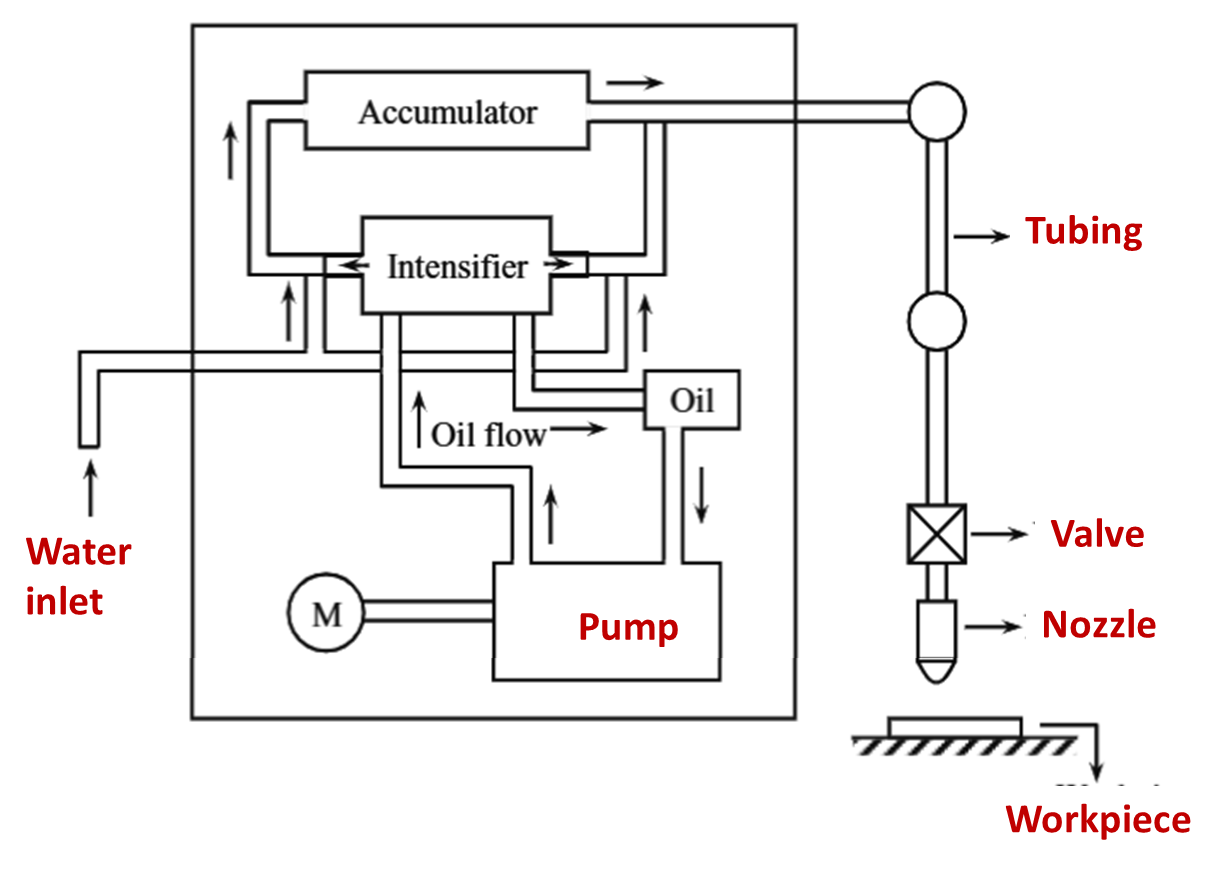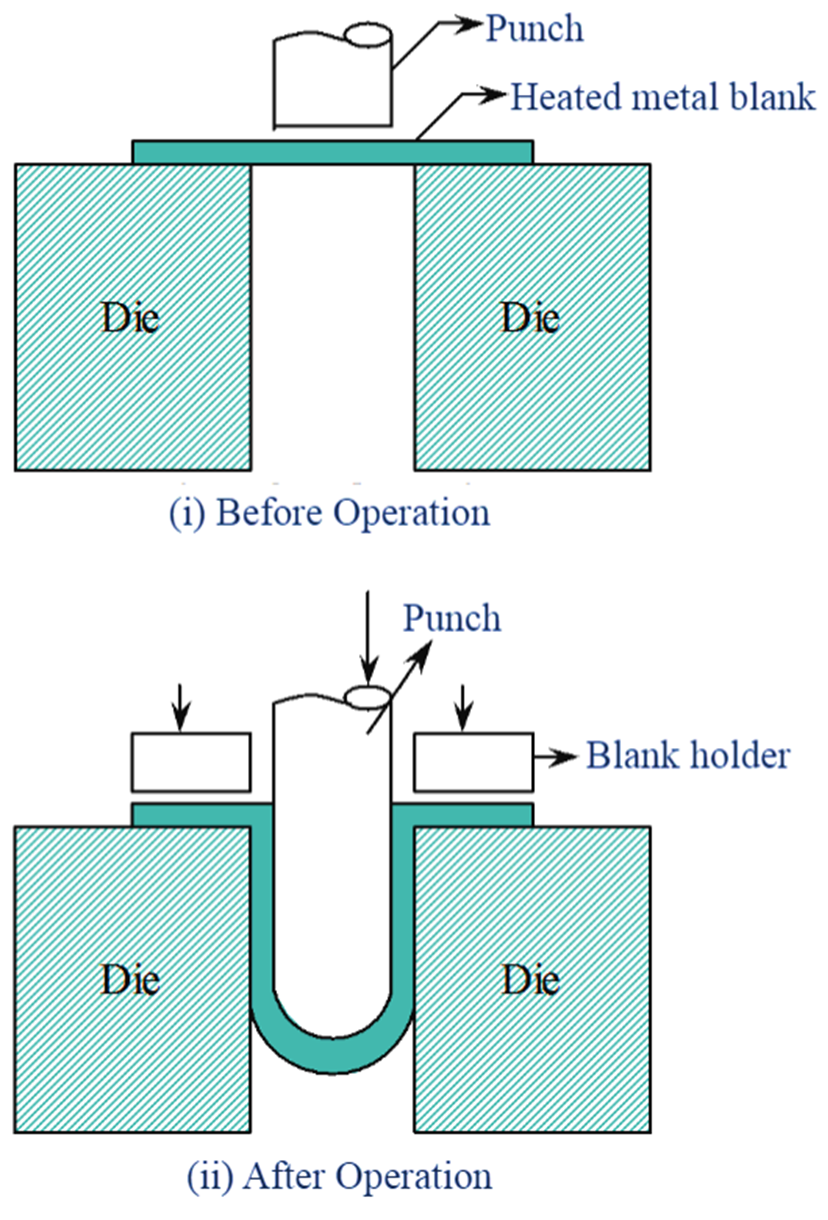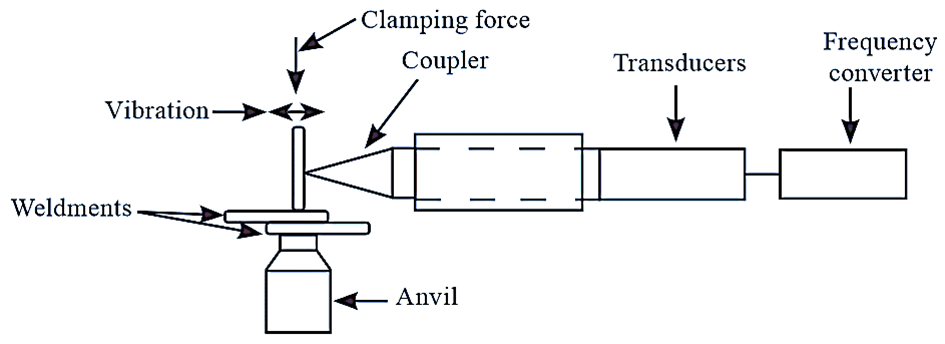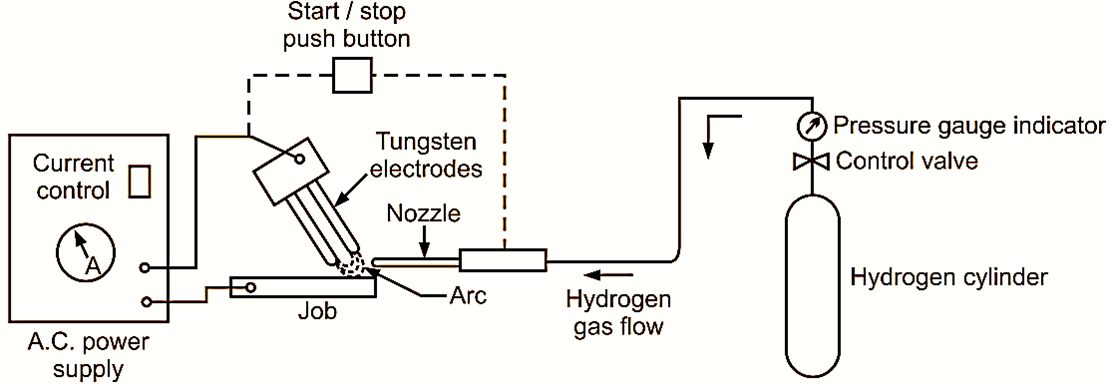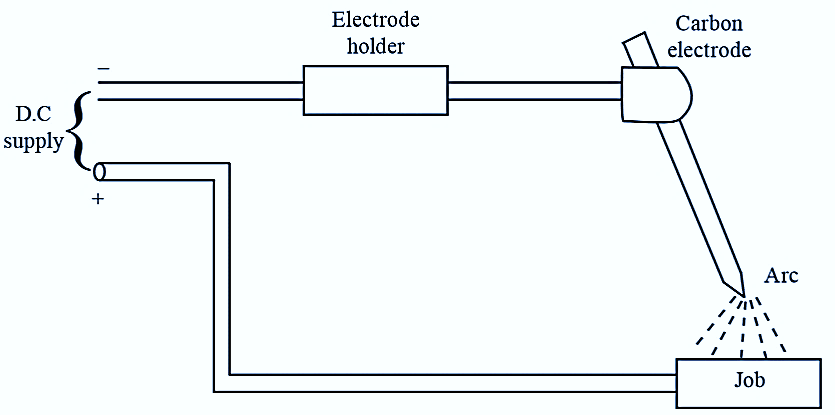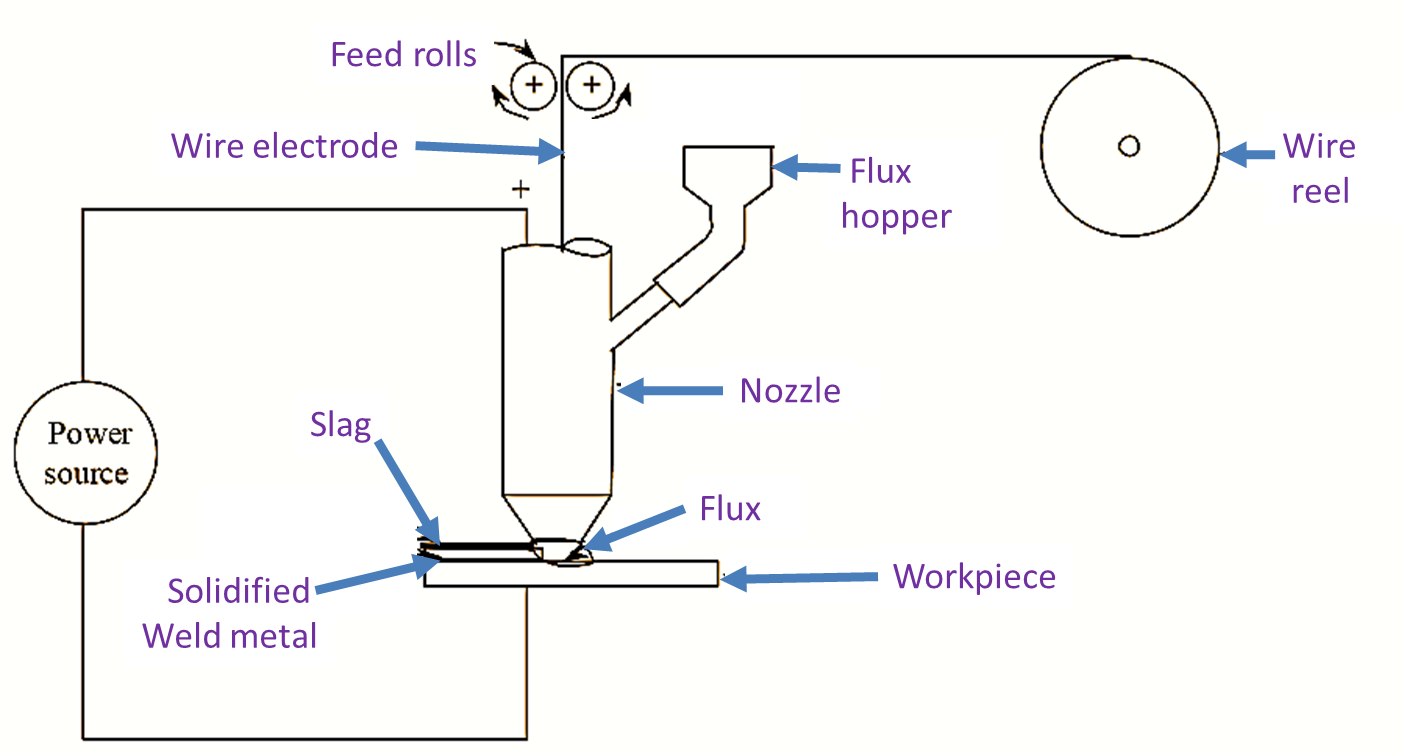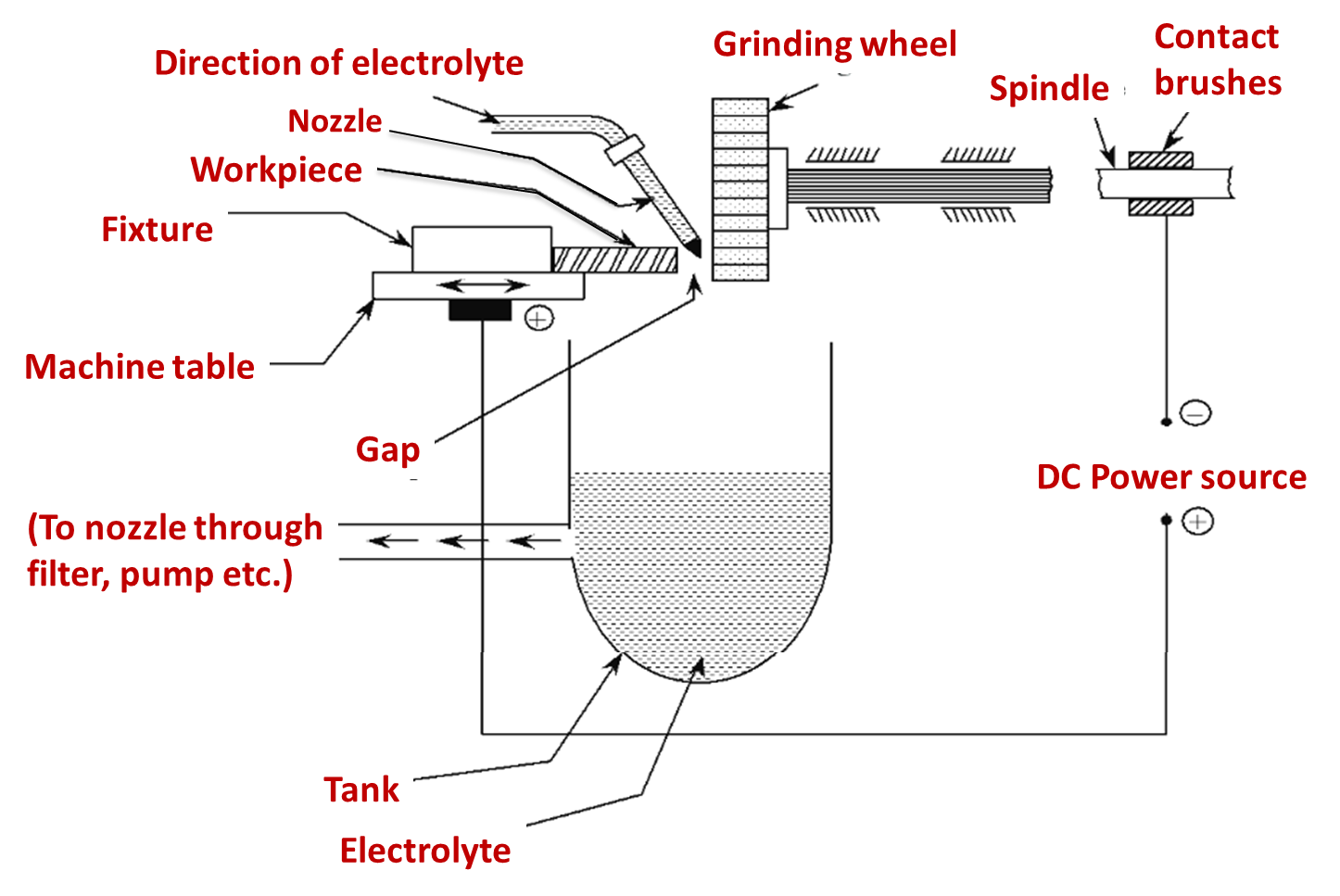
Figure 1: Electrochemical Grinding (ECG)
Depending upon the improvement of electrochemical machining process, the electrolytic process is developed. In the electrochemical grinding process, the removal of material takes place by electrochemical deposition (90%) as well as material abrasion (10%). Continue reading What is Electrochemical Grinding (ECG)? Process, Diagram, Advantages & Applications