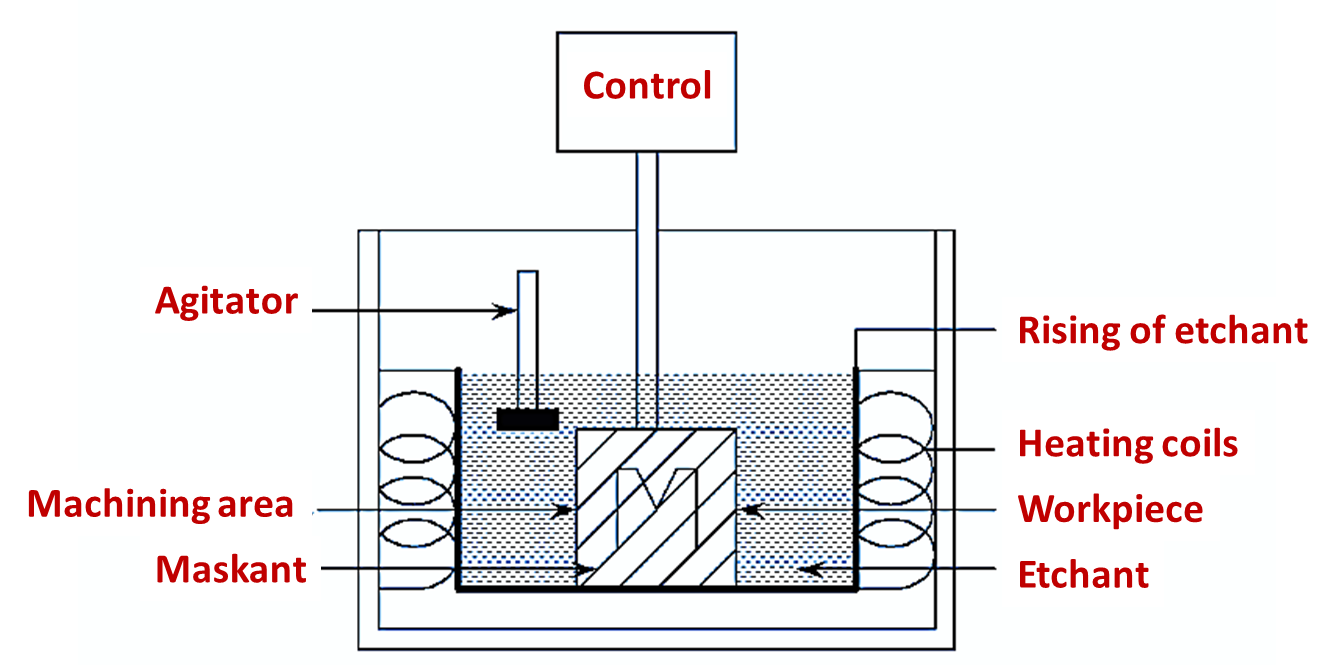
Figure 1: Chemical Machining.
Working Principle of Chemical Machining
Chemical machining is a process used for removing the material by dipping it into a chemical solution which dissolves all the material of the workpiece. Depending upon the requirement the material is removed from the workpiece portions which are uncovered with the masks.
Steps involved in Chemical Machining
The various steps involved in chemical machining process are as follows.
- Initially, clean the workpiece thoroughly, such that the masking material can stick easily to the workpiece. This reduces the chances of stray etching on the workpiece, that occurs due to maskant de-bonding.
- Then, apply the chemical resistant mask on the workpiece surfaces.
- Dip the workpiece in a chemical solution called etchant for sufficient time period.
- Maintenance is required to strengthen the chemical solution as it becomes weak with the time by the absorption of workpiece material.
- Finally, remove the mask and clean the workpiece.
Various Maskants used in Chemical Machining
Maskants are the resistant materials used for covering the parts of the workpiece that are not to be machined. These substances are acidic or alkaline in nature and acts as resistance to etchant, so that etchant does not get penetrated into workpiece material. Based on the method of application, the maskants are classified as cut and peel, screen printing and photochemical. The characteristics of various maskants are,
Cut and Peel Maskants
- It gives high chemical resistance.
- Depth of etchant is restricted to 13 mm.
- It is not suitable for obtaining critical dimensional tolerances.
- Re-scribing of maskant is possible.
- It is used in batch size production.
Screen Printing Maskants
- It is limited to parts with area not more than 1 m × 1 m.
- Accuracy obtained is low i.e., ( ≤ ± 0.2 mm).
- It is suitable for flat surfaces or simple contours.
- It is used for high volume production.
Photochemical Maskants
- It is suitable for thin materials (upto 0.8 mm thickness).
- Accuracy obtained is very high compared to other maskants.
- It is used for complicated and accurate shapes or surfaces.
- Machining with these maskants gives repeatability of about 0.0005 mm.
The different types of maskants used in chemical machining are neoprene, butyl and vinyl based materials such as vinyl polymer, neoprene polymers, polyethylene, etc.
Advantages of Chemical Machining Process
- It is a versatile process based on the design aspect.
- It is possible to machine both the surfaces of the workpiece together.
- The hard and brittle materials can be easily machined by this process.
- The complicated contours in chemical machining can be machined without any difficulty.
- There is no presence of burrs on the workpieces.
- Tools are available at lower costs.
- The tooling time is considerably less compared to other processes.
Limitations of Chemical Machining Process
- It is a time consuming process.
- It requires maximum floor space.
- An expertise operator is required for performing the operation.
- It does not generate the sharpened corners.
- The cost incurred for manufacturing is more.
- It machines the minimal thickness of metal.