In the Regenerator heat exchanger, the hot and cold fluids are made to flow alternatively through the same space. When hot fluid flows through the space, it gives away heat energy, which is stored in the space in the form of internal energy. This energy is then transferred to the cold fluid, which then flows through the same space. This cycle repeats giving periodic heat exchange. Hence, the heat exchanger is also known as ‘Periodic Heat exchanger’.
Types of Regenerator
Regenerator type Heat exchanger is classified as:
- Rotating matrix type.
- Stationary matrix type.
Rotating Matrix Type
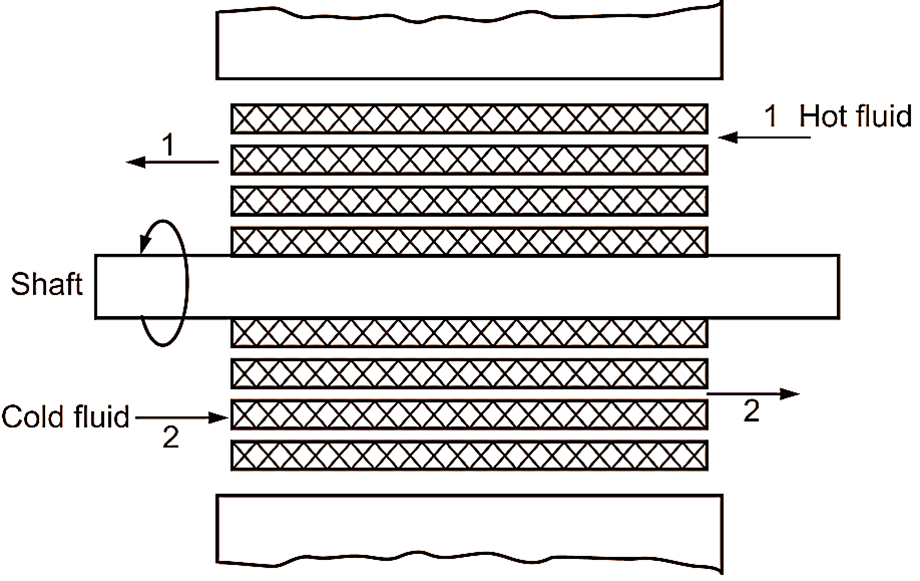
Fig. 2: Rotating matrix type regenerator
In this type, the heat storing matrix is continuously rotating about its axis, so that, its half portion (say upper) passes from hot fluid zone and cold fluid zone alternatively. At the same time, lower half portion is also passing from cold fluid zone and hot fluid zone alternatively. Rotating matrix type heat exchanger is not preferred over other types of heat exchangers due to chances of mixing of two fluids. . When matrix continuously rotates from hot fluid zone to cold fluid zone and back, some fluid also moves along with it. This may result in mixing of both fluids.
Stationary Matrix Type
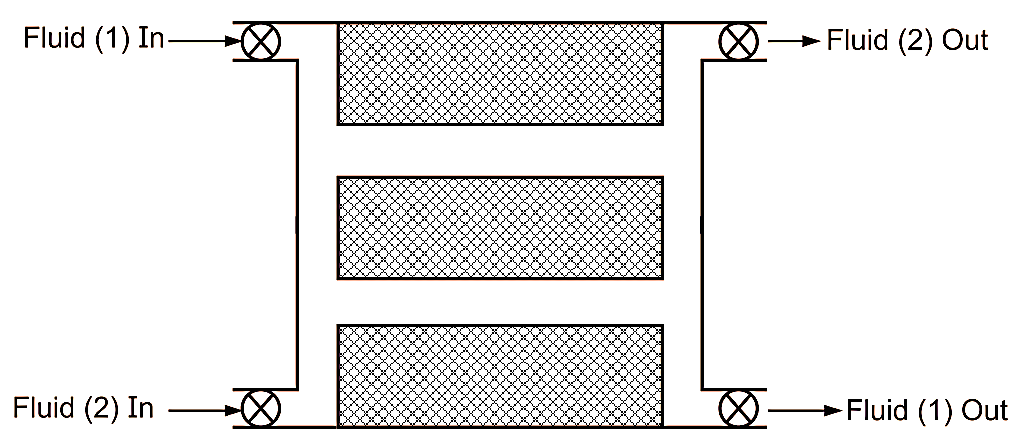
Fig. 1: Stationary matrix type regenerator
In this type, the heat storing matrix is stationary, while the flow of fluid is controlled using different valves. For example, initially hot fluid is made to flow through the heat storing matrix. Thus, heat given by hot fluid is stored in the walls. Now, the cold fluid enters the matrix and absorbs heat from matrix walls during its flow. Thus, the two fluids flow over the matrix intermittently and hence do not get mixed with each other.
Advantages of Regenerators
- Maximum heat transfer.
- Minimum pressure loop.
- High efficiency.
- Less weight per kW of plant.
Disadvantages of Regenerators
- Costly
- Leakage creates problems.
Applications of Regenerators
- I.C. Engines.
- Gas Turbines.
- Open hearth and glass melting furnaces.
- Air heaters of blast furnaces.