In this topic, you study Split Phase Motor – Construction, Diagram, Working, Applications & Torque Speed Characteristic.
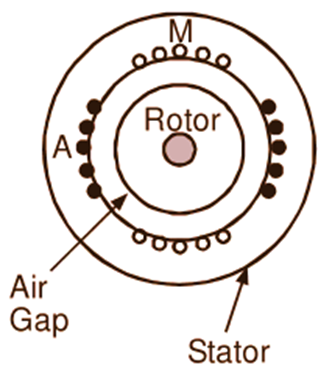
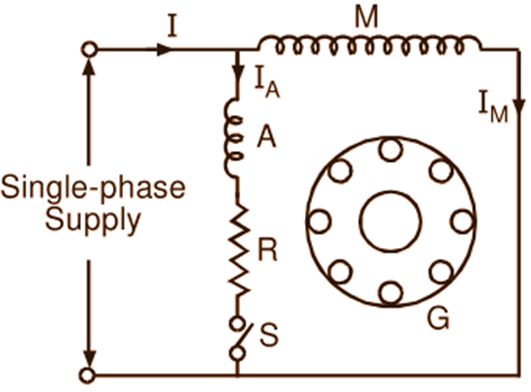
These motors are commonly known as split phase induction motors or Resistance split phase Motors. The stator of this type of motor carries two windings, one called the main winding (M) and the Other known as auxiliary winding (A) or starting winding. The axes of these windings are displaced from each Other usually by an angle of 90 electrical degrees in space. The rotor (G) of the motor is of normal cage type. Fig. 1 (a) shows the motor schematically and Fig. 1 (b) shows its connection diagram.
(a)
(b)
(c)
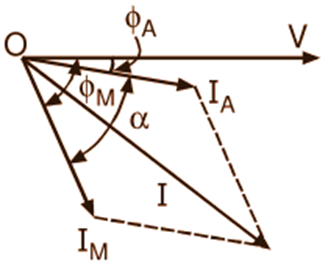
Fig. 1 : (a) Schematic representation of a split-phase type single-phase induction motor, (b) Connection diagram, (c) Phasor diagram
The auxiliary winding along with the series resistor (R) is connected across the main winding. Instead of connecting externally such a high resistance in series with an auxiliary winding, its resistance may be increased by choosing a high resistance fine copper wire for winding purposes. The resistance to reactance ratio of the auxiliary winding circuit being higher than the main winding, currents through them are nearly in quadrature (Fig. 1 c). The resulting fluxes due to these currents are, therefore, displaced in space through 90o and have considerable time phase difference. A rotating magnetic field is, therefore, produced (as in a two-phase motor). The motor thus develops a starting torque. Once the motor is started, the auxiliary winding is disconnected with the help of a centrifugal switch (S) at about 75 to 80% of the synchronous speed.
Torque-Speed Characteristic of Split Phase Motor
Fig. 2 shows the torque-speed characteristic of a resistance split-phase motor. The starting torque of this type of motor is generally 125 to 150 % of the full-load torque.
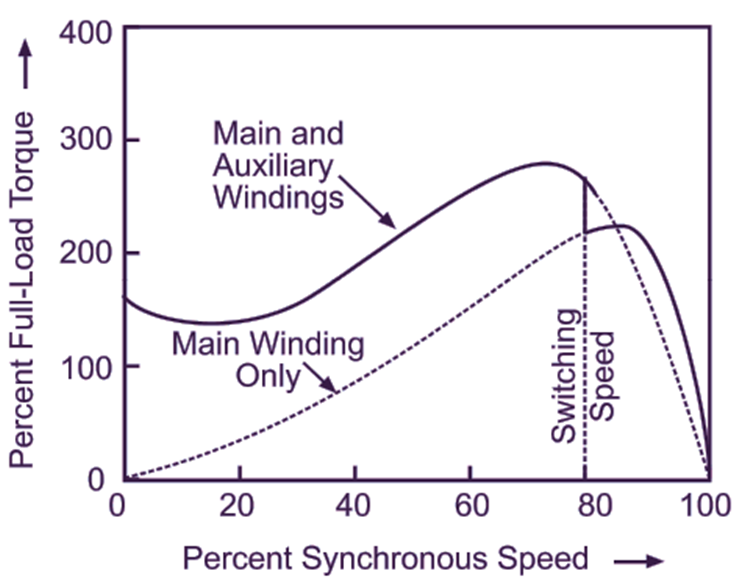
Fig. 2: Typical torque-speed characteristic of a resistance split-phase motor
Reversal of Rotation of Split Phase Motor
The direction of rotation of this type of motor can be reversed by reversing the terminal connections of either the main or the auxiliary winding.
Applications of Split Phase Motor
These motors are commonly used in small electric tools, fans, blowers, centrifugal pumps, domestic refrigerator units, oil burners, washing machines, etc.