Drum brakes are widely used in different applications. They are the cheapest as compared to other types of brakes. Drum brake consists of a rotating brake drum mounted on the wheel and two semi-circular brake shoes attached on a stationary back plate. Pressing of brake shoes against the circumference or periphery of rotating drum causes friction resulting in braking.
Construction of Drum Brake
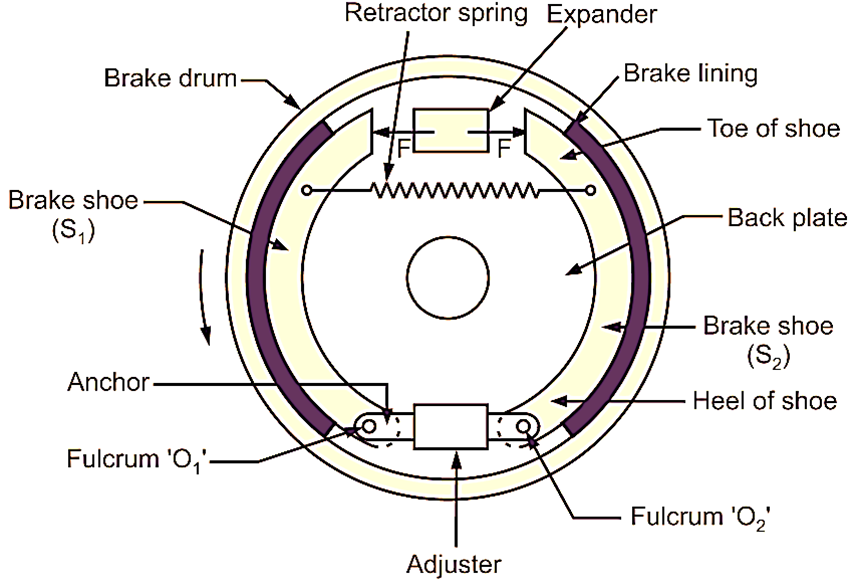
Fig. 1: Internal Expanding Shoe Brakes (Drum Brake)
Brake drum is hollow cylinder type construction made up of cast iron. It is mounted concentric to the axle hub and rotates along with the automobile wheel. A separate back plate is mounted on the stationary axle casing, behind the brake drum. The back plate houses the assembly of two semi-circular brake shoes mounted on an anchor. The back plate along with the brake shoe assembly remains stationary. It also covers the entire brake assembly, thereby protecting it from dirt, dust and mud. Above mentioned two semi-circular shoes S1 and S2 are pivoted at fixed fulcrums O1 and O2 respectively as shown in Fig. 1, i.e. One end of each shoe is pivoted at fulcrum, O1 or O2, and the other end is subjected to actuating force.
Actuating force on both shoes is applied by an expander. This expander mounted between two brake shoes is connected to brake pedal through mechanical linkages. A retrieving (retractor) spring is mounted between the brake shoes. This compression type retractor spring always try to pull both brake shoes inwards.
Working of Drum Brake
When brake is applied
When the brake pedal is pressed, the braking effort is transferred to expander, through an activation mechanism. Due to this, a force ‘F’ is induced on each brake shoe. This force ‘F’ acts against the spring force. Due to this force, the brake shoes are pushed outward against the brake lining (friction lining) and hence, inner surface of rim of brake drum. Friction between shoes and drum produces braking torque causing the drum to retard or stop completely.
When brake is released
When the brake pedal is released, the retractor spring pulls the brake shoes inward to disengage the brake. An adjuster is also provided to compensate for the wear and tear of brake shoes. When the actuating force is released, the helical tension spring (i.e. retractor spring) retracts the shoes to their original position. Internal expanding shoe brakes are having at least one self-energizing or self-actuating shoe per wheel. For anti-clockwise rotation of drum, the left shoe is known as leading or forward or primary shoe and right shoe is known as trailing or rear or secondary shoe.
Applications of Drum Brake
- Motor cars and light trucks,
- Motorbikes.