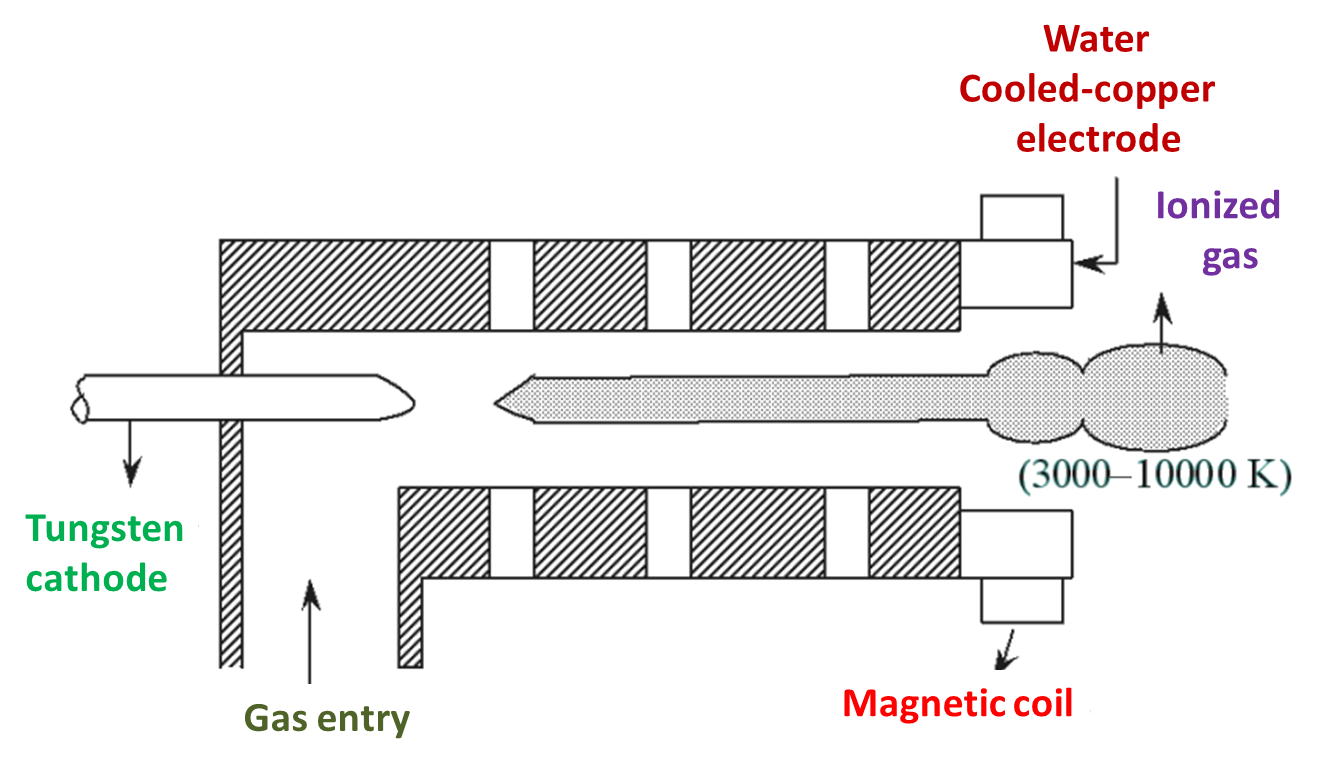
Figure 1: Plasma Arc Machining (PAM).
Working Principle of Plasma Arc Machining (PAM)
The gas molecules at room temperature consists of two or more atoms. When the temperature of gas molecules is heated to 2000°C, the molecules dissociated out as atoms. If the temperature is further increased to about 3000°C, the atoms dissociate their electrons and the gas becomes ionized (ions and electrons). The gas in this condition or state is known as plasma. The plasma is commonly developed by direct current generation method as shown in figure 1. It consists of hot tungsten cathode and water-cooled copper anode. The gas is allowed to pass around the cathode and it is made to flow out through the anode. The temperature of plasma depends on the orifice diameter of cathode. The smaller the orifice diameter, the greater is the temperature i.e., 28000°C. Thus, the plasma arc with such high temperature impinges on the workpiece, due to which the material undergoes melting and vaporization. As a result, the material is removed by the stream of ionized gas. The materials which have high thermal conductivity, good oxidation resistance and large heat capacity properties can be cut easily by Plasma Arc Machining (PAM).
The Plasma Arc Machining system use DC power source under following medium.
Dual Gas System
This system requires two types of gases i.e., plasma gas and secondary gas. Generally nitrogen is used as plasma gas. The gases such as argon-hydrogen, carbondioxide, oxygen, etc., are used as secondary gas for shielding of machining zone and they are selected based on material to be cut. The sharp corners on the top portion of the cut edges can be retained by using secondary gas system.
Water Injected Torch
In this system nitrogen is used as plasma gas at pressure more than 1 MPa. Water is used as secondary gas and it is injected through a ceramic nozzle normally at pressure of 1.2 MPa, either radially or swirling vertically about 10 percent of this injected water gets evaporated and forms thin layer of vapour. The nozzle is insulated and plasma is constricted by the steam layer. By using this system less smoke is generated, nozzle life is increased and reduces generation of oxides on the machined edge of the work component. Also, one of the cut edge is obtained exactly straight when water is injected swirling vertically.
Water Muffler
It is a hollow shell which is positioned around the plasma torch. The gap between the shell and plasma torch provides passage for water. Smoke and noise generation is controlled by using water muffler.
Metal removal mechanism of Plasma Arc Machining
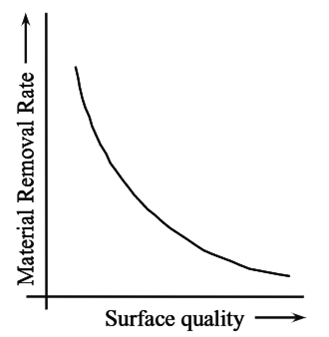
Figure 2: Mechanism of Plasma Arc Machining.
The main reason behind the removal of metal in PAM is due to the production of high temperature. The workpiece gets heated by direct electron bombardment and also due to the convection heating from the high temperature plasma. The heat that is produced has the capacity to raise the temperature of the workpiece above its melting point. The molten metal is blown away by the high velocity gas stream. It is possible to remove the metal if 45% of the electrical power is supplied to the torch. On a specific part of the workpiece, the arc heat is concentrated to raise the temperature to its melting point. The metal removal mechanism involves the quality of cut with which the metal is removed, depending upon the distribution of heat flow. If the heat is supplied uniformly throughout the thickness of the material then a better quality of cut can be obtained. The speed with which the metal is removed also depends upon the distribution of heat flow. The surface quality of the material mainly depends on the material removal rate. As the material removal rate decreases (i.e, less amount of material is removed from the machined surface), there is an increase in the surface quality of the material Thus. surface quality and material removal rate are inversely proportional to each other and their effect is shown in figure 2.
Applications of Plasma Arc Machining
The applications of plasma arc machining are as follows,
- It consists of multiple torch system hence can be used to cut a variety of shapes from single plate at a time.
- PAM is most commonly used to prepare ends of a pipe section before the welding has been done.
- CNC types PAM systems are used for performing operations such as punching and shape cutting. Shape cutting operations are performed on light duty plates which are complicated to machine by oxy-fuel system.
- Suitable for machining materials such as stainless steel, aluminium and copper.
- The operations which are complicated to turn or cut the material is done by using PAM method.
Limitations of Plasma Arc Machining
- Surfaces contain metallurgical alterations.
- It requires secondary machining on the surfaces.
- Operator requires eye shielding and noise protection.
- High initial cost of the equipment
- Shielding may be needed, as the oxidation and scale formation takes place.
Safety Precautions are taken in performing Plasma Arc Machining
The safety precautions that are to be taken while performing plasma arc machining are as follows,
- It is essential to protect the eyes from the ultraviolet and infrared radiations. These radiations are generated from the plasma flame and if observed in large quantity, it will be harmful to the eye. Hence, more care must be taken while working with plasma.
- The over-exposing of ultraviolet and infrared radiation causes the reddening of eyes and due to loss of sleep a gritty feeling will be observed by an operator
- And overexposing of ultraviolet rays may lead to painful skin bums and cancer in most of the cases.
- Therefore, it is very essential that before going near to the torch. the worker should wear proper glasses and dresses
- The worker should cover the most of his body and quality of glasses must be good, so that it can protect from ultraviolet and infrared rays.
- The torches are required to be operated in an airy room so that toxic gases such as No2, O2, etc., can be synthesized in the atmosphere.
- While operating the torch; it may be noticed that the noise levels are very high. Hence, ear plugs should be used to protect the ears.
- While operating the hand torches, the worker should wear asbestos gloves having leather as inner layer.
- Every operator seek a consultation by a health physician depending upon the hours limit in operating the plasma torch.