Sudden rise in the voltage for a very short period on the power system is known as a voltage surge or transient voltage. When lightning strucks a line; the surge rushes along the line just as flood of water along a narrow valley.
The lightning introduces a steep fronted wave. Steeper the wavefront, more rapid is the build-up of voltage at any point in the network as shown in Fig. 1. The voltage surge is generally specified in terms of rise time t1 to react and the time t2 to decay to half of the peak value (Em / 2) If time t1 = 1 μsec. and t2 = 50 μsec, the surge is specified as 1/50 μsec. The travelling wave damages the terminal apparatus. The damage depends upon the amplitude of the surge (i.e. Em) and also upon the steepness of the wavefront (i.e. if t1 is very very small).
If purpose of installing a “surge absorber” is to reduce the steepness of the wavefront of the surge. Surge absorber is therefore a protective device which reduces the steepness of wavefront of a surge by absorbing surge energy.
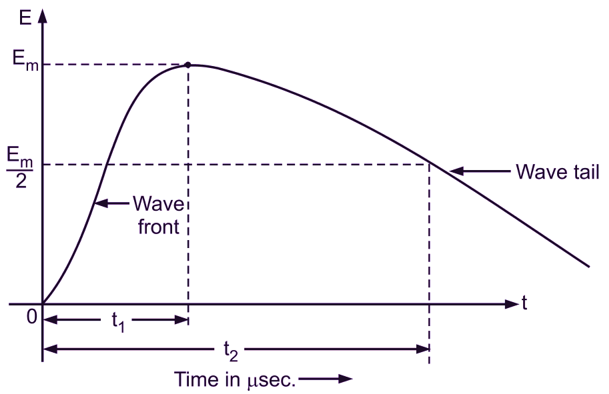
Fig. 1: Voltage surge wave
Types of Surge Absorbers
- Condenser surge absorber.
- Chock and resistance surge absorber.
- Ferranti surge absorber
Condenser Surge Absorber
Capacitive reactance XC = 1 / 2πfC i.e. it is proportional to frequency. At power frequency (50 Hz), XC is large and hence no current flows from line to earth at normal voltage and normal frequency of the line as shown in Fig. 2.
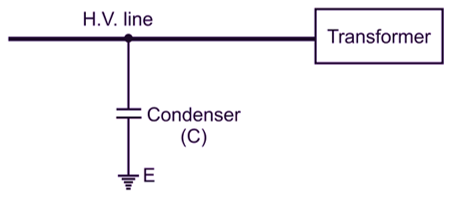
Fig. 2: Condenser Surge Absorber
But when overvoltage appears due to transients or surges due to the high frequency of the surge voltage XC becomes very small and shorted and thus immediately the current (energy) passes to the ground. Hence, capacitor absorbs surge energy and allows it to dissipate in the ground and the equipment like transformer windings are protected from surges.
Chock and Resistance Surge Absorber
In this type of absorber, a resistance and inductor coil connected in parallel forming a series circuit of line, R and L and the equipment (transformer).
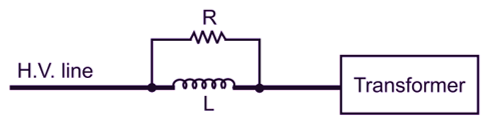
Fig. 3: Chock and Resistance Surge Absorber
At the normal conditions and power frequency XL (= 2πfL) is small. But in case of surge voltage developed in the line XL becomes very large and the current passes through the resistance where the energy is absorbed (I2Rt). Thus, the surge energy is dissipated in ‘R’ to produce heat as shown in Fig. 3.
Ferranti Surge Absorber
This is the most modern type of absorber. It consists of an air-cored inductor connected in series with each line and surrounded by a grounded metallic sheet. This surrounding metal is insulated from inductor and connected to the ground (earth). This sheet is called as discipator. The sheet is thus magnetically coupled to inductor but electrically isolated from it by air as shown in Fig. 4.
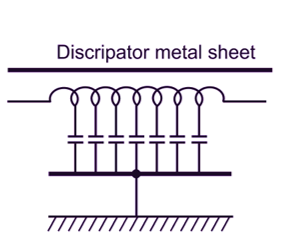
Fig. 4: Ferranti Surge Absorber
This arrangement acts as a air-cored transformer whose primary is an inductor coil and metallic discipator is a short circuited secondary of a single turn as shown in Fig. 5. Whenever, the travelling wave is incident on the surge absorber, the energy contained in the wave is discipated in the form of heat generated in the discipator sheet (i) due to current set up in it by ordinary transformer action and (ii) by eddy currents. The steepness of the wavefront is also reduced because of the series inductance of the inductor coil.
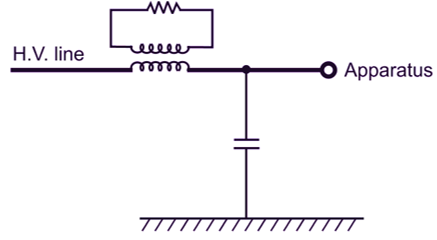
Fig. 5: Surge Absorber Equivalent Circuit
Difference between Surge Absorber and Surge Diverter
| Surge Absorber | Surge Diverter/Lightning Arrester |
| Absorbs the surge energy to eliminate the surge and to protect the equipment. | Diverts the surge to the earth and eliminate the surge to protect the equipment. |
| Construction is very simple and less costly. | Construction is not so simple but somewhat costly. |