In this topic, you study Synchroscope Method of Synchronization of Generator (or Alternator).
In this method, the incoming alternator is synchronized with the other alternator/s already connected to the bus-bars with the help of a more accurate device called synchroscope. Fig. 1 shows the necessary circuit diagram.
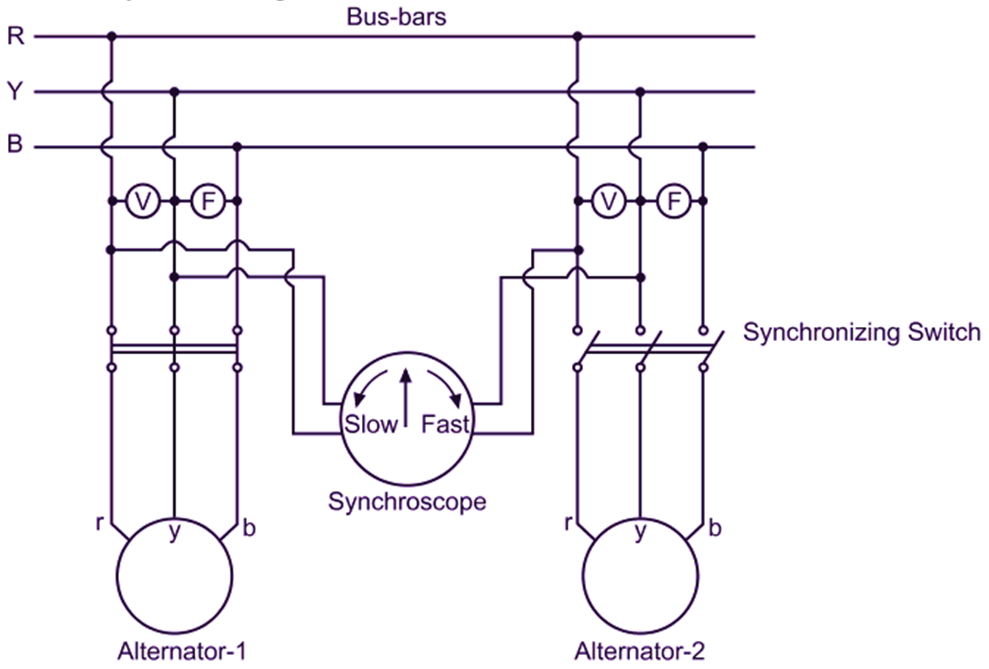
Fig. 1. Synchronizing of three-phase alternators using synchroscope method
Procedural Steps of Synchroscope Method
Step-1 to Step-4: These initial steps are identical to those followed in Dark lamp methods.
Step-5: The instant of synchronizing is determined with the help of a synchroscope. The synchroscope is essentially a split-phase motor. The voltages from the corresponding phases of the incoming alternator and bus-bars are applied to the synchroscope (Fig. 1). A pointer which is attached to the rotating part of the instrument moves over the dial face if there is a difference in frequencies of the incoming alternator and bus-bars. The anticlockwise rotation of the pointer indicates that the incoming alternator is running slower whereas its clockwise rotation indicates that the incoming alternator is running faster. The speed of the prime mover of the incoming alternator is finally adjusted such that the pointer rotates with a very low speed and synchronizing switch is then closed when the pointer just reaches the vertical position.
Advantages of Synchroscope Method
- Synchroscope is a more accurate device as compared with the lamps.
- The element of personal judgement of the operator regarding the exact instant of synchronizing is nearly eliminated.
Disadvantages Synchroscope Method
- Synchroscope is expensive as compared to the ordinary lamps.
- Being a single-phase instrument, synchroscope does not indicate the phase sequence.