In this topic, you study Torque Speed Characteristics of Induction Motor.
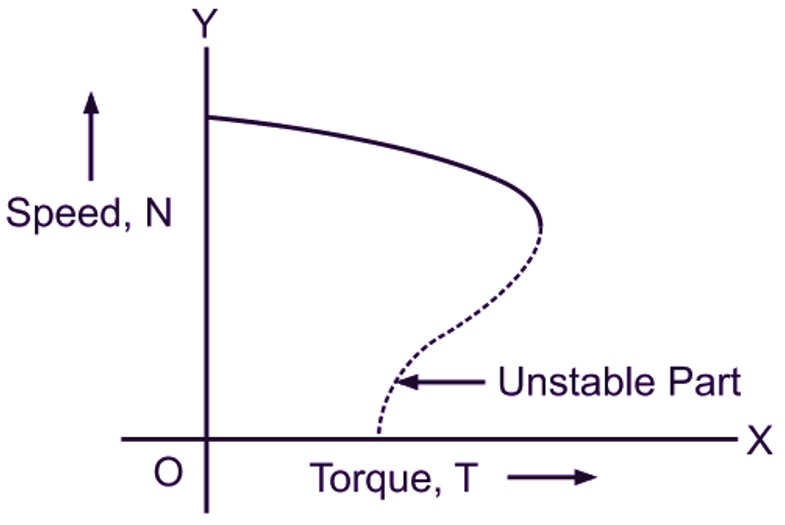
The behaviour of the motor under changing load can be very well studied from its speed torque characteristic. The fall in speed from no-load to full-load condition being only about 4 to 5 % in small motors and 1.5 to 2 % in large motors, the induction motor is practically a constant-speed motor. Hence, over the normal operating range, the speed-torque characteristic of a three phase induction motor (Fig 1) is similar to that of a dc shunt motor. As said earlier, at no load, the torque required is only to overcome friction, windage and other no-load losses, and speed is very nearly synchronous. When the load on the motor is increased, the speed falls. This causes an increase in relative speed between the rotating magnetic field produced by the Stator and the rotor conductors and hence increase in rotor emf and current. This results into increased motor torque. Correspondingly, the motor draws increased current from the supply. Thus, the motor meets the increased demand for the torque by the load. The load may be increased until the speed is such that maximum value for the torque is reached. As said earlier, this limiting torque is known as break-down torque or pull-out torque. If the load is increased beyond this limit, the motor is unable to supply the necessary torque and it stops. Hence, the dotted portion of the characteristic curve represents this unstable condition.