Function of thermostatic switch
“To maintain the desired temperature in the refrigerator”. As soon as the desired temperature (which might be 5° to 7°C in domestic refrigerators) is reached, thermostatic switch should function and the electric supply to the motor should automatically get switched off and motor should stop, thus stopping the further cooling process, so long, as this temperature is maintained. Thermostatic switch should remain in this position, so that, supply to the motor remains off, but as soon as the temperature rises, thermostatic switch should function in such a way that, electric supply to the motor is again restarted and motor starts working till the desired temperature in the refrigerator is again attained. Thermostatic switch is provided with an arrangement, so that, it could be set at different settings for attaining any predetermined temperature inside the refrigerator, In the freezer, the temperature might remain between – 7°C to – 15°C, while the temperature inside the remaining part of the refrigerator might vary between 7°C to 15°C.
Construction of Thermostatic Switch
Fig. 1 shows the sketch of thermostatic switch. A lever ‘AB’ is controlled by spring on one side and a bellow on the other side. The be low pressure is the pressure in the bulb, which is located, where temperature control is intended. This lever moves another ever ‘CD’ having electrical contacts. The end of second lever moves in a slot of the first lever.
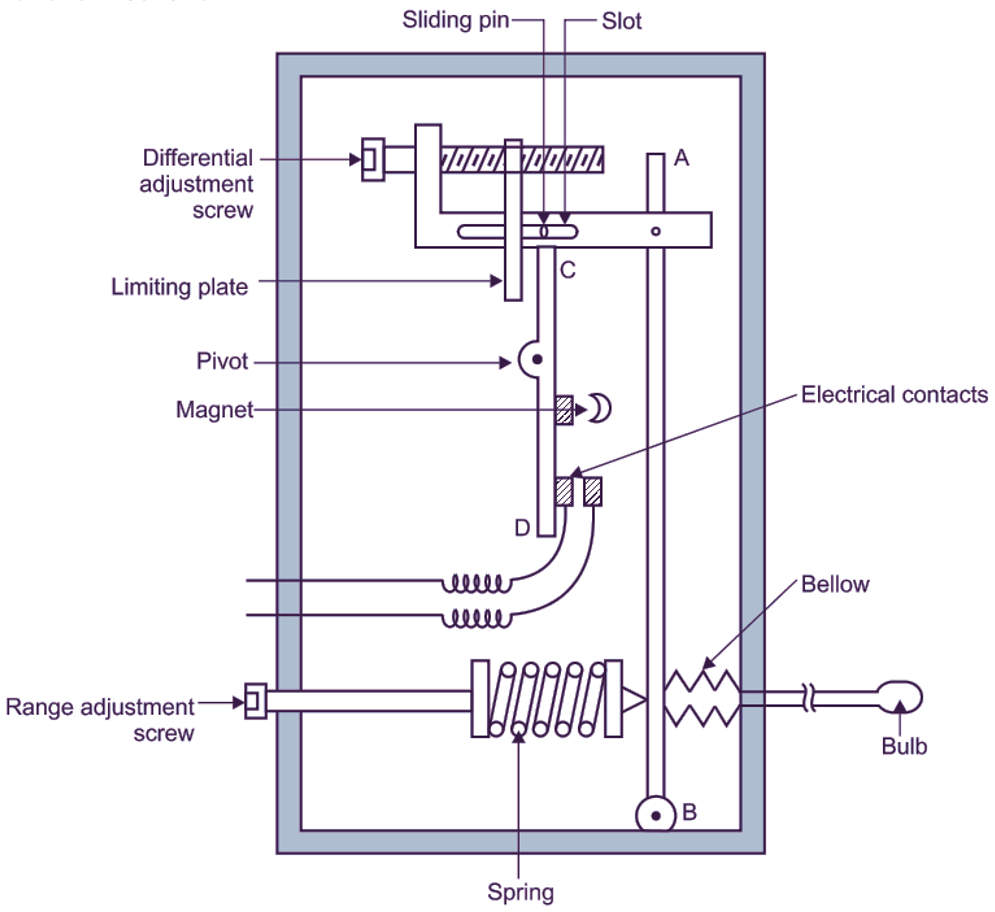
Fig. 1: Thermostatic switch
Working of Thermostatic Switch
When temperature increases, the bellow pushes ‘AB’ lever, but the second lever ‘CD’ does not move as its end slides till the slot. When the temperature reaches cut-in temperature, the second lever also moves as, its end reaches the edge of the slot. Due to this movement, the second lever makes electrical contact and starts the compressor motor. When the temperature reduces, the bellow gets compressed and the first lever ‘AB’ is moved by spring. However, the second lever ‘CD’ does not move as its end sides in the slot of first lever ‘AB’. At cut-out temperature, the end of lever ‘CD’ reaches the edge of the slot and this movement of second lever ‘CD’ breaks the electrical contact and stops the motor. The length of the slot can be changed by the movement of the limiting plate. The length of slot also decides the differential between cut-in and cut-out temperatures. Therefore, the screw adjusting the position of the limiting plate is known as the differential adjustment screw. This is generally set by the manufacturer to protect the compressor motor. The screw adjusting the spring pressure either raises or lowers the cut-in and cut-out temperatures both. so, this screw is known as the range adjustment screw. This adjustment can be done by the user to suit his/her temperature requirement. A toggle jack mechanism or magnet ensures that, electrical contacts are made or broken (i.e. electric supply ON or OFF respectively) quickly to prevent spark.