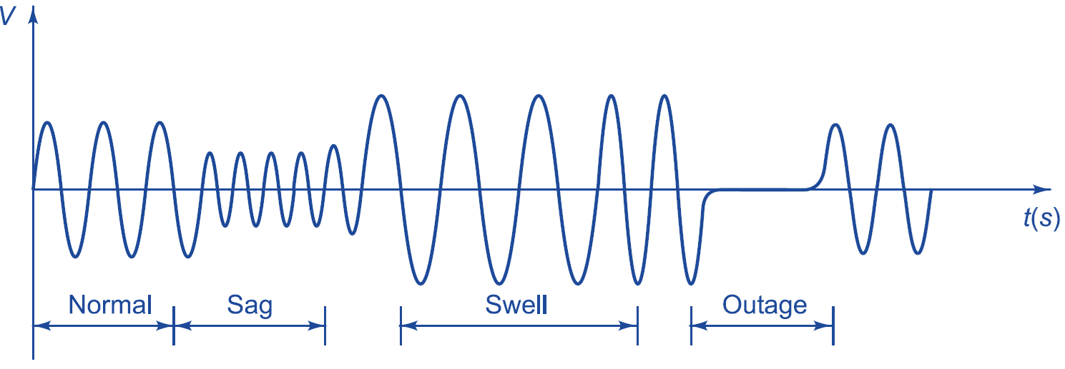
Fig.1: Voltage sag, voltage swell, and outage.
Voltage swells: A momentary voltage rise in rms voltage for durations of 0.5 cycle to 1 min. The voltage swell waveform is shown in Fig. 1.
Outage: When voltage zero for a few seconds to several hours. The voltage outage waveform is shown in Fig. 1.
Over voltage: A steady state voltage having a value greater than the nominal voltage for a time greater than 1 min.
Under voltage: A steady state voltage having a value less than the nominal voltage for a time greater than 1 min.
Transients: A transient can be a unidirectional impulse or a damped oscillatory wave for an extremely short duration as compared to voltage sag and swell. The transient waveform is shown in Fig. 2.
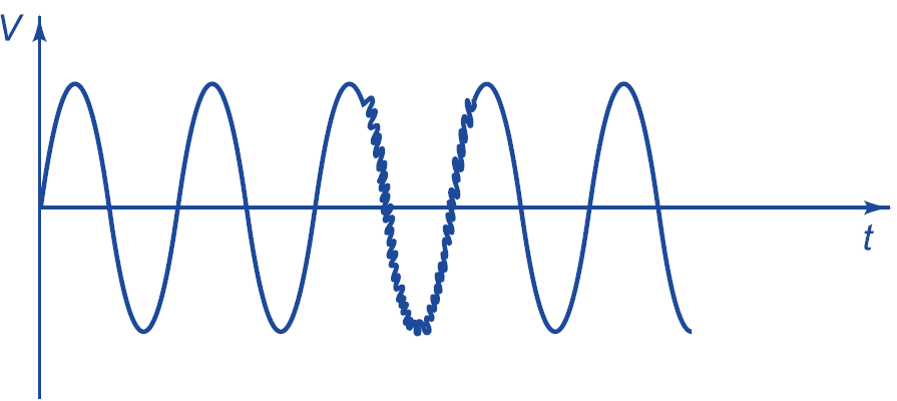
Fig.2: Transient voltage (oscillatory)
Harmonic:
Harmonics are sinusoidal voltage/current having frequencies that are integer multiple of Fundamental frequency. The harmonic distortion waveform is shown in Fig. 3. Harmonics in the system can:
- Make relays maloperate.
- Increase loss in capacitances, noises.
- Telephonic cross talks.
- Can cause increase in resonance
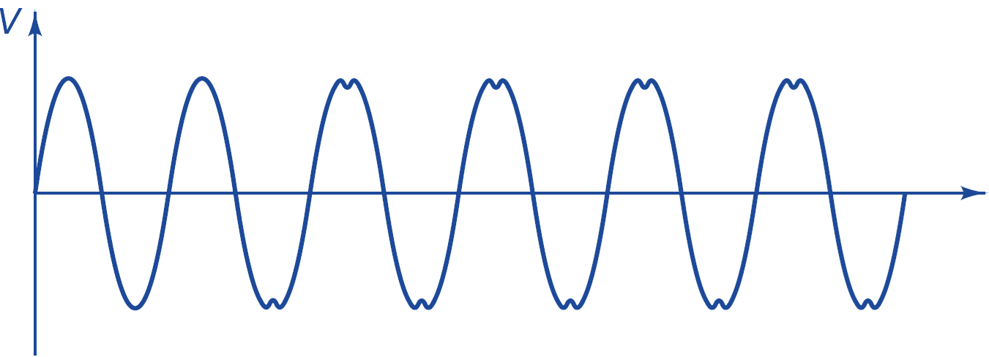
Fig.3: Harmonic distortion
Power Quality Standards
Due to the poor power quality, the customers facing a number of problems such as equipment failure, mal-operation, interruption in the process, and loss of production. Thus, several standards have been developed, modified, recommended, to improve the power quantify. Table 1 shows a list of some standards on power quality.
Table 1 List of some standards and its Description.
| Standards | Description |
| IEEE Standard 519-1992 | Harmonic Control in Electrical Power Systems |
| IEEE Standard 1159-1995 | Monitoring Electric Power Quality |
| IEEE Standard 1100-1999 | Powering and Grounding Sensitive Electronic Equipment |
| IEC 61000-3-2 | Limits for Harmonic Current Emissions |