Primary function of domestic refrigerator: “To provide food storage space or cabinet maintained at low temperature (0°C to 4°C) for the preservation of food.” Secondary function of domestic refrigerator: “Formation of ice cubes.”
Refrigeration cycle used: Vapour Compression Cycle (V.C.C.).
Commonly used Refrigerant: R -134a.
Capacity of domestic refrigerator: It is expressed in terms of “Litres”. Standard refrigerators of capacity 90, 165, 210, 300, 420 litres etc. are available in market.
Construction of Domestic Refrigerator
Refrigeration system of domestic refrigerator consists of following main components:
- Hermetically sealed compressor.
- Fin and Tube type evaporator.
- Accumulator.
- Thermostat.
- Air cooled condenser.
- Capillary tube.
- Drier and strainer.
Domestic refrigerator has a cabinet shape. Compressor is located in its basement, whereas, condenser and receiver are located at the back side. Refer Fig. 1. Compressor is a back dome shaped machine. Suction, discharge and charging tubes are fitted to the compressor. On the compressor body, control devices such as relay, overload protector etc. are fitted. Evaporator remains exposed inside the storage cabinet. Ice trays are kept in the ice box, which is a part of evaporator for producing small quantity of ice. Condenser is a black coloured wounded coil or tube generally kept at backside. By adjusting thermostat knob, desired temperature in the evaporator can be set. Strainer is provided to remove impurities from the refrigeration system. Drier is provided to remove moisture (i.e. water vapour associated with refrigerant) from the refrigeration system. A soft rubber gasket with magnetic wire is provided at the door of cabinet to provide air tight seal so as to prevent atmospheric air from entering into the refrigerator cabinet through small openings.
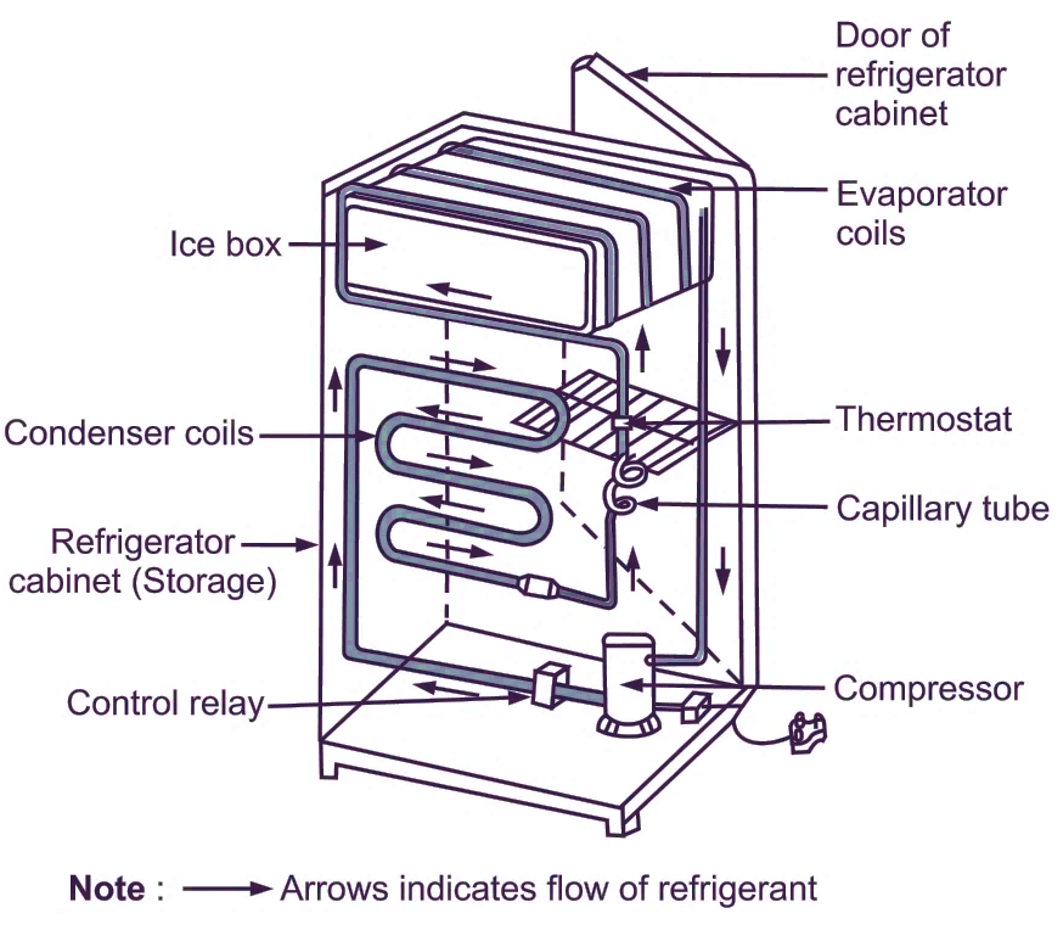
Fig. 1: Domestic refrigerator
Working of Domestic Refrigerator
Low pressure, low temperature liquid refrigerant enters Into the evaporator, absorbs heat from the space to be refrigerated or cooled and gets converted into low pressure, low temperature vapour refrigerant. It creates cooling effect in the space to be refrigerated, Refer Fig. 2. This low pressure vapour refrigerant is sucked by the compressor, where its pressure and temperature are increased by compression. High pressure and high temperature vapour refrigerant delivered by compressor is cooled and condensed to liquid state in the condenser. Thus, heat is rejected by the refrigerant in the condenser. Then, this high pressure liquid refrigerant is passed through capillary tube, where it undergoes throttling expansion and due to expansion, its pressure is reduced to obtain low pressure liquid refrigerant. Low pressure and low temperature liquid refrigerant is suppred to evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the space to be cooled. This completes one cycle. The above cycle is repeated again and again, till the desired refrigerating effect is achieved.
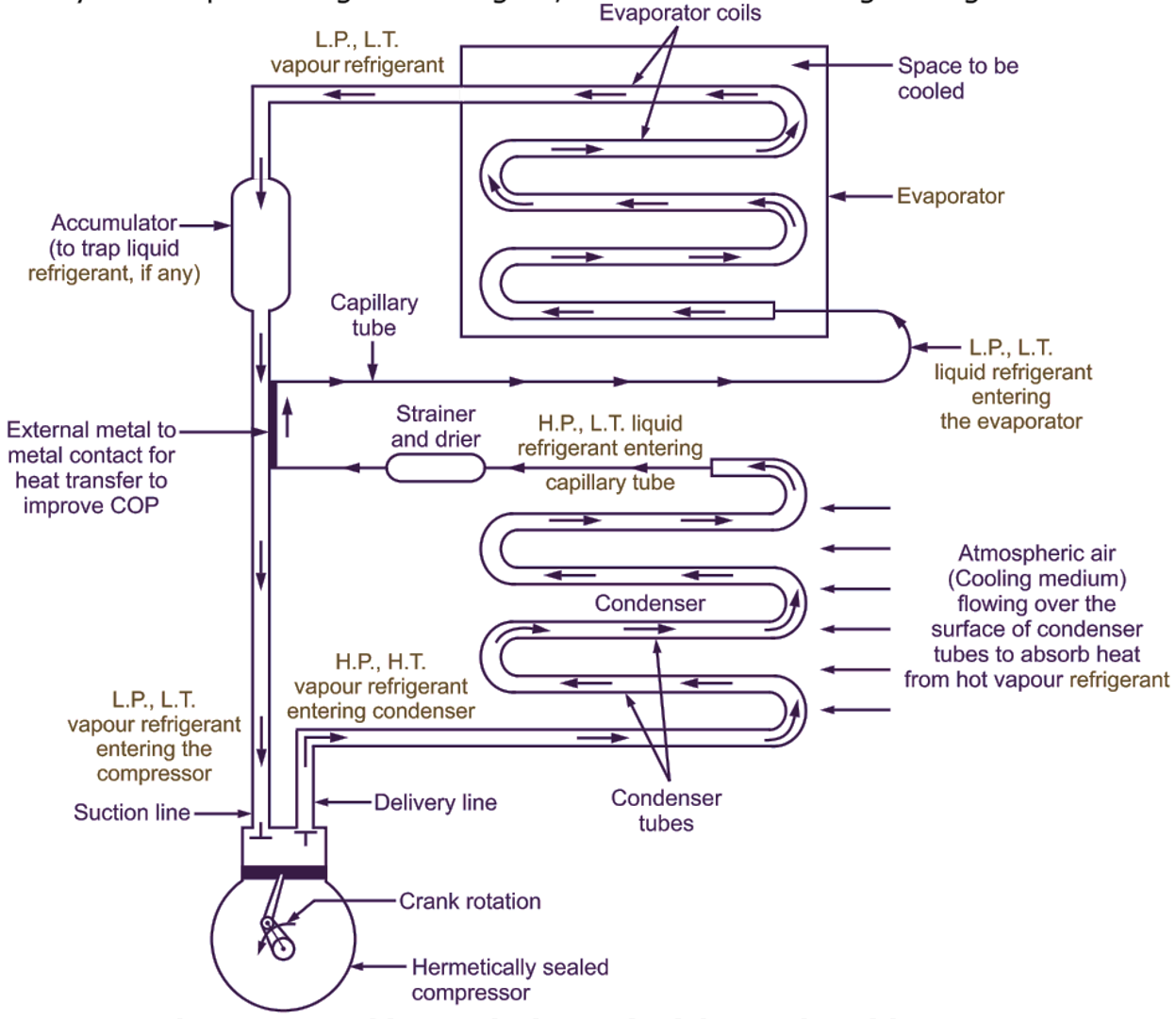
Fig. 2: Working cycle (V.C.C.) of domestic refrigerator