Air filtration is defined as, “the process of reducing or eliminating the unwanted particles or gases from the air”. Atmospheric dust is a complex mixture of smoke, mists, fumes, dry granular particles, and fibres suspended in air. In addition to the above, the air may contain living organisms such as bacteria, plant pollens etc., which may cause diseases. Air conditioning systems generally have provisions for removing some of these objectionable air contaminants. Air filtration is usually concerned with removal of particles of sizes ranging from 0.1 to 200 microns.
Air Filters
Both, fresh air and re-circulated air contain dirt, dust, smoke and suspended impurities. Flters are used in air conditioning systems to remove dust and other contaminants from air in order to purify it. It is assumed that, there is no pressure drop across the filter.
Filters improve the performance of air conditioning by,
- Maintaining air purity,
- Increasing life of system, and
- Reducing maintenance of system.
Functions of Air Filters
Primary function of air filter: “To clean the air, before it is supplied to conditioned space”.
Secondary functions of air filter are:
- Protection of human health and comfort: By removing dust particles related to serious respiratory problems such as asthma.
- Protection of equipments: Some equipments may not operate properly or may wear out faster, if air is not clean. Some manufacturing processes are particularly sensitive to atmospheric contaminants.
- Protection of the air conditioning machinery.
- To maintain cleanliness of room surfaces and furnishings.
Factors to be Considered, while Selection of Air Filters
Flters are selected on the basis of following factors:
- Degree of air cleanliness required.
- Volume of air to be handled.
- Method used for disposal of dust.
- Type and amount of particulate matter (PM) in air to be removed.
Classification of Air Filters
Filters can be classified as,
- Wet filter,
- Centrifugal filters.
- Viscous filters
- Dry filters,
- Electric/ Electronic filters,
Dry Filters
These are either reusable or throw-away type. Dry filter is made of cloth, coarse paper, wool or cellulose felt. Air is made to flow over a steady stream at a velocity of 10 m/min, through the dry filter to entrap dust. The ter bags are periodically cleaned by any suitable method. Refer Fig. 1 (a). These filters have a high efficiency up to 65%.
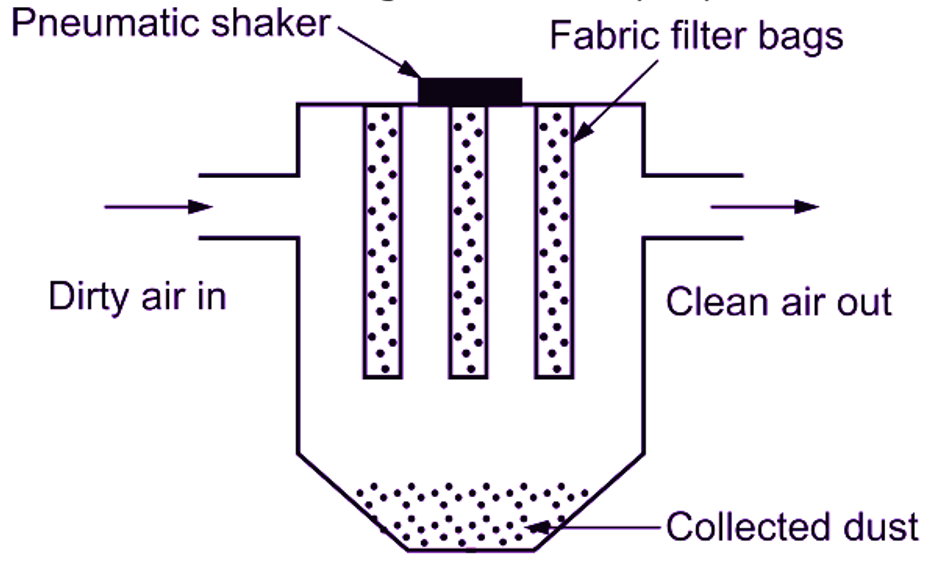
(a) Internal view
(b) Isometric view
Fig. 1: Dry filter
Wet Filters
Air washer is a type Of wet filter, Refer Fig. 2. In this filter, dust particles are wetted by water spray, It leads to settle down the heavy particles. The effectiveness of a wet filter depends upon the tendency of dust particles to get wet. Their efficiency is about 75% to 80%. These filters are used in industrial air conditioning for absorption of gases. Also, they can be used in combination with dry and viscous filters. The only disadvantage is that, these filters are ineffective for removal of greasy particles.
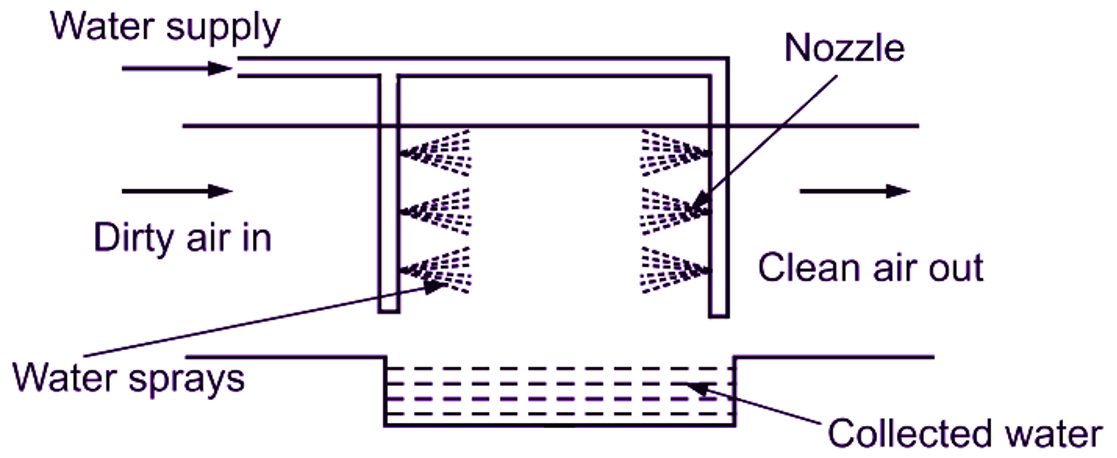
Fig. 2: Wet filter
Viscous filter
These filters are available in the form of pads or mats made up of steel wool, copper mesh or plastic. Fig. 3 shows a base pad in the form of roller. It is dipped in oil up to a suitable depth. The viscous layer of the roller traps dust and dirt particles from These filters are throw-away type only, and are discarded periodically. Care should be taken to maintain viscosity of oil exposed to hot air. The efficiency of such filters is about 75-80%.
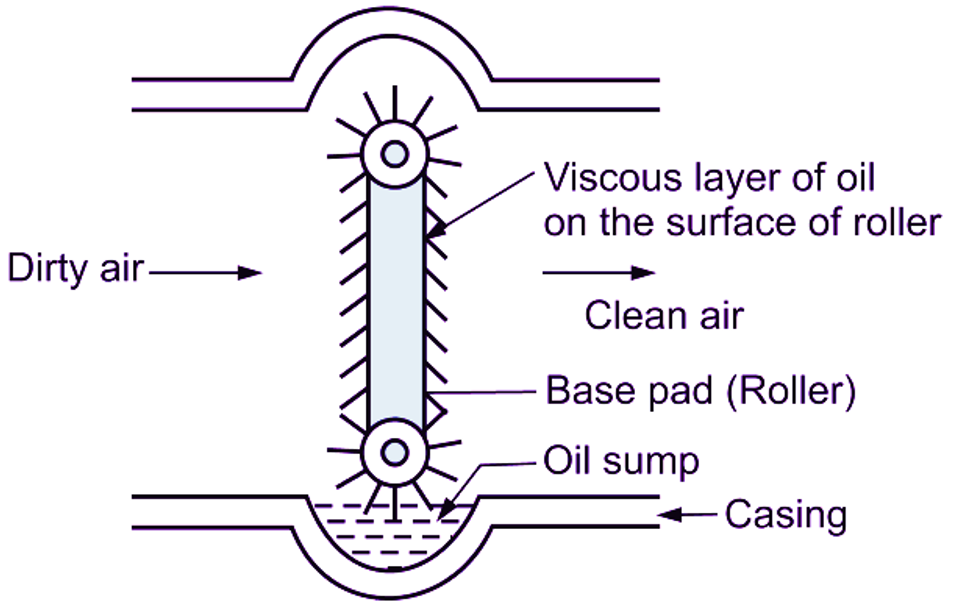
Fig. 3: Viscous filter
Electric Filters/Electronic Filters
Electric filters/Electronic filters use the method of ionisation to capture dust particles in air. They are also termed as electronic filters. The particles in air get ionised while passing through the electric field. This ionised air is passed through a collection chamber. The collection chamber has metal plates, which are alternatively charged as positive and negative. The positive ion particles are attracted towards negatively charged plates and negative ion particles are attracted towards positively charged plates. Thus, dust particles get deposited/collected on the plates and we obtain clean air. After collection, the plates are washed by water sprays to remove the collected dust particles. The efficiency of electric or electronic filters ranges around 70 to 90%.
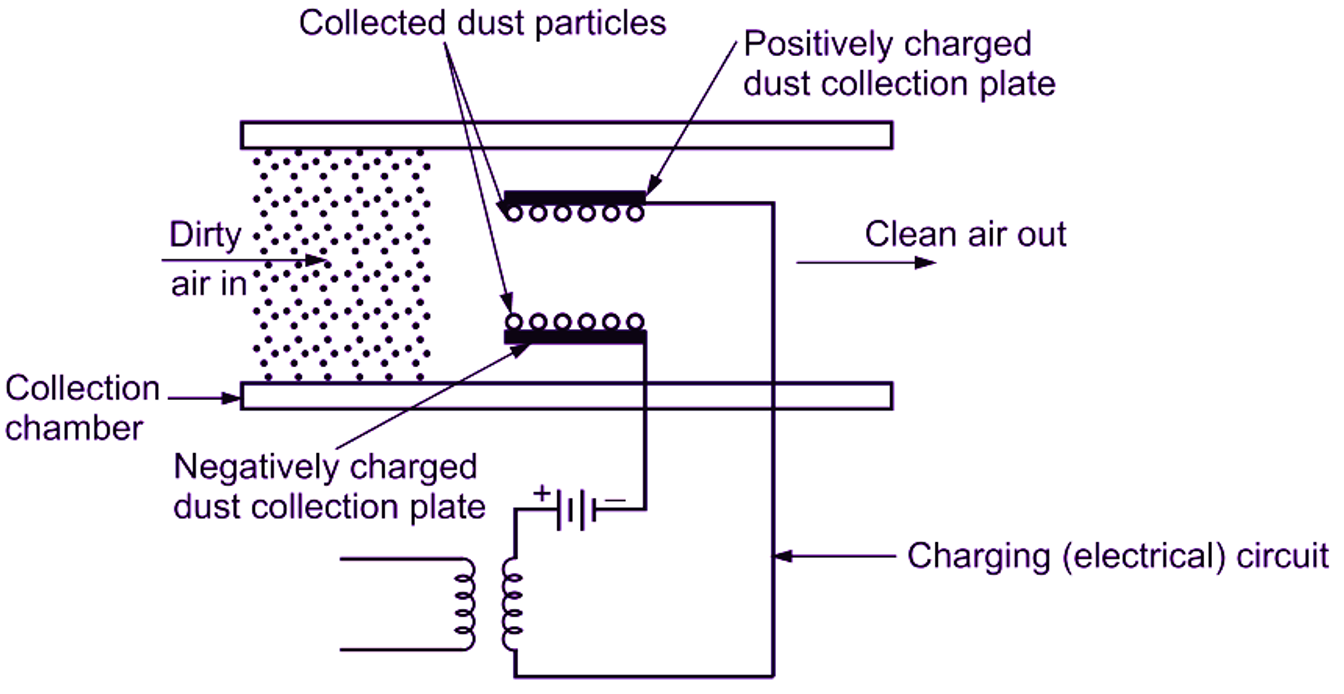
(a) Schematic view
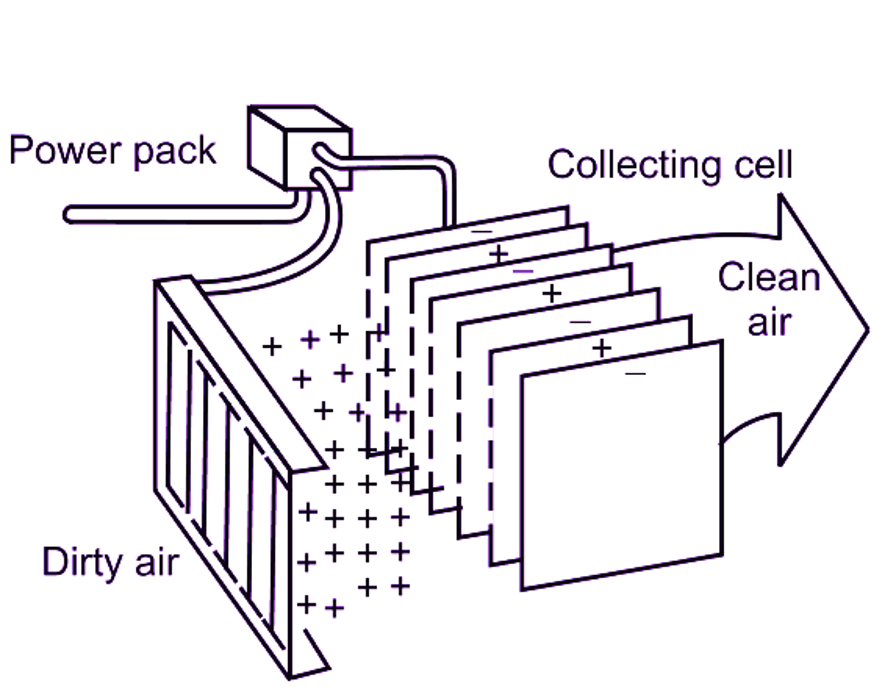
(b) Isometric View
Fig. 4: Electric or Electronic filter
Advantages of Electric filters/Electronic Filters
- Ease of operation,
- Low running cost,
- Compactness,
- Low maintenance cost, and
- Effectiveness for high-dust concentration air streams.
Disadvantages of Electric Filters/EIectronic Filters
- They need high voltage supply, which increases the possibility of danger of sparking,
- Efficiency of filter decreases, if air quantity increases.
Centrifugal Filters
For powder processing or asbestos industries, dust collected can be reused. In this filter, a high-velocity air stream is used to produce a whirl in a chamber. Centrifugal force separates light and heavy dust particles. Heavy particles move towards the inner side of chamber and fall down. They are collected in the dust co lector pan and then removed, from the bottom. Lighter particles remain at the centre, whereas, clean air is collected from the top of the chamber. The efficiency of this filter is to 75%. These dust collectors are commonly used in industrial applications, due to their effectiveness.
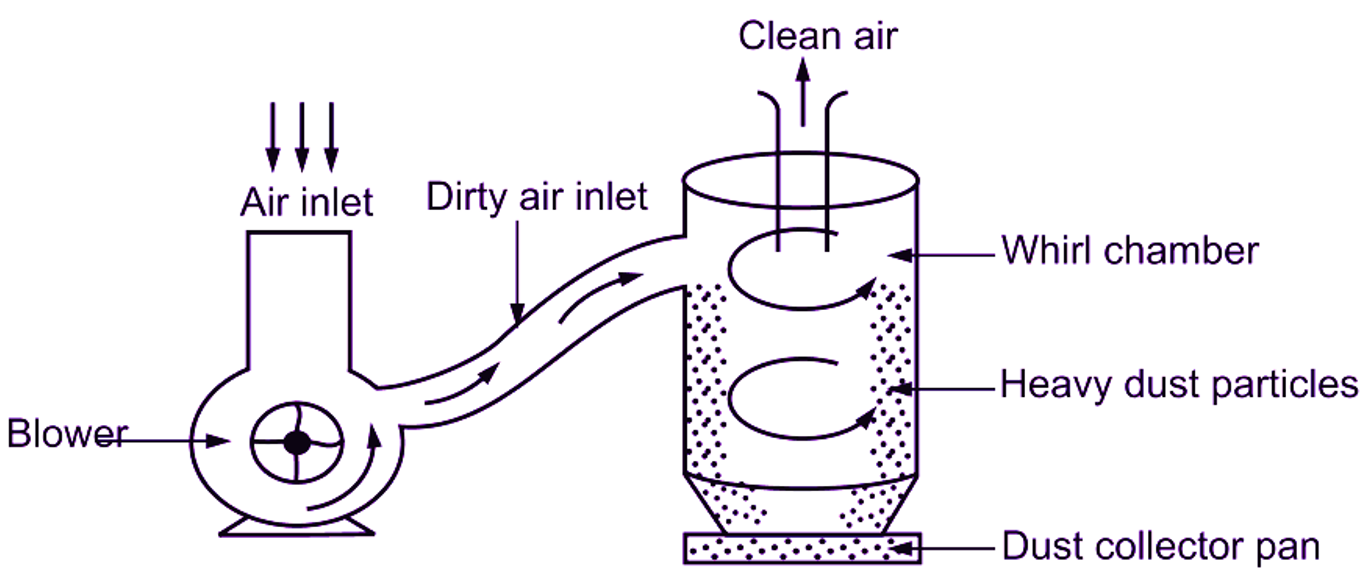
Fig. 5: Centrifugal filter
Advantages of Centrifugal Filters
- Rigid construction.
- More Durability.
Disadvantages of Centrifugal Filters
- High power consumption.
- Noisy Operations
HEATING AND COOLING COILS
Function: These coils are used either for heating or cooling of the air to be conditioned.
Material used: Copper or Stainless steel.
Description
The heating and cooling coils may be either separate or an integral part of the air conditioning unit. Generally, coils are bundled together in a rectangular frame, which can be fitted easily in the air handling unit. Steam or hot water may be circulated through the heating coil for heating purpose. Sometimes, the heating coil may be electric resistance coil. Chilled water, cold refrigerant, cooled gas or secondary refrigerant like brine may be used for cooling purpose in case of cooling coil. The flow rate of heating or cooling medium passing through the coil can be varied to control the amount of heating or cooling of the air. Maximum surface area of coil is exposed to the air to allow maximum heat transfer.