In this topic, you study Avalanche Breakdown – Definition & Theory.
When reverse voltage applied to the junction is increased, the amount of energy of minority carrier is increased i.e. velocity of minority carrier increases as they diffuse across the junction. As the reverse bias is increased further, the minority carriers acquire more kinetic energy. Due to increase in energy these carriers collide with Silicon (or Germanium)atoms within the crystal structure. This collision breaks a covalent bond and generates additional carrier. This generated carrier again picks up energy from applied voltage bias and generates more and more carriers. This process of carrier generation is called carrier multiplication. As a result of this, the reverse current increases rapidly. This cumulative process of carrier multiplication is known as avalanche breakdown or avalanche multiplication. Fig. 1 shows I–V characteristics of avalanche breakdown in comparison to zener breakdown.
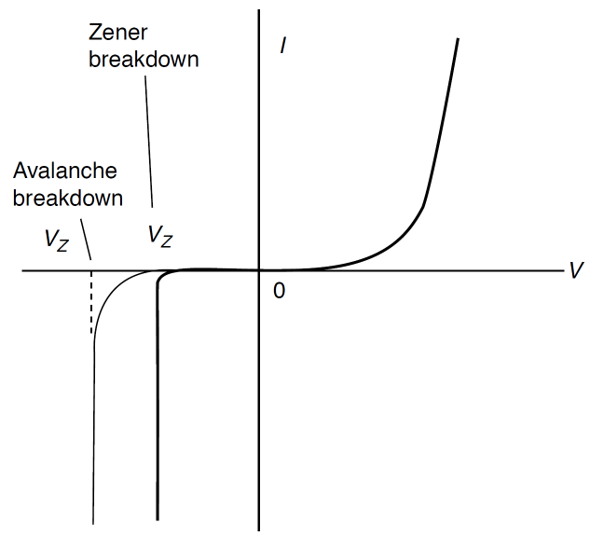
Fig. 1: The I–V characteristics of avalanche
breakdown