In this topic, you study Coefficient of Coupling.
As the two coils A and C shown in Fig. 1 are brought close together, all the flux Φ1 produced by current I1 in coil A does not link coil C. Only a fraction K1 of this flux i.e. K1Φ1 (where K1 < 1) links with coil C.
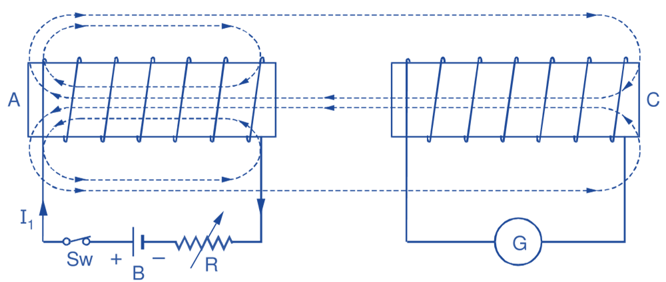
Fig. 1: Mutual induction
Thus the Equation for the coefficient of mutual induction under this condition is given by
\[\text{M}=\frac{{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{{\phi }_{\text{1}}}}{{{\text{I}}_{\text{1}}}}….(1)\]
Similarly, if the current I2 flowing in coil C produces flux Φ2 and the fraction K2 of this flux i.e. K2Φ2 (where K2 < 1) links with coil A, then the coefficient of mutual induction is also given by
\[\text{M}=\frac{{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{{\phi }_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}}….(1)\]
Multiplying Equation (1) by Equation (2), we get
\[{{\text{M}}^{2}}={{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\times \frac{{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}{{\phi }_{\text{1}}}}{{{\text{I}}_{\text{1}}}}\times \frac{{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\phi }_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}}\]
\[{{\text{M}}^{2}}={{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{L}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{L}}_{\text{2}}}\]
\[\text{since, L}=\frac{\text{N}\phi }{\text{I}}\]
where L1 and L2 are the coefficients of self induction of the coils A and C respectively.
\[\text{M}=\text{K}\sqrt{{{\text{L}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{L}}_{\text{2}}}}\]
or,
\[\text{K}=\frac{\text{M}}{\sqrt{{{\text{L}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{L}}_{\text{2}}}}}\]
where $\text{K}=\sqrt{{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}}$
The constant K in the above expression is called the coefficient of coupling. If the flux due to one coil completely links with the other coil, then K1 = K2 = K = 1. Under this condition, the mutual inductance between the two coils is maximum and given by
\[\text{M}=\sqrt{{{\text{L}}_{\text{1}}}{{\text{L}}_{\text{2}}}}\]
Therefore,
The coefficient of coupling of the coils A and C can be defined as the ratio of the actual mutual inductance present between the two coils to its maximum possible value.
It should be noted that if K1 = K2 as is the usual case, then Co-efficient of coupling,
K = K1 = K2
When the flux due to one coil completely links with the other coil i.e. when K = 1, the coils are said to be tightly coupled, on the other hand, when only a small fraction of the flux of one coil links with the other, the coils are said to be loosely coupled.