Much more attention be given to this job as the reliability of service depends on proper methods of laying, attachment fittings i.e. cable joints, joint boxes, connection etc.
Following steps are involved in cable lying system:
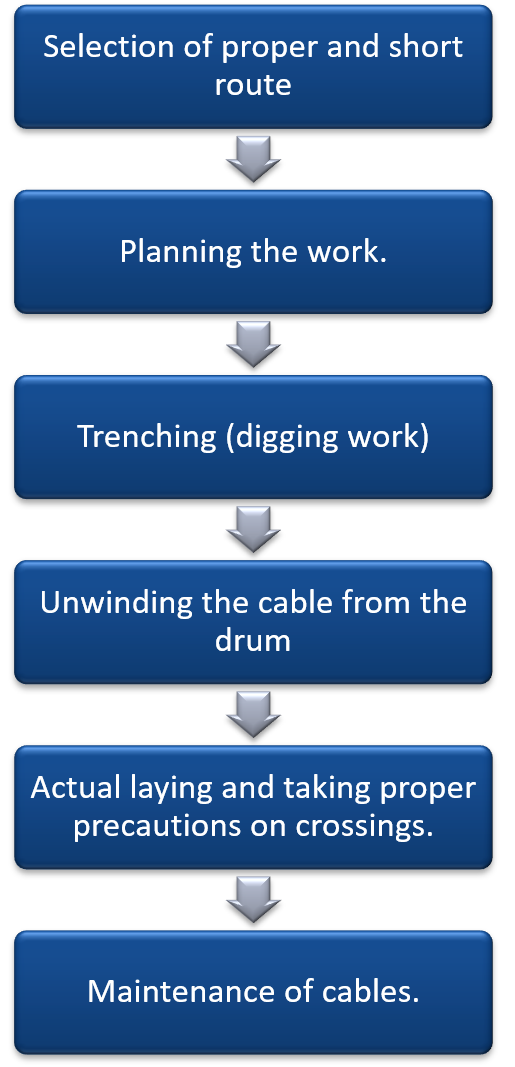
- Selection of proper and short route
- Planning the work.
- Trenching (digging work)
- Unwinding the cable from the drum
- Actual laying and taking proper precautions on crossings.
- Maintenance of cables.
Methods of Cable Laying
- Direct Laying
- Using Troughs
- Drawing into Pipes or Ducts
Direct Laying
This method is most popular. A trench of 0.5 m width and 1.5 m deep is dug in the ground as per the layout of the route as shown in Figure 1. Soil is taken out. A layer of sand of 10 cm is spread at the bottom of trench then cable is laid carefully on this sand bed. Again a layer of sand over the cable and over it a layer of brick along the length of the cable. The remaining portion is covered by soil. By this provision, the cable is protected mechanically and possibility of moisture is avoided by the use of sand layers. This cable must have the outermost layer (serving) of bituminised paper and hessian tape for protecting it from corrosion and electrolysis-chemical reaction.
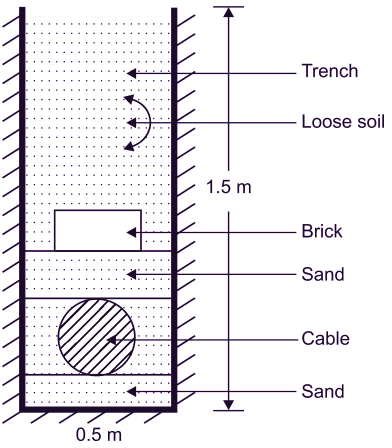
Fig. 1: Direct Laying.
Advantages
- Very simple
- Requires less time, less cost.
- Gives best condition for heat dissipation.
- Clean and safe.
Disadvantages
- Load extension not possible.
- Maintenance cost much more.
- Alteration ¡n route ¡s a tedious job.
- Fault location difficult.
- Not suitable in dense populated and crowded areas.
Using Troughs
The troughs may be made of cement concrete or stoneware or cast iron as shown in Fig. 2. After placing the troughs along the route in the trench, the cable is laid down. The space in the trough is filled with bituminous compound and covered and the trench is filled up with soil.
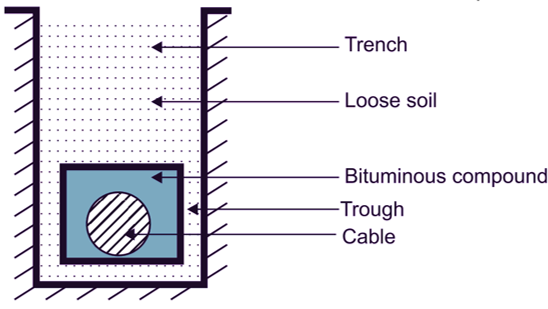
Fig. 2: Using Troughs.
Advantages
This method has the advantages:
- Best mechanical protection to the cable.
- Corrosion and chemical reactions not possible.
Drawbacks
- More expensive.
- Skilled labour is required
- Good weather conditions required.
- Dissipation of heat less effective, so current carrying capacity reduces.
Drawing into Pipes or Ducts
Pipes may be of stoneware, fibre, steel, wrought iron. Ducts may be of stoneware, cement concrete. Pipes or ducts are laid in the ground with manholes or suitable possessions along the cable route. The cables are pulled into the position from manholes. 4-way underground duct line is shown in Fig. 3. The distance between the two manholes must be appropriate so that pulling through the ducts is easy. Cables need not layer not to damage while pulling.
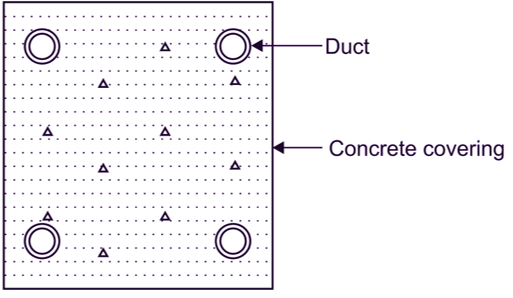
Fig. 3: Drawing into Pipes or Ducts.
Advantages
- Strong mechanical production
- Chances of faults are rare
- Non-armoured makes cable joining easier.
- Without opening the ground, the repairs, replacements, alterations are
Disadvantages
- Initial cost is much higher
- Suitable in dense populated area.
- Heat dissipation is poor, therefore, current carrying capacity reduces.