An air cooled condenser is one, in which, the removal of heat is done by air (cooling medium). It consists of steel or copper tubing, through which, the refrigerant flows. The size of tube usually ranges from 6 mm to 18 mm outside diameter, depending upon the size of condenser. Generally copper tubes are used, because of excellent heat transfer ability. The condensers with steel tubes are used in ammonia refrigerating systems to avoid problem of corrosion. The tubes are usually provided with plate type fins to increase the surface area for increasing heat transfer rate, as shown in Fig. 1. The fins are usually made from aluminium, because of its light weight property. The fin spacing is quite wide to reduce dust clogging.
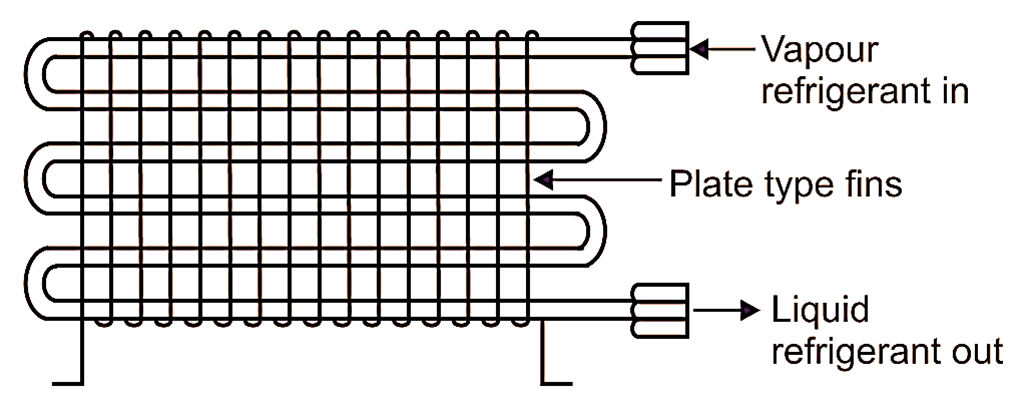
Fig. 1: Air cooled condenser
Working of Air Cooled Condenser
Refrigerant flows inside the tubes or coils and air flows over the external surface of condenser tubes. Atmospheric air (i.e. surrounding air) comes in contact with the warm condenser tubes and absorbs heat from the refrigerant. The warm air moves up due to decrease in density. In natural convection, heat transfer rate is slow, so it requires large surface area of condenser as compared to forced convection condenser. The major disadvantage of an air cooled condenser is that, it operates at a higher condensing temperature than water cooled condenser. The higher condensing temperature causes the compressor to work more and hence, compressor consumes more power.
Natural Convection Air Cooled Condensers
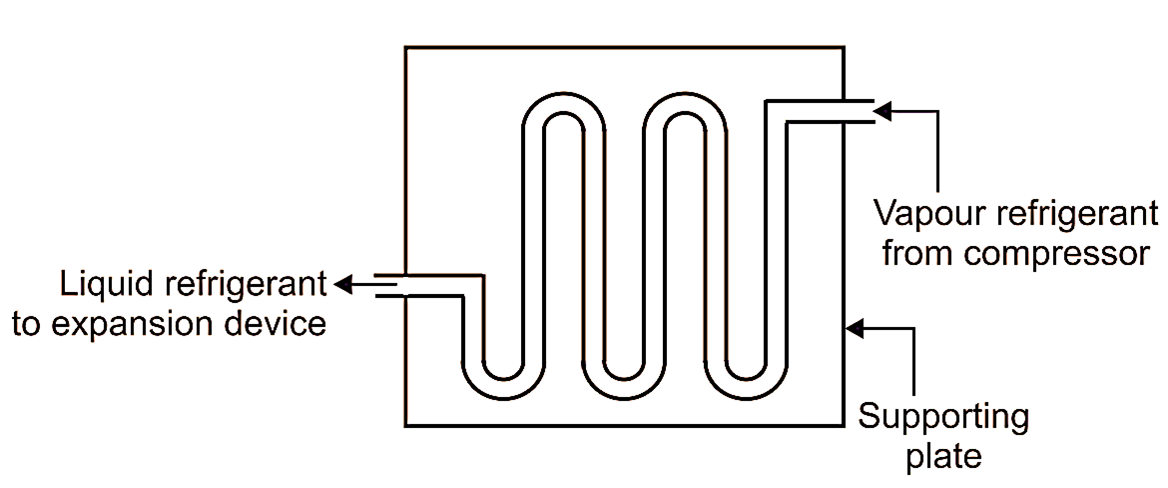
Fig. 2: Natural convection air-cooled condenser
Here, heat is transferred from the refrigerant inside condenser coils to the outside atmospheric air (cooling medium) due to natural convection. No external source of fan (artificial cooling) is provided. As the air comes in contact with the warm condenser tubes, it absorbs heat from the refrigerant and thus, the temperature of air increases. This warm air being lighter, rises up and gets displaced by the cold air coming from bottom. This cold air rises up near the condenser coils to take away the remaining heat from the condenser. This cycle repeats again and again, till the condensation of vapour refrigeration is achieved. Since the rate of heat transfer in natural convection type condenser is slower, therefore, it requires a larger surface area as compared to forced convection condenser.
Advantages of Natural convection Air Cooled Condenser
- Very little maintenance.
Forced Convection Air Cooled Condenser
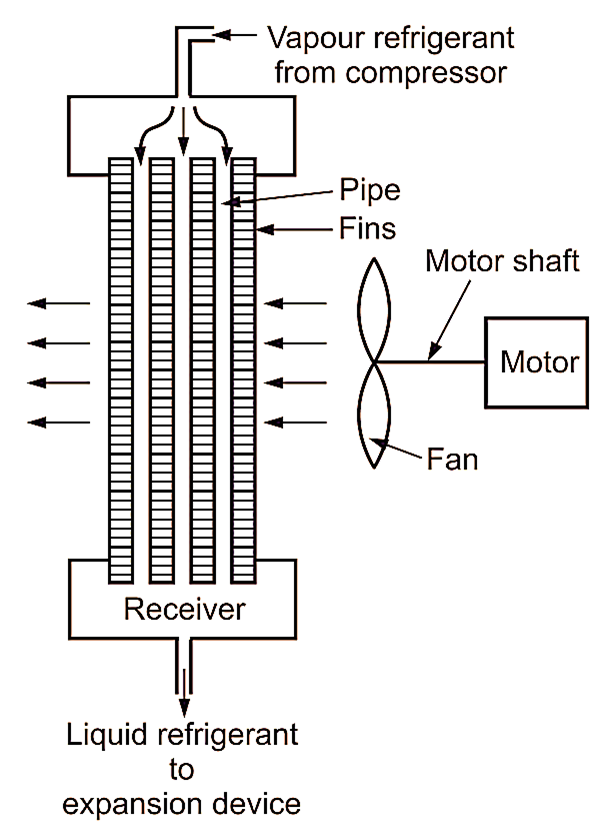
Fig. 3: Forced convection air
In forced convection air cooled condensers, the fan is used to force the air to pass over the external surface of condenser coils to increase its heat transfer capacity. The fan may be either propeller type or centrifugal type. The forced convection condensers may be divided into the following two groups:
- Base mounted, and
- Remote air cooled condensers.
Advantages of Air Cooled Condenser
- Air cooled condensers are simple in construction, since no pipes are required for air.
- Air is freely available in abundant quantity. Therefore, running cost is negligible.
- Disposal of warm air is not a problem.
- The fouling of condenser is not a problem, which is normally found in water cooled condensers.
- Low maintenance cost.
Disadvantages of Air Cooled Condenser
- Since specific heat of air (Cp = 1.005 kj/kg.K) is one fourth of specific heat of water (Cp = 4.187 kj/kg.K) and density of water (ρwater = 1000 kg/m3) is thousand times more density of air (ρwater = 1 kg/m3), therefore, volume flow rates of air required are very large.
- Thermal conductivity is small; hence heat transfer coefficient is also very small.
- Air is available at dry bulb temperature (i.e. atmospheric temperature), while water is available at a lower temperature, which is 2 to 3° C above the wet bulb temperature.
- The temperature rise of air is much larger than that of water for same amount of heat absorbed. Therefore the condenser temperature increases, reducing COP.
- Its use is normally restricted to capacity of 10 TOR.
- The cost of air cooled condensers is two to three times more than water cooled condensers.
Applications of Air Cooled Condensers
- Air Cooled Condenser is used in small capacity systems, such as,
- Domestic Refrigerator,
- Split Air Conditioner,
- Freezers etc.
- Window Air Conditioner,
- Water Cooler,
Advantages of Air Cooled Condensers over Water Cooled Condensers
- Simplicity of construction.
- No handling problems.
- No need of piping arrangement for carrying the air.
- No problem of disposal of used air.
- Negligible or even no fouling problems as compared to water cooled condensers.
- Less installation and maintenance costs.
- High flexibility.
Disadvantages of Air Cooled Condensers as compared to Water Cooled Condensers
- Poor heat carrying capacity.
- It requires very large quantity of air to be circulated (300 mg per tonne of refrigeration per hour).
- Not used for refrigeration plants having capacity more than 5 TOR, because power required to drive the fan becomes excessive, which also leads to objectionable fan noise.
- They give owest efficiency, when the outside temperature is highest.