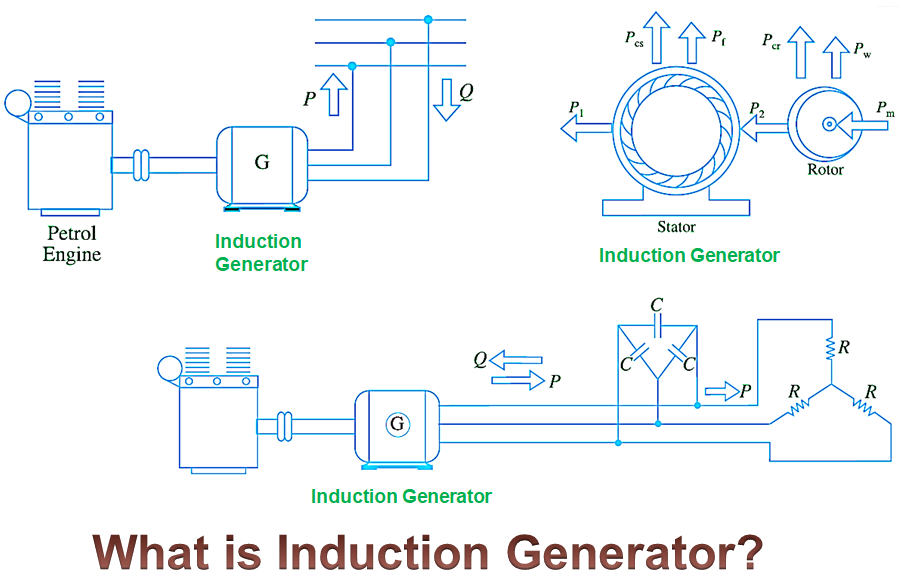
In this topic, you study Induction Generator – Construction, Diagram, Torque Slip Characteristics, Advantages & Applications.
If the terminals of the stator winding of a three-phase induction motor are kept connected to a three-phase supply of constant voltage and frequency, and at the same time, it is driven at a speed higher than the synchronous speed with the help of a suitable prime mover mechanically coupled to its shaft, it is observed that the motor starts supplying the electrical energy to the AC mains. Thus, the motor under this condition acts as a generator and is referred to as an induction generator or an asynchronous generator. As shown in Fig. 1, the induction machine working as a generator and supplies active power to the mains.
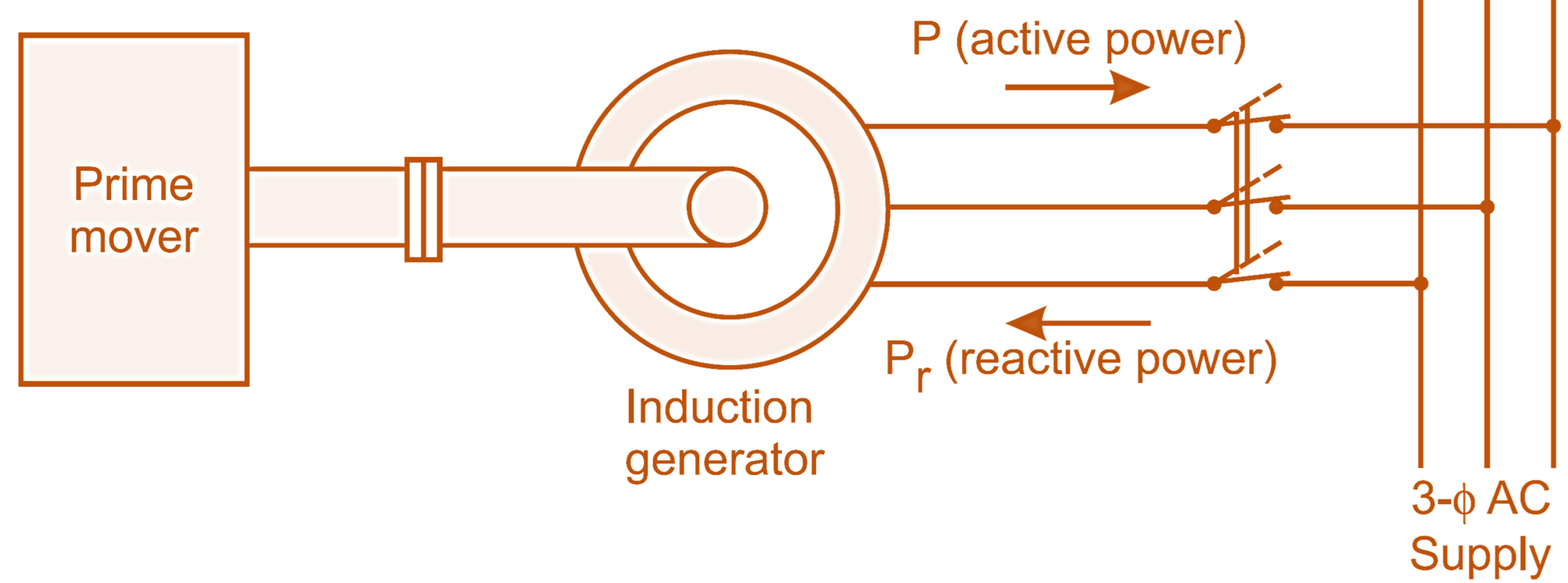
Fig. 1: Induction machine working as a generator
The three-phase induction motor that for motor operation, the slip lies between zero and unity, and for this case we have a conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. When the rotor of an induction motor is driven with the help of a suitable prime mover at a speed higher than the synchronous speed, we have a negative slip. Hence, a negative slip corresponds to a generator operation. We know that in the case of an induction motor, the rotating magnetic field is produced by the magnetizing current supplied to the stator winding from the three-phase supply. This supply of the magnetizing current must be available when the machine is operating as an induction generator. An induction generator may be self-excited by providing the magnetizing reactive power by using a capacitor hank. ¡n such a case, an external ac source is not necessary.
Construction of Induction Generator
The construction of the induction generator is similar to that of an induction motor. Whether the machine runs as a motor or generator depends upon the condition of whether the slip (S) is positive or negative. Induction generators are nearly always provided with squirrel-cage rotors.
Torque Slip Characteristics of Induction Generator
In an induction generator, since the rotor is moved above synchronous speed and the rotating field remains ¡n the same direction, the direction of cutting of the rotor conductors is reversed so that the rotor e.m.f. is reversed, the rotor current is reversed and hence the torque is reversed (this is obvious from the torque equation of the motor. When the slip is negative, the torque is negative). Fig. 6.11 shows the torque-slip characteristic of an induction machine for generator and motor modes.
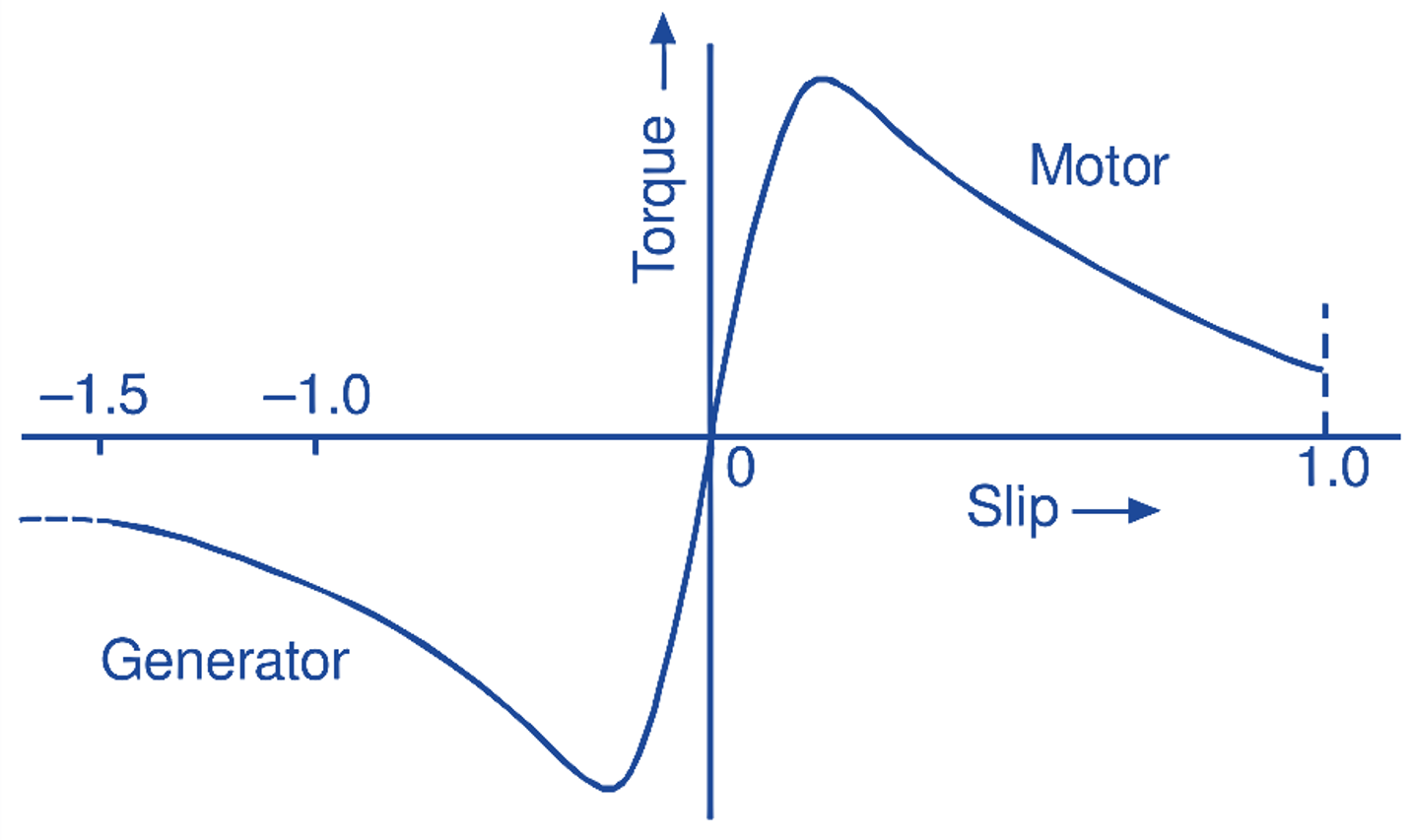
Fig. 1: Torque-slip characteristic of an induction machine for generator and motor modes.
Induction Generator versus Synchronous Generator
An induction generator differs from the synchronous generator (i.e. alternator) mainly in the following respects
- The induction Generator does not require dc excitation.
- The induction Generator generates alternating current only when its stator is connected to a line of fixed frequency, its exciting current being the magnetizing current drawn from the line.
- The frequency of the magnetizing current fixes the frequency of the alternating current supplied by the induction generator. Thus, the frequency is not affected by the speed at which the induction generator is driven.
- No synchronizing is required, since the machine cannot generates any e.m.f. until it is connected to the mains.
Advantages of Induction Generator
Following are some of the distinct advantages of the induction generator-:
- Simple and robust construction.
- Cheaper in cost.
- Requires less maintenance.
- Free from hunting.
- No synchronization is required.
- Frequency of the alternating current supplied being controlled by the frequency of the excitation current, speed variations of the prime mover are comparatively less important.
- Under short-circuit conditions, it delivers little power because its excitation quickly becomes zero. This provides some self-protection.
Disadvantages of Induction Generator
The main drawbacks of the induction generator are as follows:
- It cannot be operated independently and the method of providing sell-excitation by connecting suitable capacitors across its terminals is of limited practical importance in view of the capacity (i.e. rating) of the capacitors required.
- It can supply only leading current whereas most commercial loads require lagging current.
Applications of Induction Generator
Induction generators have very limited applications. Some of them are mentioned below
- The principal use of the induction generator is for braking purposes (because of its negative torque). The generator action prevents an induction motor from overspeeding when the mechanical power is supplied to its shaft by the load. e.g. Induction generators arc commonly used in hoists to brake the loads moving at high speeds under gravity. They are also used for the braking purpose in railway work (i.e. traction). When the induction motors are left connected across the line on a downgrade, any tendency of the train to drive them above synchronous speed is accompanied by the generator action. Therefore, in addition to braking the train, the generators pump energy hack into the line. This is called regenerative braking.
- Induction generators are very useful for small variable-speed constant-frequency generating stations. e.g. Small and variable water power which do not call for the setting up of a normal hydropower station can be utilized with the help of a water wheel-driven induction generator. When there is an adequate water supply, the machine gets automatically switched on o an overhead line energised from another normal power station. On the other hand, when the water supply is insufficient to drive the machine above synchronous speed, it is automatically switched off.
- Induction generators are increasingly used in windmill applications.