It is the process of welding without the use of flux or flux coated electrode, which are generally highly corrosive. The heat for welding is produced by an arc struck between non-consumable tungsten electrode and the work. The electrode is mounted centrally in a gas nozzle through which an Inert gas, argon or helium is passed. The gas forms a protective shield around the weld against atmospheric action on the molten metal. The inert gas completely envelops the tip of the electrode and the work below It. The torch is either air cooled or water cooled. Filler rod supplies the additional metal if necessary, depending upon the type of work. Welding may be done on A.C. or D.C. supply.
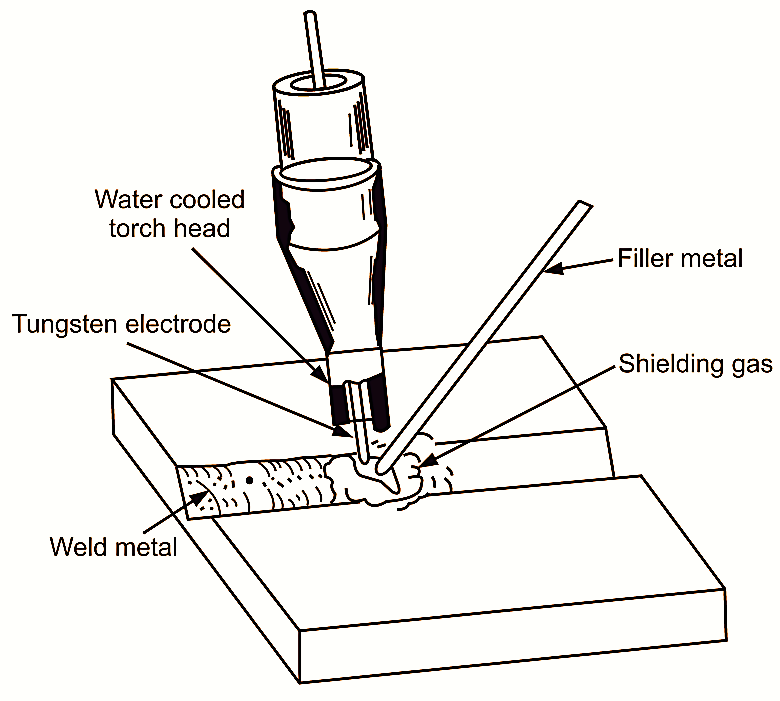
Fig. 1: Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
In general, D.C. is used for stainless steel and copper alloys. A.C. is used for welding steel, cast iron, aluminium, stainless steel or copper alloys.
Advantages of Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
- This welding process is better controlled by welder, because of clear visibility of produced arc and melting base metal.
- High quality of welding is obtained on thin metal from TIG welding process.
- No flux inclusion is occurred in welding joint, because there is no need of any kind of flux for welding.
- All welding positions can be performed by this process.
- Minimum cleaning is required after welding.
Applications of Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
- Welding the sheet and thinner section metals.
- Spaceship vehicles, motor chamber welding.
- It can weld the copper, aluminum, nickel and their alloys, zirconium, titanium etc.
- Weld the bellows, instruments, diaphragms, transistor cases joints.
- Precision Instrument can be welded by TIG welding process.