Class B commutation or Resonant-Pulse commutation is one of the types of forced commutation. In this type of forced commutation, a resonant pulse generated by an LC circuit is used to turn OFF the SCR. Fig. 1 (a) shows the circuit diagram of a class-B (or resonant pulse) commutation of SCR and Fig 1 (b) shows its waveforms.
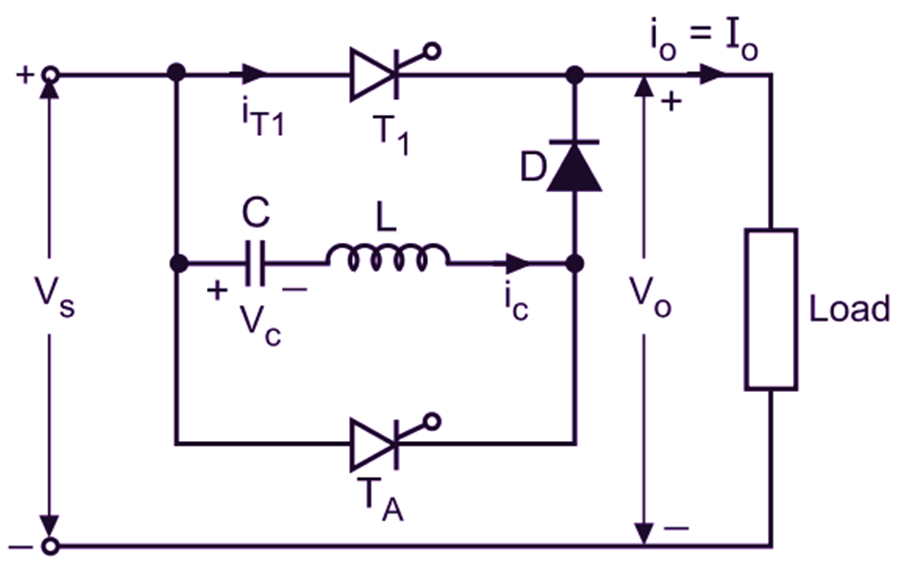
Fig. 1: Resonant pulse (class-B) commutation Circuit Diagram.
Waveforms of Class B Commutation
The waveforms of class-B (resonant pulse) commutation are as shown in Fig. 1 (b). This method of commutation is called as “Resonant-Pulse Commutation” method or Current Commutation.
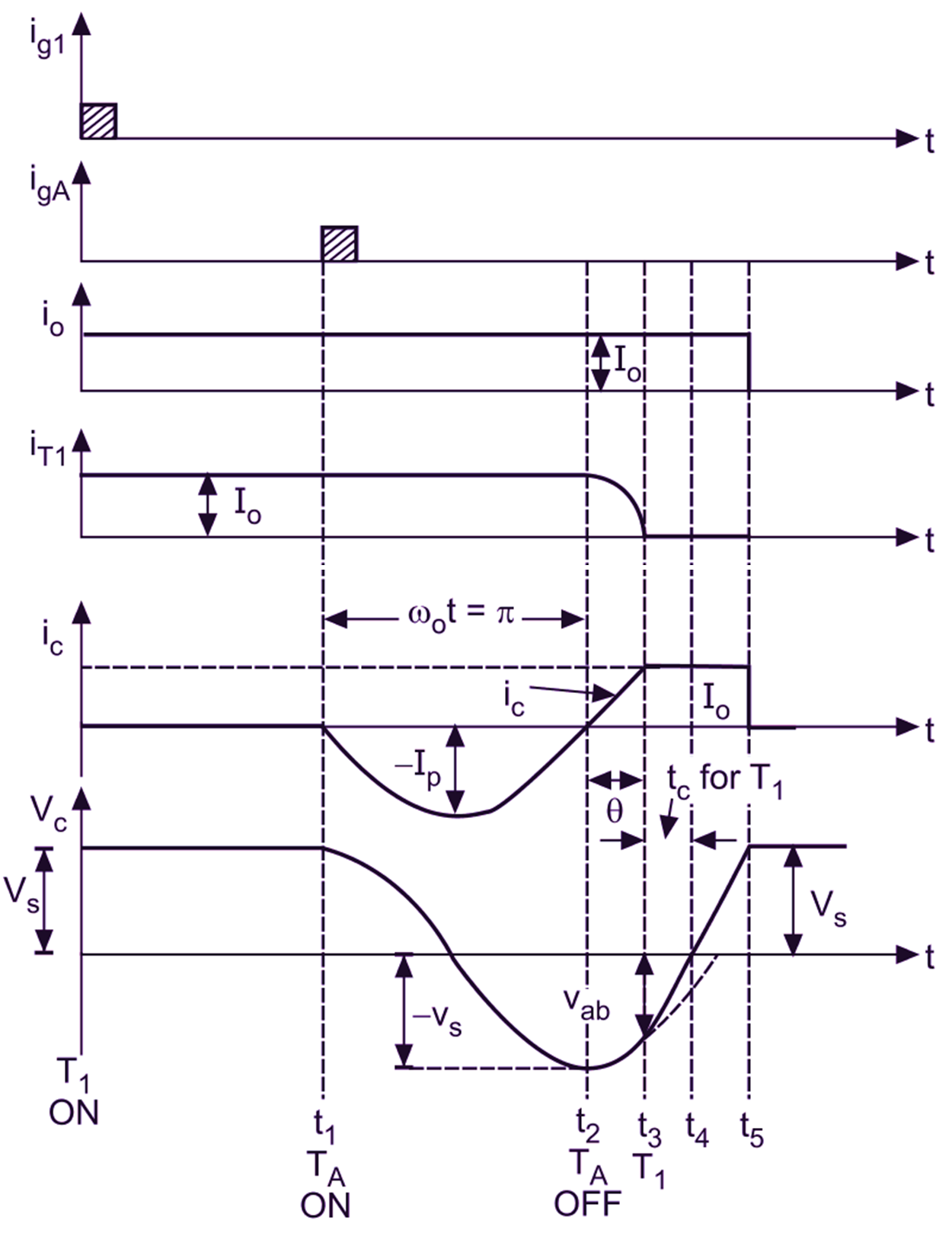
(b) Waveforms
Fig. 2: Resonant pulse (class-B) commutation waveforms
Working of Class B Commutation
Initially, it is assumed that the capacitor is charged to voltage VS with left plate positive. As VC = VS; the charging current iC = 0. At t = 0; main SCR (T1) is fired or triggered by ig hence the main SCR turns ON due to which io = Io and iT1 = Io
To turn OFF the main SCR at desired instant t1, applied to auxiliary SCR (TA). Hence, the capacitor begins to discharge through TA and iC becomes negative and is resonant due to which VC starts decreasing. At the half cycle of t1 from instant t1 i.e. at time t2, the current through capacitor iC becomes zero causing T1 to turn OFF. Therefore, VC = – VS and also io = iT1 = Io because T1 (main SCR) is still conducting . As TA turns OFF, the right plate of the capacitor gets positive VS. Here the resonant current iC builds up through C, L, D and T1 which flows in opposite direction of iT1 due to which iT1 begins to drop and hence the voltage across the capacitor begins to reverse once again i.e. it increases.
At time t3; iC becomes equal to Io. The current through T1 reduces to zero and the main SCR turns OFF; whereas by time t4, the voltage across the capacitor becomes zero. The output current will continue to flow till the capacitor charges to + VS i.e. its left plate becomes positive. After this, T1 and TA are OFF and the current through the capacitor is zero. Therefore, io = 0.
Advantages of Class B Commutation
The advantages of class-B commutation method of an SCR are as under:
- It is simple.
- The commutating components L and C do not carry load current.
Applications of Class B Commutation
The application of class-B commutation method is as under
1. It is used in d.c. chopper circuit.